- ホーム
- Cisco
- 300-410J - Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (300-410日本語版)
- Cisco.300-410J.v2025-05-23.q336
- 質問162
有効的な300-410J問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、300-410J試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新300-410J試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com 300-410J試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここで300-410J問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
300-410J問題集最新版のアクセス
「615問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
ドラッグアンドドロップの質問
Cisco IOS デバイスの SNMP 属性を、右側の適切な SNMPv2c または SNMPv3 カテゴリにドラッグ アンド ドロップします。

Cisco IOS デバイスの SNMP 属性を、右側の適切な SNMPv2c または SNMPv3 カテゴリにドラッグ アンド ドロップします。

正解:
