有効的なPMP-JPN問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、PMP-JPN試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新PMP-JPN試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com PMP-JPN試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここでPMP-JPN問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
PMP-JPN問題集最新版のアクセス
「1975問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
左側の項目を、右側の正しいプロジェクト アプローチ内の一致する用語にドラッグします。


正解:
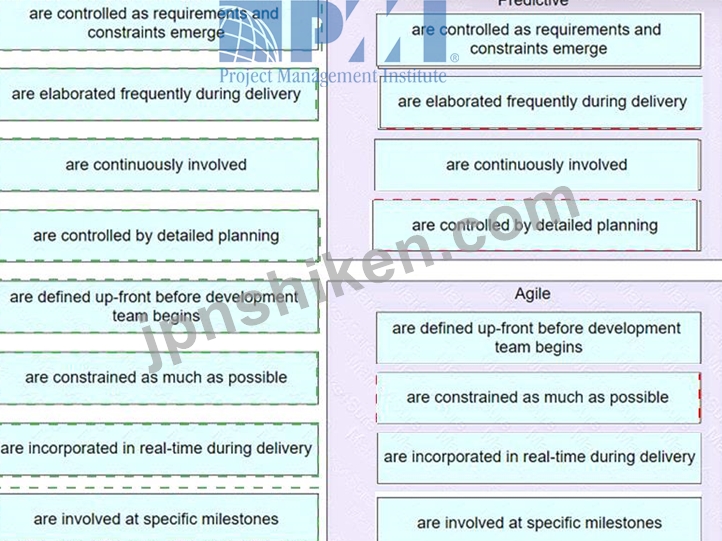
Explanation:
* Predictive:
* Requirements: are controlled as requirements and constraints emerge.
* Changes: are elaborated frequently during delivery.
* Risk and Cost: are continuously involved.
* Key Stakeholders: are controlled by detailed planning.
* Agile:
* Requirements: are defined up-front before development team begins.
* Changes: are constrained as much as possible.
* Risk and Cost: are incorporated in real-time during delivery.
* Key Stakeholders: are involved at specific milestones.
The predictive project approach, often referred to as the waterfall model, is characterized by its sequential phase-to-phase development where requirements and planning are done up-front. In contrast, the agile approach is iterative and incremental, with requirements and solutions evolving through collaboration between self-organizing cross-functional teams.
In the predictive approach:
* Requirements are detailed early in the project and changes are managed through a formal process.
* Changes are not expected to be frequent and are carefully managed.
* Risk and Cost are analyzed and assessed as part of the initial planning.
* Key Stakeholders are identified and their needs are addressed through detailed planning.
In the agile approach:
* Requirements are often co-created with stakeholders and can evolve as the project progresses.
* Changes are expected and embraced as part of the methodology to adapt to evolving needs.
* Risk and Cost are managed in real-time, allowing for quick responses to change.
* Key Stakeholders are engaged continuously, with their feedback incorporated into the project iteratively.
References: The PMBOKGuide1 and the Agile Practice Guide provide a framework for understanding these approaches. The PMP Examination Content Outline2 also details the differences between predictive and agile methodologies, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right approach based on the project's needs and environment.
- 質問一覧「709問」
- 質問1 実行段階のプロジェクトに新しいプロジェクトマネージャーが割り
- 質問2 プロジェクトマネージャーは、ハイブリッドプロジェクトでスクラ
- 質問3 プロジェクト マネージャーはプロジェクトの開始を終えたところ
- 質問4 アジャイル プロジェクトは、実行最小限の製品 (MVP) を定義する...
- 質問5 プロジェクト マネージャーとプロジェクト チームは、障害をマッ...
- 質問6 プロジェクト マネージャーは、アジャイル チームと協力して製品...
- 質問7 プロジェクト マネージャーは、新しく形成されたアジャイル チー...
- 質問8 ある企業は、プロジェクトの予測的実施から機敏な実施に移行しつ
- 質問9 ベンダーのプロジェクト マネージャーとチームは、組織全体にソ
- 質問10 プロジェクト憲章が承認され、プロジェクト マネージャーがプロ
- 質問11 プロジェクト マネージャーは、主要な成果物の一部として集中的
- 質問12 ある企業は、既存のシステムの統合を開発するプロジェクトに取り
- 質問13 チームメンバーはいつも仕事に遅れます。プロジェクト マネージ
- 質問14 プロジェクト マネージャーはプロジェクトを主導するよう求めら
- 質問15 保護チームはリモートでソリューションに取り組んでいます クラ
- 質問16 一部の業界の利害関係者は、プロジェクトマネージャーをバイパス
- 質問17 ゼネコンの CEO は、プロジェクト マネージャーに、特定のトレー...
- 質問18 最近、プロジェクト マネージャーが、これから始まる新しいプロ
- 質問19 プロジェクト マネージャーは、規制要件に準拠するためにハイブ
- 質問20 プロジェクト マネージャーは、進行中の複雑なプロジェクトに割
- 質問21 アジャイル チームは、ビジネス価値を提供するために 2 週間のス...
- 質問22 ある企業は、既存の製品の 1 つを強化するプロジェクトを開始し...
- 質問23 航空機製造会社で働くスクラム チームは、重要なプロジェクトの
- 質問24 プロジェクト マネージャーは、スケジュールやコストに影響を与
- 質問25 スプリント計画中、製品所有者はビジネス価値の高い項目を優先し
- 質問26 プロジェクト マネージャーは、大企業のイノベーション プロジェ...
- 質問27 ベンダーが新しいシステムの構築に従事しているプロジェクトに、
- 質問28 品質レビュー中に複数の問題が発見されたため、プロジェクトが遅
- 質問29 プロジェクト マネージャーは、独自の企業文化を持つ複数の組織
- 質問30 毎日のチームスタンドアップミーティングでは、チームメンバーは
- 質問31 プロジェクト マネージャーがハイブリッド プロジェクトを管理し...
- 質問32 プロジェクトが終了しようとしており、プロジェクト マネージャ
- 質問33 ある企業が既存のプロジェクトの製品所有者を変更しました。新し
- 質問34 プロジェクト マネージャーは、アプリケーション開発の人材をト
- 質問35 ある企業は移行し、現在、予測アプローチではなくハイブリッド
- 質問36 プロジェクト マネージャーは、顧客の受け入れに関していくつか
- 質問37 プロジェクトが終了し、最終成果物が顧客に受け入れられました。
- 質問38 プロジェクト マネージャーは、実行段階にあるプロジェクトを指
- 質問39 会社のプロジェクトマネージャーは、組織の高性能なジュニアメン
- 質問40 プロジェクト マネージャーが、アジャイル フレームワークを使用...
- 質問41 高リスク プロジェクトのプロジェクト マネージャーは、スケジュ...
- 質問42 プロジェクトは 12 か月前に開始され、現在 14 回中 12 回目の反...
- 質問43 新しいオンライン ランディング プラットフォームを実装するプロ...
- 質問44 チームには、チームメンバーごとに個別の毎日の開始時間が設定さ
- 質問45 プロジェクト マネージャーは大規模なプロジェクトを管理してい
- 質問46 プロジェクト チームのメンバーは、最新の要件文書が約 1 週間前...
- 質問47 プロジェクト チームは、新しいテクノロジーを製品として含む複
- 質問48 プロジェクトは、プロジェクトの成功に積極的に関与していないチ
- 質問49 プロジェクト マネージャーは会社の重要なプロジェクトに割り当
- 質問50 プロジェクト チームのモテ経験のあるメンバーの中には、プロジ
- 質問51 電気通信プロジェクトは、文化の異なる複数の国にまたがる部門で
- 質問52 プロジェクトチームは約2年間一緒に働いてきました。チーム メン...
- 質問53 プロジェクト マネージャーのチーム メンバーの 1 人が継続的に...
- 質問54 プロジェクト契約によると、納期は近づいていますが、重要な資材
- 質問55 新しいチームメンバーは、会社のイントラネットに存在する組織プ
- 質問56 プロジェクトの初期段階で、チーム メンバーが 3 回のチーム ミ...
- 質問57 左側のステージの特性を右側の適切な Tuckman Ladder ステージに...
- 質問58 プロジェクトのチームリーダーが組織を離れたため、経営陣はエン
- 質問59 プロジェクト マネージャーは、プロジェクトの承認基準を逸脱し
- 質問60 プロジェクト マネージャーは、新しいツールを開発するプロジェ
- 質問61 プロジェクト マネージャーは、アジャイルに移行中の企業のプロ
- 質問62 プロジェクト マネージャーは、さまざまな種類の利害関係者がい
- 質問63 プロジェクト マネージャーはプロジェクト スポンサーからプロジ...
- 質問64 プロジェクト マネージャーは、展開を正常に完了したばかりで、
- 質問65 プロジェクト チームのメンバーは、プロジェクトの主要サプライ
- 1コメント質問66 プロジェクト マネージャーは、地理的に分散した仮想チームを率
- 質問67 プロジェクト マネージャーはプロジェクト サイトで納品物を受け...
- 質問68 ある企業は、自社の生産ラインの 1 つで生産コストを削減するこ...
- 質問69 実績のある確立されたプロジェクト チームが 1 年間プロジェクト...
- 質問70 プロジェクトは開始されたばかりであり、経営陣の期待は、最初の
- 質問71 プロジェクト マネージャーは、主要な利害関係者がプロジェクト
- 質問72 プロジェクトの成果物をレビューするためのワークショップの終わ
- 質問73 プロジェクト マネージャーは、範囲がすでに確立されている後に
- 質問74 プロジェクト マネージャーは、設計段階の途中にある歯科用機器
- 質問75 プロジェクト チームは計画段階にあり、活動のリストを作成し、
- 質問76 アジャイルプロジェクトマネージャーには、実装するかなりのソフ
- 質問77 ビジネス変革プロジェクトには 4 段階の実施計画があります。プ...
- 質問78 ある中堅企業は、新製品の発売に関して新しいマーケティング戦略
- 質問79 最後のスプリント レビュー中に、ママの関係者は、製品に期待し
- 質問80 プロジェクトの受け入れ基準には、システムの新規ユーザー向けの
- 質問81 プロジェクト マネージャーは、開発者のプロジェクト チームのス...
- 質問82 ある国のプロジェクト マネージャーは、別の国の新しいソフトウ
- 質問83 プロジェクト マネージャーは、ビジネスとのコラボレーションが
- 質問84 プロジェクト マネージャーが、政府機関の主要プロジェクトを主
- 質問85 現在のスプリントに対する進捗状況を評価する毎日のスタンドアッ
- 質問86 プロジェクト スポンサーがプロジェクト憲章とビジネス ケースを...
- 質問87 プロジェクトが完了に近づいている 予備時間が費やされている 最...
- 質問88 プロジェクト マネージャーは、望ましい結果を達成するために必
- 質問89 サーバント リーダーが機密のアジャイル研究プロジェクトを開始
- 質問90 組織に初めて加わったプロジェクト マネージャーは、リソース不
- 質問91 プロジェクト マネージャーは、マーケティング アナリストから、...
- 質問92 ハイブリッド プロジェクトでは、製品のアジャイルな配信とマー
- 質問93 上級管理チームのメンバーがアジャイル プロジェクト リーダーに...
- 質問94 プロジェクト マネージャーには、世界中のさまざまなタイムゾー
- 質問95 金融会社では、予測アプローチを使用する戦略的プロジェクトが計
- 質問96 アジャイル リーダーは、チームを確実に成功に導くために何をす
- 質問97 プロジェクト計画の会議中に、顧客は新しい製品をどのように構築
- 質問98 ポートフォリオバックログの重要なプロジェクトを提供する必要が
- 質問99 あるプロジェクト マネージャーは、機能マネージャーがスタッフ
- 質問100 プロジェクト管理オフィス (PMO) ディレクターは、ソフトウェア...
- 質問101 外部関係者への依存関係を含むプロジェクトの要件をすべて収集し
- 質問102 運用機能内でプロジェクトを実行しているときに、プロジェクト
- 質問103 プロジェクト マネージャーは、多数の成果物を含む複雑なプロジ
- 質問104 プロジェクト マネージャーは、プロジェクトの範囲で定義されて
- 質問105 ある企業が新製品を市場に導入するプロジェクトを開始しました。
- 質問106 プロジェクト チームは、予測アプローチからアジャイル アプロー...
- 質問107 チームには、新規顧客向けの概念的な製品を構築するためのアジャ
- 質問108 プロジェクト マネージャーは、政府所有の企業のプロジェクトを
- 質問109 ある会社の取締役会は、今月末に大規模な人員削減が行われると発
- 質問110 チーム メンバーの 1 人が時間内にタスクを完了しなかったため、...
- 質問111 振り返り中に、チーム メンバーの 1 人が、機能マネージャーがタ...
- 質問112 振り返りミーティング中に、プロジェクト マネージャーは、製品
- 質問113 既存のソフトウェア プロジェクトを引き継ぐプロジェクト マネー...
- 質問114 非常に複雑なプロジェクトに関連した経験を持つ上級従業員が、プ
- 質問115 プロジェクトマネージャーは、スポンサーと合意したプロジェクト
- 質問116 成果物のフォローアップ中に、チーム メンバーが他のチーム メン...
- 質問117 新しいプロジェクト マネージャーとの最初のプロジェクト会議中
- 質問118 戦略的イニシアチブのプロジェクト マネージャーは、新しい利害
- 質問119 プロジェクトマネージャーは、組織全体で新しいプロセスを実装す
- 質問120 プロジェクト マネージャーは、達成価値管理 (EVM) を通じて主要...
- 質問121 プロジェクト マネージャーは、複数のグローバル オフィスを持つ...
- 質問122 プロジェクト マネージャーは、特定された問題に対する対応アク
- 質問123 プロジェクト マネージャーは、非常に初期段階の社内プロジェク
- 質問124 プロジェクト マネージャーはクライアントとの進捗会議に出席し
- 質問125 アジャイル プロジェクト チームは新しいプロジェクトを任されて...
- 質問126 プロジェクトがプロジェクト終了フェーズに近づいているとき、プ
- 質問127 システム移行プロジェクトは最終段階に入っています。プロジェク
- 質問128 進行中のプロジェクトの第2フェーズに新たにプロジェクトマネー
- 質問129 チームが望ましい設計について相互の合意に達すると、利害関係者
- 質問130 組織はアジャイルな変革を遂げています。経営幹部チームは、プロ
- 質問131 ある企業は、作業範囲を提供するためにベンダーを雇用し、プロジ
- 質問132 プロジェクト マネージャーは、プロジェクト チームが同じプロジ...
- 質問133 自己組織化されたチームは、内部の問題をプロジェクト マネージ
- 質問134 プロジェクトマネージャーが数百万ドルのプロジェクトに任命され
- 質問135 イテレーションベースのマーケティング プロジェクトでは、製品
- 質問136 プロジェクトが完了に近づいています。スポンサーはすでにプロジ
- 質問137 プロジェクトは実行段階にあります。クライアントは初期段階では
- 質問138 複数のサプライヤーとのプロジェクトの終わりに、プロジェクトマ
- 質問139 プロジェクト マネージャーは、開発中のプロジェクトに割り当て
- 質問140 プロジェクト チームのメンバーがプロジェクト ステータス レポ...
- 質問141 石油とガスの探査活動の影響を受けるコミュニティのためにプロジ
- 質問142 チーム メンバーの 1 人は常にチーム ミーティングに欠席します...
- 質問143 新しい金融システムの展開は実行段階にあります。先月、プロジェ
- 質問144 プロジェクト チームのメンバーは、チームが計算を実行するため
- 質問145 プロジェクト マネージャーは、チームとともにスプリントの目標
- 質問146 クロージング プロセス中に、プロジェクト マネージャーは、1 つ...
- 質問147 アジャイルプロジェクトは、暗号通貨の固定価格に基づいてクライ
- 質問148 プロジェクト マネージャーは、90% 完了したプロジェクトを指揮...
- 質問149 大規模プロジェクトのアジャイル チームのプロジェクト マネージ...
- 質問150 プロジェクト マネージャーは、アジャイル環境で同じ作業範囲に
- 質問151 医療組織は、医療コンプライアンスのニーズを確実に満たすために
- 質問152 年末までに新製品を市場に導入する予定の企業は、保管および配送
- 質問153 市は新しい路面電車駅を建設することを決定した。このプロジェク
- 質問154 専門チームのメンバーは、数週間オフィスを離れなければならない
- 質問155 アジャイル チームが人事 (HR) アプリケーション システムのイン...
- 質問156 顧客は新製品を市場に投入したいと考えており、このプロジェクト
- 質問157 プロジェクト チームは、複数回の反復を計画した製品に取り組ん
- 質問158 ある銀行は、近隣の 3 つの都市のいずれかに別の支店を建設する...
- 質問159 チームは終了フェーズの準備をし、次のフェーズの計画を構築して
- 質問160 自己組織化されたチームが約束通りの成果を上げていました。チー
- 質問161 プロジェクト スポンサーからの重要な電子メールには、バックロ
- 質問162 あるプロジェクト マネージャーが最近組織に加わりましたが、プ
- 質問163 プロジェクトが期待される利益を継続的に提供できるようにするた
- 質問164 プロジェクトの実行中に、経験豊富なチーム メンバーがプロジェ
- 質問165 主な関係者は、プロジェクトのステータス会議に継続的に参加でき
- 質問166 ある顧客が、新しいプロジェクトのコストと期間が同じであること
- 質問167 重要な国家プロジェクトが実行段階に入っています。時間制限のあ
- 質問168 プロジェクトは 2 か月間正常に実行されています。定期的なプロ...
- 質問169 世界規模のプログラムが開始され、さまざまな分散チームがこの取
- 質問170 2 つの大企業が合併した後、プロジェクトにはプロジェクト マネ...
- 質問171 自己組織化チームの新しいチーム メンバーは、プロジェクトで使
- 質問172 コンポーネント開発プロジェクトの 2 回目の反復後、プロジェク...
- 質問173 プロジェクトの実行中に、重要な利害関係者が、プロジェクトの実
- 質問174 主要な意思決定者が会議を開き、新しいデータベース移行プロジェ
- 質問175 プロジェクト マネージャーは複数年にわたるプロジェクトに割り
- 質問176 統合プロジェクトにはハードウェアとソフトウェアの両方の相互作
- 質問177 チームはハイブリッド プロジェクトに取り組んでいます。プロジ
- 質問178 プロジェクト マネージャーは、期限を過ぎ続けているスクラム チ...
- 質問179 プロジェクト チームは、顧客の要件を理解した後、ユーザー スト...
- 質問180 プロジェクト マネージャーは、顧客のアカウント マネージャーか...
- 質問181 プロジェクト チームはメガプロジェクトを実行しており、いくつ
- 質問182 プロジェクト マネージャーは、複数の作業パッケージを含むプロ
- 質問183 プロジェクトでは、データ統合チームとデータ移行チームが重複す
- 質問184 ある組織は最近、予測型配信アプローチからアジャイル配信アプロ
- 質問185 プロジェクト管理オフィス (PMO) は、ハイブリッド アプローチを...
- 質問186 プロジェクト マネージャーは、厳しいスケジュールと固定予算を
- 質問187 プロジェクト マネージャーは、品質向上に関する期限付きの社内
- 質問188 ドラッグドロップ 左側の対人スキルを右側の適切なシナリオにド
- 質問189 建設プロジェクトの実行中に、近隣の企業の 1 つが、現在の建物...
- 質問190 ソフトウェア配信プロジェクトに技術的な障害が発生し始めました
- 質問191 ハイブリッド プロジェクトで、顧客はプロジェクト設計の大幅な
- 質問192 アジャイルなリーダーは、チーム メンバーの 1 人が常に期限内に...
- 質問193 プロジェクトマネージャーがプロジェクトに割り当てられ、Projec...
- 質問194 顧客の技術責任者がプロジェクト マネージャーと新機能について
- 質問195 プロジェクトの終了時に、プロジェクト マネージャーは、規制要
- 質問196 建設会社は、建物の特定のコンポーネントを交換するための確定的
- 質問197 プロジェクトマネージャーは、大規模な建設プロジェクトに割り当
- 質問198 プロジェクト マネージャーは、プロジェクト チーム メンバーが ...
- 質問199 プロジェクト マネージャーは、マトリックス組織で複数の情報技
- 質問200 8 人の高度な資格を持つ専門家が集められ、組織の製品開発プロセ...
- 質問201 プロジェクト管理オフィス (PMO) によるプロジェクト ステータス...
- 質問202 最近、2 週間後に開始予定の複雑なプロジェクトを率いるために、...
- 質問203 プロジェクト チームのメンバーは、プロジェクト ガバナンスの新...
- 質問204 多国籍プロジェクトでは、関係者は異なるタイムゾーンにいます。
- 質問205 プロジェクト マネージャーはアジャイル プロジェクトの管理を始...
- 質問206 プロジェクト マネージャーが自動化プロジェクトを主導していま
- 質問207 ソフトウェア開発会社のプロジェクト マネージャーは、プロジェ
- 質問208 ある企業は、これまで不採算だった販売チャネルを廃止するプロジ
- 質問209 装置ベンダーは顧客企業のために新しい生産ラインを導入します。
- 質問210 ある企業は、アジャイル アプローチを使用して変革プロジェクト
- 質問211 製品チームはコンサルタントとスタッフ メンバーで構成されます
- 質問212 プロジェクトの途中で、プロジェクトのスポンサーが、それまでプ
- 質問213 新しいプロジェクト マネージャーがアジャイル プロジェクトを主...
- 質問214 プロジェクト マネージャーがプロジェクトの途中で、主要なプロ
- 質問215 プロジェクトの完了中に、プロジェクト マネージャーは顧客から
- 質問216 プロジェクトでは、過去 4 回のレビューでスケジュール パフォー...
- 質問217 プロジェクトの終わりに向けた範囲検証の演習中に、プロジェクト
- 質問218 大きなプロジェクトの実行段階の途中で、プロジェクトに馴染みの
- 質問219 システムのデモ中に、プロジェクト関係者が最新のユーザー スト
- 質問220 プロジェクトの主要な利害関係者が解雇され、別の利害関係者が後
- 質問221 プロジェクトの進行段階で、プロジェクト状況報告書を受け取って
- 質問222 ある保険会社は、中核となるアプリケーションに大きな変更を加え
- 質問223 プロジェクト マネージャーは、複数の国で事業を展開しているチ
- 質問224 (Exhibit) 過去 7 日間のスプリントのこのバーンアップ チャート...
- 質問225 重要なプロジェクトに割り当てられた経験豊富なチーム メンバー
- 質問226 プロジェクトの範囲は、半径 10 km 以内の道路標識の交換です。...
- 質問227 チームメンバーは過去のプロジェクトで個人的な衝突を経験してお
- 質問228 プロジェクト マネージャーは、プロジェクト スポンサーからプロ...
- 質問229 新しいプロジェクトの計画の最後に、プロジェクト マネージャー
- 質問230 懸念を抱いたプロジェクト チーム メンバーは、チーム ミーティ...
- 質問231 プロジェクト マネージャーは、予測プロジェクト管理アプローチ
- 質問232 プロジェクト マネージャーは、主要製品の新バージョンをリリー
- 質問233 大企業が環境プロジェクトのビジネスケースに合意しました。この
- 質問234 プロジェクトのさまざまな段階でさまざまな関係者から大量の大き
- 質問235 組織はプロジェクト管理にハイブリッド アプローチを使用してい
- 質問236 プロジェクトの実行中に、プロジェクト マネージャーは、完了時
- 質問237 プロジェクト マネージャーは、クライアントのレポートを作成す
- 質問238 チームは、プロジェクトが現在のイテレーションを完了するために
- 質問239 長期プロジェクトの計画中に、プロジェクト マネージャーは、チ
- 質問240 グローバルプロジェクトチームによるプロジェクトが始まろうとし
- 質問241 プロジェクト マネージャーは、70 人の関係者が関わる大規模プロ...
- 質問242 プロジェクト チームは、視覚的な管理ツールの 1 つを使用して依...
- 質問243 ハイブリッド プロジェクトのプロジェクト マネージャーは、利害...
- 質問244 営業マネージャーが製品所有者に新機能リクエストを送信すると、
- 質問245 プロジェクトの過程で、プロジェクトが前進するのを妨げているい
- 質問246 予測プロジェクトの経験を持つ若手プロジェクト マネージャーが
- 質問247 アジャイル チームはプロジェクトの開発サイクルの初期段階にあ
- 質問248 プロジェクト マネージャーは、複数のワークストリームを含むプ
- 質問249 プロジェクト マネージャーは、サブリージョン内の異なるタイム
- 質問250 プロジェクトの実行段階で、プロジェクト マネージャーは、プロ
- 質問251 技術者は、勤務スケジュールが異なる 3 人のリモート コールセン...
- 質問252 プロダクト オーナーが、数人の主要関係者との会議から戻ってき
- 質問253 プロジェクト会議中に、プロジェクト マネージャーはリスク オー...
- 質問254 プロジェクトのスケジュールは遅れており、プロジェクト マネー
- 質問255 テクノロジー プロジェクトは、新しいプラットフォームで新しい
- 質問256 チームはキックオフ後に形成段階に入り、プロジェクトの目標が特
- 質問257 キャンセルされたプロジェクトの終了後、プロジェクト マネージ
- 質問258 プロジェクト マネージャーは、チームが手順を定義し、データを
- 質問259 アジャイル プロジェクトでは、学習は 1 回の反復で 40 ストーリ...
- 質問260 プロジェクト マネージャーは新しいプロジェクトに割り当てられ
- 質問261 プロジェクト スポンサーは、主要な関係者が、プロジェクト マネ...
- 質問262 プロジェクト マネージャーは、200 人のエンド ユーザーに新しい...
- 質問263 機敏なチームが、主要な政府製品への変更の実装を義務付けるプロ
- 質問264 不測の事態により、請負業者は対面での会議や議論を行うために必
- 質問265 海外のクライアントがソフトウェア製品を構築するためにソフトウ
- 質問266 プロジェクトが始まろうとしています。プロジェクト マネージャ
- 質問267 ある企業は、新しいプロジェクトに必要なリソースを決定する最初
- 質問268 私たちアーキテクトは、次のスプリントに含まれる開発の特定のコ
- 質問269 プロジェクト マネージャーは、プロジェクトの実施にハイブリッ
- 質問270 プロジェクト マネージャーはプロジェクトを計画し、特定のプロ
- 質問271 プロジェクトの実施中に、あるチームは、主要なプロジェクト成果
- 質問272 ある企業が本社を別の都市に移転します。この割り当てを担当する
- 質問273 プロジェクト マネージャーは、毎週のリスク管理会議のためにク
- 質問274 プロジェクト マネージャーは、初めてアジャイル プロジェクトを...
- 質問275 グループは1か月間協力しています。毎日の会議中、チームメンバ
- 質問276 プロジェクト チームは、川に建設される橋のプロジェクト リスク...
- 質問277 ソフトウェア開発プロジェクトでは、製品所有者と開発チームがス
- 質問278 プロジェクト マネージャーは、長期プロジェクトの予算に取り組
- 質問279 プロジェクト マネージャーは、以前の同様のプロジェクトに基づ
- 質問280 新しいプロジェクトマネージャーが環境プロジェクトに割り当てら
- 質問281 プロジェクト チームのメンバーは、プロジェクト チームの会議中...
- 質問282 上級プロジェクト マネージャーは、まだ利益を上げていない会社
- 質問283 ある顧客は、これまでに公開されたユーザー ストーリーには専門
- 質問284 グローバル プロジェクトでは、主要な定義が A 国で開発され、プ...
- 質問285 チーム メンバーが、正常に終了したプロジェクトで直面したもの
- 質問286 クライアントへの納品を妨げているいくつかの品質問題の原因につ
- 質問287 プロジェクトが承認された後、主要な利害関係者は、現在のプロジ
- 質問288 最近プロジェクトが始まりました。プロジェクト マネージャーは
- 質問289 プロジェクト マネージャーは、1 年間にわたるプロジェクトに割...
- 質問290 高価な製造プロジェクトのいくつかのコンポーネントが顧客から返
- 質問291 プロジェクト マネージャーはプロジェクトを評価しており、その
- 質問292 プロジェクトの終了が近づくと、顧客は一部の成果物が満たされて
- 質問293 アジャイル プロジェクト チームは、プロジェクトの品質基準の策...
- 質問294 プロジェクト マネージャーは、予測アプローチを使用して、同じ
- 質問295 プロジェクト マネージャーは、組織の運用モデルを変革するプロ
- 質問296 主要な関係者とプロジェクト管理計画を検討した結果、プロジェク
- 質問297 マルチメディア展示設計プロジェクトの開始段階で、プロジェクト
- 質問298 CEO がプロジェクト マネージャーに、4 年間に渡る長期プロジェ...
- 質問299 12 か月のプロジェクトの開始が 2 か月遅れました。 プロジェク...
- 質問300 企業のプロジェクト管理オフィス (PMO) は、より適応性のあるテ...
- 質問301 プロジェクト マネージャーは、予算を超過するリスクがあるプロ
- 質問302 プロジェクト チームが数か月間プロジェクトに取り組んだ後、プ
- 質問303 チーム メンバーの 1 人が、ブレーンストーミング セッション中...
- 質問304 プロジェクト マネージャーは、テスト段階にある医療組織の戦略
- 質問305 左側の項目を、右側の正しいプロジェクト アプローチ内の一致す
- 質問306 プロジェクト チームは最近、フリート管理システムの 2 つの機能...
- 質問307 プロジェクト マネージャーは、プロジェクトの基本スケジュール
- 質問308 複雑なプロジェクトの実行中、プロジェクト マネージャーはさま
- 質問309 プロジェクト マネージャーは、アジャイルを初めて使用するチー
- 質問310 プロジェクトの進行中、プロジェクト マネージャーは、実行され
- 質問311 複数の業界に関わる企業で働くプロジェクト マネージャーが、政
- 質問312 IT プロジェクト マネージャーは、品質保証のプロフェッショナル...
- 質問313 新しいソリューションの展開のためにプロジェクト マネージャー
- 質問314 技術研究プロジェクトにはプロジェクトマネージャーが割り当てら
- 質問315 チーム リードはプロジェクトに深く関与しており、指揮系統や権
- 質問316 ある企業は、アジャイル アプローチを使用してプロジェクトの管
- 質問317 プロジェクト マネージャーが新しいアジャイル プロジェクトを主...
- 質問318 プロジェクト チームは重要な成果物を顧客に提供しました。お客
- 質問319 メンテナンス プロジェクトの実行中に、請負業者が追加作業のオ
- 質問320 エネルギー使用量を削減するためのビジネス改善の機会が特定され
- 質問321 プロジェクト マネージャーは、予定通りに予算内でプロジェクト
- 質問322 プロジェクト マネージャーは、社内および社外の関係者が関与す
- 質問323 左側の組織特性を右側の正しいシナリオにドラッグします。 (Exhi...
- 質問324 プロジェクトマネージャーは、サプライヤーから、規制変更により
- 質問325 調達チームのリーダーが他のプロジェクト チームのメンバーと毎
- 質問326 チームメンバーの一人が巻き込まれた事件の後、チームの士気はこ
- 質問327 プロジェクト マネージャーは、厳密に定義された要件を持つ政府
- 質問328 プロジェクト マネージャーは、新製品のプロジェクト憲章を受け
- 質問329 プロジェクトのライフサイクルの終わりに、最先端の製品が納品さ
- 質問330 企業は現在のビジネス モデルを変更しています。この変更には、
- 質問331 キーリソースがプロジェクトに新たに割り当てられます。以前のプ
- 質問332 チームは、中規模プロジェクトでこれまでに構築されたソフトウェ
- 質問333 プロジェクト マネージャーが新しいマーケティング キャンペーン...
- 質問334 プロジェクトは 7 回中 6 回目のイテレーションを開始しています...
- 質問335 プロジェクトでは、プロジェクト文書に記載され、プロジェクト
- 質問336 プロジェクトの 3 回目の反復中に、メイン スポンサーが会社を退...
- 質問337 チームメンバーは、回顧展中に議論された別のチームメンバーのパ
- 質問338 プロジェクト マネージャーは、主要な関係者、プロジェクト スポ...
- 質問339 新しく割り当てられたプロジェクト マネージャーは、プロジェク
- 質問340 ビル管理システム (BMS) プロジェクトは試運転段階にあり、運用...
- 質問341 あるプロジェクト マネージャーは、機能マネージャーがスタッフ
- 質問342 ある企業は成長戦略を実行するために新しい生産施設を建設してお
- 質問343 プロジェクト マネージャーは最近アジャイル プロジェクトに割り...
- 質問344 プロジェクト マネージャーは、あらゆる年齢層の多様な個人から
- 質問345 チームはアジャイルなアプローチを使用してプロジェクトのバック
- 質問346 ある小売会社は、プロモーションやセールス ポイントについて顧
- 質問347 プロジェクト マネージャーは、歯科用ワイヤー ベンディング マ...
- 質問348 プロジェクトの実行中、プロジェクト タスクの 1 つは、サービス...
- 質問349 重要なプロジェクトの自己組織化チームは、コミットメントに従っ
- 質問350 ある企業は、経済の変化に備えて大規模な変革プロジェクトに着手
- 質問351 ある会社の CEO は、プロジェクトのコミュニケーションの頻度に...
- 質問352 財務プロジェクトの実行中、プロジェクト マネージャーはプロジ
- 質問353 利害関係者は、コンプライアンス関連のいくつかのギャップと問題
- 質問354 プロジェクト スポンサーがプロジェクト チームに、プロジェクト...
- 質問355 チームメンバーがスタンドアップミーティング中に、昨日のタスク
- 質問356 プロジェクト マネージャーには、クライアント プロジェクトに取...
- 質問357 新しいシステムを展開するプロジェクトを主導するプロジェクト
- 質問358 ある新興企業が、プロジェクト経験のない CEO を任命したところ...
- 質問359 建設プロジェクトの実施段階で、顧客は主要な下請け業者に作業パ
- 質問360 大企業がプロジェクトをアジャイル アプローチに移行中です。 移...
- 質問361 下請け業者はプロジェクト マネージャーに、プロジェクトに主要
- 質問362 ある企業は、アジャイル手法を使用して大規模な変革プロジェクト
- 質問363 プロジェクト マネージャーは、顧客との現在の反復におけるプロ
- 質問364 プロジェクト マネージャーがソフトウェア開発プロジェクトに割
- 質問365 チームとは、企業内で従来のプロジェクトにアジャイル手法を使用
- 質問366 プロジェクトの技術チームは、最近この役割に昇進したリーダーに
- 質問367 プロジェクト マネージャーは、スクラム フレームワークを使用し...
- 質問368 チームメンバーは非常に優れた技術スキルを持ち、リーダーシップ
- 質問369 エンタープライズ リソース プランニング (ERP) システムの導入...
- 質問370 プロジェクト マネージャーがプロジェクト チームのビジネス ア...
- 質問371 ある企業は過去数年間に複数の人員配置と業務変更を行い、企業文
- 質問372 アジャイル プロジェクトの実行中に、プロジェクト マネージャー...
- 質問373 ある企業は、非効率な販売チャネルを廃止するプロジェクトを開始
- 質問374 プロジェクト スポンサーによって他の重要なセキュリティ パッチ...
- 質問375 地元コミュニティの支援を受けた自動化プロジェクトの契約が最近
- 質問376 プロジェクト チームでは、2 人のチーム メンバー間で対立が発生...
- 質問377 ハイブリッド プロジェクトの最後の反復中に、チームの主要メン
- 質問378 新しいエンジニアがプロジェクトに割り当てられました。エンジニ
- 質問379 最近の運営委員会の会議で、プロジェクト スポンサーはプロジェ
- 質問380 プロジェクト マネージャーは、非常に難しいクライアントとの大
- 質問381 新しい開発プロジェクトが始まろうとしていますが、プロジェクト
- 質問382 下請け会社が機能リリースを発表している 主要な関係者が製品に
- 質問383 タイトなスケジュールのプロジェクト チームは、毎日の定期的な
- 質問384 を右側の正しいシナリオにドラッグします (Exhibit)
- 質問385 アジャイルなチームは、成果物の品質という課題に直面しています
- 質問386 毎日のスタンドアップ ミーティングで、プロジェクト マネージャ...
- 質問387 アジャイル チームが新しいコンテンツ管理システムを開発してい
- 質問388 プロジェクトの範囲は、多くの仮定に基づいて作成されました。実
- 質問389 さまざまな国のメンバーがいるプロジェクト チームは、協力する
- 質問390 アジャイル プロジェクトには、高、中、低のカテゴリに優先順位
- 質問391 最近、プロジェクト マネージャーが銀行の IT プロジェクトに割...
- 質問392 相互に接続された 2 つのサブプロジェクトで構成される新しい主...
- 質問393 新製品開発プロセスに従って、マーケティング部門はビジネス要件
- 質問394 チームは 3 回の反復を伴うプロジェクトに取り組んでいます。プ...
- 質問395 昨年、いくつかのプロジェクトをサポートしてきた保護スポンサー
- 質問396 プロジェクト マネージャーは最近プロジェクトを引き継ぎました
- 質問397 アジャイル アプローチを使用するソフトウェア プロジェクトは、...
- 質問398 プロジェクト チームは、A 国に拠点を置くメンバーと、12 時間の...
- 質問399 プロジェクト マネージャーは、モバイル アプリを開発するプロジ...
- 質問400 プロジェクトの計画段階で、プロジェクト マネージャーは、標準
- 質問401 テクノロジー プロジェクトのプロジェクト マネージャーは、サイ...
- 質問402 プロジェクト マネージャーは、商社向けの会計ソフトウェアを開
- 質問403 国際企業の文書監査中に、プロジェクト マネージャー kr が担当...
- 質問404 プロジェクト管理チームのミーティングでは、チーム メンバーの ...
- 質問405 ある企業は、予測アプローチからアジャイル アプローチに移行し
- 質問406 スタンドアップ ミーティングで、チーム メンバーが 5 日間連続...
- 質問407 保護マネージャーは、クラウドベース システムの世界的な導入を
- 質問408 プロジェクト会議中に、プロジェクト マネージャーは、レポート
- 質問409 プロジェクト マネージャーは、アジャイル デリバリの使用を開始...
- 質問410 プロジェクトは 6 回の反復のうち 5 回目を終了しようとしていま...
- 質問411 プロジェクトマネージャーは、海外での新しいオフィスの開設を管
- 質問412 企業のネットワーク アップグレード中に、クライアントは、政府
- 質問413 プロジェクト マネージャーは、組織の業界標準について十分な情
- 質問414 あるプロジェクトについて、サブサプライヤーとの技術的問題によ
- 質問415 新しいチームメンバーが自己組織化チームに追加されます。新しい
- 質問416 プロジェクト実行開始時のキックオフ ミーティング中に、ベンダ
- 質問417 プロジェクト マネージャーは、いくつかの主要な成果物について
- 質問418 プロジェクトは完了に近づいていますが、予定より遅れています。
- 質問419 プロジェクト チームは、いくつかの利害関係者の要件に関して、
- 質問420 新しいソリューションが AB 国と C 国で導入されています。この...
- 質問421 若手プロジェクト マネージャーは、電気通信会社との最初のプロ
- 質問422 プロジェクト マネージャーは、顧客がオンラインの e ラーニング...
- 質問423 プロジェクトのプログラミング作業はモジュールごとに 35 日間続...
- 質問424 新製品の開発に取り組んでいるアジャイル チームは、イテレーシ
- 質問425 保護マネージャーは、さまざまな配信方法を使用する会社でプロジ
- 質問426 プロジェクトが完了に近づくと、プロジェクト スポンサーはプロ
- 質問427 プロジェクトの顧客は激怒しています。お客様がプロジェクト現場
- 質問428 プロジェクト マネージャーは、市場に迅速に展開する必要がある
- 質問429 プロジェクト チームのパフォーマンスは、活動の進行やチームの
- 質問430 プロジェクト マネージャーが既存のプロジェクトを引き継いだ 前...
- 質問431 企業はスクラムの実装を開始します。最初のスプリントの半分くら
- 質問432 プロジェクトの開始段階では、プロジェクト マネージャーとチー
- 質問433 アジャイル プロジェクトのセットアップ中に、製品所有者は、製
- 質問434 3000万ドル以上の予算を投じたイノベーションプロジェクトは、テ...
- 質問435 製品レビューの会議中に、主要な関係者が、プロジェクトに関する
- 質問436 アジャイル プロジェクトでは、チームは毎日のスクラムにファシ
- 質問437 マーケティング チームは、プロジェクトでハイブリッド アプロー...
- 質問438 チームはイテレーションごとに平均 100 ストーリー ポイントを獲...
- 質問439 大規模な水力発電所を開発するプロジェクトは実施段階にあり、ハ
- 質問440 人的資源 (HR) コスト報告書が、誤ってプロジェクト チームのメ...
- 質問441 要件が明確でないため、チームは作業を完了するのに苦労していま
- 質問442 プロジェクト マネージャーは利害関係者登録簿を作成しています
- 質問443 進行中の住宅プロジェクトのライフサイクルに入って 1 年後、プ...
- 質問444 プロジェクトの主要な関係者がプロジェクト会議に一切出席せず、
- 質問445 プロジェクト マネージャーがプロジェクトのスケジュールをママ
- 質問446 2 人の主要なチーム メンバーが、時間超過や遅延を防ぐためのさ...
- 質問447 プロジェクトの成果物の 1 つは、学生向けの資料を 2 週間ごとに...
- 質問448 外部のビジネスの影響によりプロジェクトが開始されました。プロ
- 質問449 プロジェクト マネージャーは全社規模のソフトウェア プロジェク...
- 質問450 プロジェクト マネージャーが固定価格プロジェクトを完了したと
- 質問451 プロジェクトマネージャーは大規模なグローバル企業に勤めていま
- 質問452 ハイブリッド プロジェクト マネージャーが、厳しく規制された環...
- 質問453 プロジェクト ゲート レビュー ミーティング中に、プロジェクト...
- 質問454 プロジェクト計画活動中に特定されたリスクの 1 つは、優先ベン...
- 質問455 プロジェクト会議で、ビジネス アナリストはタスクに取り組み続
- 質問456 プロジェクト マネージャーがハイブリッド プロジェクトに割り当...
- 質問457 経験豊富なプロジェクト マネージャーが合併・買収プロジェクト
- 質問458 プロジェクト B のリーダーは、プロジェクト A のチーム メンバ...
- 質問459 IT 導入プロジェクトに取り組んでいる営業チームは、プロジェク...
- 質問460 ソフトウェア テクノロジー プロジェクトのプロジェクト マネー...
- 質問461 プロジェクト マネージャーは、共同アプリケーション開発モジュ
- 質問462 研究開発部門は、組織に新しいビジネスラインを導入する製品を開
- 質問463 プロジェクト マネージャーは、実行フェーズの終わりに近づいて
- 質問464 アジャイル プロジェクトのプロジェクト マネージャーは、予算を...
- 質問465 新しいプロジェクト マネージャーが、2 週間前に開始された進行...
- 質問466 新しい関連プロジェクト関係者が、実行途中でプロジェクト パラ
- 質問467 重要なアジャイル プロジェクトにプロジェクト マネージャーが割...
- 質問468 Learn メンバーに数日間続く可能性のある突然の緊急事態が発生し...
- 質問469 ストレスの多い状況がチームにいくつかの課題をもたらした。プロ
- 質問470 ジュニアスタッフが最近チームに割り当てられました。新しいチー
- 質問471 プロジェクト マネージャーが新しいプロジェクトに割り当てられ
- 質問472 2 つのチーム (A と B) によるプロジェクトの反復 2 中に、プロ...
- 質問473 建築建設プロジェクトのプロジェクト マネージャーは、プロジェ
- 質問474 新しいソリューションの展開のためにプロジェクト マネージャー
- 質問475 ある企業がクライアントの革新的な製品の発売を支援しています。
- 質問476 仮想チームによる多国籍、複数拠点のプロジェクトで、プロジェク
- 質問477 プロジェクト マネージャーはプロジェクトの進捗状況を確認して
- 質問478 新しいプロジェクトチームが結成され、プロジェクトマネージャー
- 質問479 プロジェクトの利点を追跡しようとすると、プロジェクト マネー
- 質問480 プロジェクトの利害関係者は、すぐに怒り、プロジェクトに対して
- 質問481 プロジェクト マネージャーは、多くの相互接続されたプロジェク
- 質問482 ある企業は、厳しい期限を設定して重要なプロジェクトを開始して
- 質問483 製品所有者は、デモンストレーション式典には定期的に出席しませ
- 質問484 プロジェクト チームは、開発範囲を大幅に縮小する、購入可能な
- 質問485 プロジェクト マネージャーは、チームに特定の分野の主題専門家 ...
- 質問486 プロジェクト マネージャーが顧客の保護の途中で予期せぬ問題を
- 質問487 プロジェクト マネージャーは、厳しい時間制約のあるプロジェク
- 質問488 ここ数週間プロジェクト マネージャーが不在だったプロジェクト
- 質問489 アジャイル プロジェクトのリード プロジェクト マネージャーは...
- 質問490 新しい建築プロジェクトはライフサイクルの途中にあります。 プ
- 質問491 アジャイル チームでは、チーム メンバーの一部が、プロジェクト...
- 質問492 学習は 2 か月間作業を続けていますが、計画されたユーザー スト...
- 質問493 プロジェクト マネージャーが、実際のチーム メンバーとともに、...
- 質問494 プロジェクト チームは、世界中に配布される新しいソリューショ
- 質問495 チーム会議中、プロジェクト マネージャーは、全員が自分自身と
- 質問496 プロジェクト チームのメンバーは、後続の反復で特定の困難なタ
- 質問497 ある企業は、アジャイル アプローチを使用して新製品を開発する
- 質問498 プロジェクト マネージャーは、厳格な品質基準に合格したらすぐ
- 質問499 プロジェクト マネージャーは最近、重要なプロジェクトを主導す
- 質問500 ある企業は、競争の激しい市場で自社製品の商業価値を高めたいと
- 質問501 プロジェクト マネージャーは製品開発プロジェクトに取り組んで
- 質問502 数年前にアジャイルを採用した組織は、各スプリントで生成される
- 質問503 製品所有者は、新製品の初期発売に向けて優先順位を付けたバック
- 質問504 アジャイル プロジェクト チームは、ロボットと接続する産業用シ...
- 質問505 プロジェクトのスプリント計画中に、バックログ項目の相対的なサ
- 質問506 世界的に分散したアジャイル チームのアジャイル コーチとテクニ...
- 質問507 プロテクトは反復設計段階を経ています。チーム メンバーの 1 人...
- 質問508 プロジェクトの実施中に、プロジェクト チームが新しい機会を発
- 質問509 プロジェクトのライフサイクル中に解決されたにもかかわらず、プ
- 質問510 プロジェクト マネージャーは、高い成果を実現するために基本予
- 質問511 アジャイル プロジェクトには、さまざまなユーザー プロファイル...
- 質問512 プロジェクト マネージャーは、ハイブリッド アプローチを使用し...
- 質問513 2 つのチーム内でダイバーシティとインクルージョンを改善するた...
- 質問514 ソフトウェア開発プロジェクトに取り組んでいるプロジェクト マ
- 質問515 プロジェクト マネージャーが、水へのアクセスを緊急に必要とし
- 質問516 新しい販売ソフトウェアの開発プロジェクトが進行中です。新しい
- 質問517 プロジェクト マネージャーは 3 つの仮想チームでプロジェクトに...
- 質問518 アジャイルなプロジェクト チームの上級メンバーが突然組織を辞
- 質問519 プロジェクト ソフトウェアに影響を与える必須のコンプライアン
- 質問520 コンポーネントの未納品が原因でプロジェクトが遅延しました。こ
- 質問521 顧客との会議中に、会議の参加者が重要な設計文書の異なるバージ
- 質問522 プロダクト所有者が変わると、アジャイル プロジェクトは 25% 完...
- 質問523 ある企業は、アジャイル アプローチを使用してプロジェクトの管
- 質問524 プロジェクト管理者は、5 つのイテレーションに分割された 100 ...
- 質問525 ある企業が最新の小売管理システムを導入し、プロジェクトが運用
- 質問526 プロジェクトの実行中、リスク所有者は、最終的に定義されたリス
- 質問527 プロジェクト マネージャーは、新しいプロジェクトのテスト フェ...
- 質問528 大規模なプロジェクトの実行段階では、非常に多くの変更要求が発
- 質問529 マーケティング チームは、プロジェクトに対して予測アプローチ
- 質問530 プロジェクト マネージャーは、チーム メンバー全員を対象とした...
- 質問531 新しいチームメンバーがアジャイルチームに加わります。以前の役
- 質問532 新しいプロジェクト マネージャーが、新しく最適化されたクレジ
- 質問533 プロジェクト マネージャーは非常に複雑なプロジェクトに取り組
- 質問534 一部のアクティビティの遅延により、プロジェクト チームのメン
- 質問535 ある企業は予測アプローチに従っており、製品の品質を評価する前
- 質問536 あるグローバル企業は、レガシー エンタープライズ システムをア...
- 質問537 主要な関係者との製品デモ中に、チームは、機能の 1 つが期待ど...
- 質問538 最初の反復レビューの結果、関係者のフィードバックは、ビジネス
- 質問539 チームは毎日のスタンドアップ ミーティングで次の障害を報告し
- 質問540 ある企業が新製品を発売しようとしていますが、それは夏のシーズ
- 質問541 経験豊富なプロジェクト チーム メンバーは、会議中に常に他のチ...
- 質問542 最近の予算削減により、アジャイル チームから 2 人のチーム メ...
- 質問543 ヘルスケア IT プロジェクトの実行段階で、プロジェクト マネー...
- 質問544 プロジェクト チームの主要メンバーがプロジェクトに高い関心を
- 質問545 プロジェクトの学習メンバーは、遅延の危険性があるプロジェクト
- 質問546 プロジェクト マネージャーはハイブリッド プロジェクトを管理し...
- 質問547 金融会社は、ハイブリッド アプローチを使用してモバイル バンキ...
- 質問548 プロジェクトの実行中に、財務チームは、自分たちがプロジェクト
- 質問549 航空宇宙設計のプロジェクトで重大な技術的問題が発生し、プロジ
- 質問550 組織変更管理チームのメンバーとして、プロジェクト マネージャ
- 質問551 数人の開発者は、毎日のスタンドアップで障害のリストを特定し、
- 質問552 プロジェクト マネージャーが長期プロジェクトに割り当てられま
- 質問553 プロジェクト マネージャーは、製品の商品化の開始に焦点を当て
- 質問554 プロジェクト マネージャーは巨大プロジェクトを管理しています
- 質問555 チームは、顧客が望んでいることを正確に説明できなかったため、
- 質問556 約 45% 完了したアジャイル プロジェクトでは、ほとんどのチーム...
- 質問557 幹部レベルの組織再編後、新しいプロジェクトスポンサーはプロジ
- 質問558 プロジェクト マネージャーは複雑なプロジェクトに取り組んでい
- 質問559 実行段階で、プロジェクト マネージャーは、チーム メンバーの 1...
- 質問560 プロジェクト チームは、製品の機能を評価するための相対的な重
- 質問561 プロジェクト マネージャーは、現在のプロジェクトのリスクを特
- 質問562 ある企業は、過去 3 年間不採算が続いていた販売チャネルを廃止...
- 質問563 新製品の開発中に、主要な関係者が製品の機能要件に関する情報が
- 質問564 企業は、範囲管理計画で定義されている特定のコンポーネントの開
- 質問565 昨年、ある企業は進行中のプロジェクトのために外部の下請け業者
- 質問566 プロジェクト マネージャーは、銀行の情報テクノロジを最新化す
- 質問567 毎日のプロジェクト会議で、チームメンバーは、プロジェクトに関
- 質問568 プロジェクト マネージャーが運用への移行を管理しています。プ
- 質問569 予算が非常に厳しいプロジェクトにプロジェクト マネージャーが
- 質問570 ある多国籍企業は、現在存在感のない新しい国に事業を拡大する計
- 質問571 プロジェクト全体を通じて、プロジェクト マネージャーはチーム ...
- 質問572 サプライヤーはプロジェクト マネージャーに、プロジェクトの主
- 質問573 新しいアジャイル プロジェクト マネージャーは、チーム ミーテ...
- 質問574 最近、プロジェクト マネージャーが、オリンピック施設の優先度
- 質問575 プロジェクト マネージャーは、品質向上に関する期限付きの社内
- 質問576 ビジネス マネージャーと製品所有者は、製品ベースラインに変更
- 質問577 アジャイルプロジェクトのプロジェクトマネージャーは、予算を30...
- 質問578 プロジェクト マネージャーは、組織全体で使用される新製品の展
- 質問579 プロジェクト マネージャーはソフトウェア開発プロジェクトを主
- 質問580 品質基準の変更が必要な品質上の問題がプロジェクトで発生した
- 質問581 プロジェクト チームの経験豊富なメンバーの中には、プロジェク
- 質問582 設備の設置が遅れているため、プロジェクトが予定より遅れていま
- 質問583 プロジェクト チームは、サードパーティ用のホスト システムを実...
- 質問584 プロジェクトマネージャーは、ハイブリッド プロジェクト管理を
- 質問585 ある組織はプロジェクトにアジャイルを導入しています。非公式な
- 質問586 プロジェクト マネージャーはハイブリッド プロジェクトを管理し...
- 質問587 ある企業は、予測アプローチからアジャイルアプローチに移行して
- 質問588 組織の管理システムは、アジャイル チームによってアップグレー
- 質問589 プロジェクト マネージャーは、プロジェクト チームのパフォーマ...
- 質問590 プロジェクトチームが振り返りを行っています。チームは、何がベ
- 質問591 プロジェクト チームは 6 回のうちの最初の反復を終了しました。...
- 質問592 新しい施設プロジェクトはハイブリッド アプローチを使用して開
- 質問593 プロジェクトの実行中に、会社は年末までに全員が休暇を取る必要
- 質問594 ある企業の CEO は、人工知能 (Al) の使用に関するカンファレン...
- 質問595 大規模なソフトウェア配信プロジェクトのプロジェクト マネージ
- 質問596 新しいプロジェクト チームの 2 人のメンバーが、問題を解決する...
- 質問597 会議で、アジャイル プロジェクトのプロジェクト マネージャーは...
- 質問598 組織はアジャイルに移行しており、パイロットとしてプロジェクト
- 質問599 アジャイル プロジェクトは 6 回の反復のうち 2 回目を実行して...
- 質問600 プロジェクト マネージャーに、正式なプロジェクト経験のない新
- 質問601 プロジェクト マネージャーは、厳格な期限と各マイルストーンを
- 質問602 下請け業者によって納品される作業の更新スケジュールがマイルス
- 質問603 石油・ガスプロジェクトは、プロジェクトに対する全額の資金を獲
- 質問604 プロジェクト マネージャーは、プロジェクト チームが作成したソ...
- 質問605 プロジェクト管理チームは、競合他社がプログラムの最新バージョ
- 質問606 プロジェクトの途中で、プロジェクト マネージャーはベンダーか
- 質問607 世界規模のプログラムが開始され、さまざまな分散チームがこの取
- 質問608 新しいアジャイルプロジェクトが始まります。プロジェクト マネ
- 質問609 プロジェクト マネージャーは、5 つのイテレーションに分割され...
- 質問610 プロジェクトは 6 回中 4 回目のイテレーション中です。イテレー...
- 質問611 運営委員会は、アジャイルの経験があるプロジェクトマネージャー
- 質問612 プロジェクトマネージャーは、長年使用されてきた製品を改造する
- 質問613 プロジェクト マネージャーが新しいプロジェクトに割り当てられ
- 質問614 アジャイル プロジェクトが開始されたばかりで、バックログに優
- 質問615 新しいプロジェクトの初期段階でプロジェクト マネージャーが交
- 質問616 プロジェクトチームは、車両と建設サービスを購入するための契約
- 質問617 アジャイル チームが製品の 2 番目のバージョンをリリースしまし...
- 質問618 アジャイルチームは、6 か国で開始されるプロジェクトに取り組ん...
- 質問619 制作チームはまもなく最初のアジャイル プロジェクトを開始しま
- 質問620 顧客は、製品の納期の遅れについて苦情を述べています。この問題
- 質問621 us グラフは、コストとスケジュールに関連した保護の現在のパフ...
- 質問622 企業用にソフトウェア システムを構築しています。システムが運
- 質問623 プロジェクト マネージャーは 6 か月間アジャイル プロジェクト...
- 質問624 スクラム マスターが同じタスクの競合するステータス更新を受信
- 質問625 チームは、飛行中に飛行機を制御するための新しいソフトウェアを
- 質問626 左側の項目を、正しいプロジェクト内の一致する用語にドラッグし
- 質問627 組織の縮小により、主要な主題専門家 (SME) のリソースが複数年...
- 質問628 プロジェクト マネージャーは、クロスカントリー パイプライン ...
- 質問629 最近 2 つの会社が合併しました。新しい取り組みのチーム憲章は...
- 質問630 プロジェクト マネージャーは、新しいリスク プラットフォームを...
- 質問631 年次評価を完了し、年次ボーナスを受け取った後に辞任を提出した
- 質問632 企業が新しいシステムを実装している プロジェクト マネージャー...
- 質問633 プロジェクト マネージャーは、継続的な保護によってもたらされ
- 質問634 スタンドアップ ミーティング中に、チーム メンバーが、次のタス...
- 質問635 関係者は、プロジェクト マネージャーにプロジェクトのステータ
- 質問636 顧客は新しいレポート システムをレビューしており、印刷モジュ
- 質問637 大規模プロジェクトの人材 (HR) 獲得プロセスが最近変更されまし...
- 質問638 プロジェクト マネージャーがハイブリッド プロジェクトを主導し...
- 質問639 プロジェクト マネージャーは、リスクに関連する緊急時対応計画
- 質問640 プロジェクト マネージャーは、グローバルな仮想チームと連携し
- 質問641 プロジェクトマネージャーは何をすべきでしょうか?
- 質問642 複雑で価値の高いアジャイル プロジェクトには、4 週間ごとに顧...
- 質問643 最近終了した品質監査が失敗し、複数のアクションアイテムが返さ
- 質問644 プロジェクト マネージャーは 2 つのアジャイル チームを管理し...
- 質問645 プロジェクト マネージャーは、チーム メンバーの 1 人とコミュ...
- 質問646 プロジェクト マネージャーがエンジニアリング プロジェクトを主...
- 質問647 プロジェクト チームのメンバー全員が、さまざまな決定を行う際
- 質問648 新しいプロセスを実装するプロジェクトはまだ開発中です。導入さ
- 質問649 税務関連プロジェクトにはプロジェクトマネージャーを配置し、ア
- 質問650 プロジェクト マネージャーは、その国の規制プロジェクトに割り
- 質問651 プロジェクトはアジャイル戦略を実装しており、実用最小限の製品
- 質問652 新しいチームメンバーが雇用され、トレーニングに予想よりも時間
- 質問653 プロジェクト マネージャーは、発電所の保守管理を支援するソフ
- 質問654 進行中のソフトウェア プロジェクトのプロジェクト チームに新し...
- 質問655 プロジェクト チームは世界中に分散しており、チーム メンバーは...
- 質問656 クリティカル パスに影響を与える品質上の問題により、大量の手
- 質問657 プロジェクト チームは、大規模なソフトウェア開発プロジェクト
- 質問658 チームは数か月間プロジェクトに取り組んでいますが、新しい知識
- 質問659 企業の主要製品は進化しており、新しいテクノロジーの使用が必要
- 質問660 プロジェクト マネージャーは、組織内でプロジェクトを実行する
- 質問661 プロジェクト チームのメンバーが調達リスクを特定し、そのリス
- 質問662 グローバルプロジェクトのプロジェクト管理計画の承認から2週間
- 質問663 プロジェクト マネージャーは、過去 2 つの建設プロジェクトと同...
- 質問664 ある企業は、厳しい期限を設定して重要なプロジェクトを開始して
- 質問665 プロジェクト マネージャーは、ハイブリッド環境でソフトウェア
- 質問666 製品所有者は、実用最小限の製品 (MVP) にはいくつかの機能が欠...
- 質問667 技術的主題の専門家 (SME) は、プロジェクトから得られた教訓と...
- 質問668 イテレーションの途中で、チーム メンバーが新しい方法を提案し
- 質問669 新しい IT ソリューションのプロジェクト実行中に、1 つの機能の...
- 質問670 プロジェクト マネージャーは大規模な IT プロジェクトに取り組...
- 質問671 新しいプロジェクト マネージャーが失敗の危険にさらされている
- 質問672 プロジェクト チームは、既存のシステムを新しいシステムに置き
- 質問673 ヘルスケア IT プロジェクトの実行フェーズ中に、利害関係者がユ...
- 質問674 この機械が目的国に到着したとき、税関当局によって阻止され、こ
- 質問675 プロジェクトマネージャーは、リモートで作業するプロジェクトチ
- 質問676 プロジェクト マネージャーは、新しいシステムを構築するために
- 質問677 Learn メンバーの 2 人は常に誤解を抱えており、協力することが...
- 質問678 取締役会のメンバーが、プロジェクト マネージャーに、実用最小
- 質問679 公共サービス プロジェクトに取り組むために、機敏なチームが雇
- 質問680 クライアントによって新たに任命された技術マネージャーがプロジ
- 質問681 継続的に稼働している工場のプロジェクト マネージャーは、市場
- 質問682 新しい建物の建設プロジェクトで、プロジェクト マネージャーは
- 質問683 ポートフォリオ管理局は、組織戦略を直接サポートしない進行中の
- 質問684 プロジェクト マネージャーは、厳しい期限と予算制限のあるプロ
- 質問685 ある町はコミュニティセンターを建設したいと考えており、プロジ
- 質問686 プロジェクト マネージャーは、会社の他の部門の複数の関係者と
- 質問687 最近プロジェクトマネージャーが入社しました。面接では、プロジ
- 質問688 ある組織は、ビジネス プロジェクトにハイブリッド配信アプロー
- 質問689 プロジェクトの成果物のリストをレビューしているときに、関係者
- 質問690 ある組織はデジタル変革のプロセスを開始し、予測的なアプローチ
- 質問691 ワークライフバランスが良好な組織では、1 つのチームに継続的に...
- 質問692 ある大規模な世界的組織が、地方自治体の規制への準拠を必要とす
- 質問693 プロジェクト マネージャーは 10 年以上予測手法を使用しており...
- 質問694 スクラム チームは、最初のリリースで特定の機能を提供すること
- 質問695 チーム メンバーがイベントを主催し、仕事カレンダーを通じて数
- 質問696 新しいプロジェクト マネージャーがハイブリッド プロジェクトを...
- 質問697 プロジェクト マネージャーは、新しい規制に準拠するための一連
- 質問698 プロジェクト管理中、プロジェクト マネージャーは、過去数か月
- 質問699 プロジェクト マネージャーが、計画プロセス中に異なる地域のチ
- 質問700 プロジェクトの関係者間で意見の相違があるため、プロジェクト
- 質問701 プロジェクトは開始する準備ができており、リソースが割り当てら
- 質問702 プロジェクトマネージャーは、非常に複雑で実行期間が長いプロジ
- 質問703 新製品は特定の市場向けに設計されています。この製品は、その地
- 質問704 ある会社が採掘プロジェクトに参加しています。外部利害関係者の
- 質問705 実装中に、新しいプロジェクト マネージャーがプロジェクトに割
- 質問706 プロジェクトの実行中、グローバル プロジェクト チームはビデオ...
- 質問707 プロジェクト運営委員会の会議で、数人の関係者が、プロジェクト
- 質問708 プロジェクト マネージャーは、辺境の町の中小企業の発展を対象
- 質問709 プロジェクト マネージャーは、人工知能 (AI) ベースのソフトウ...

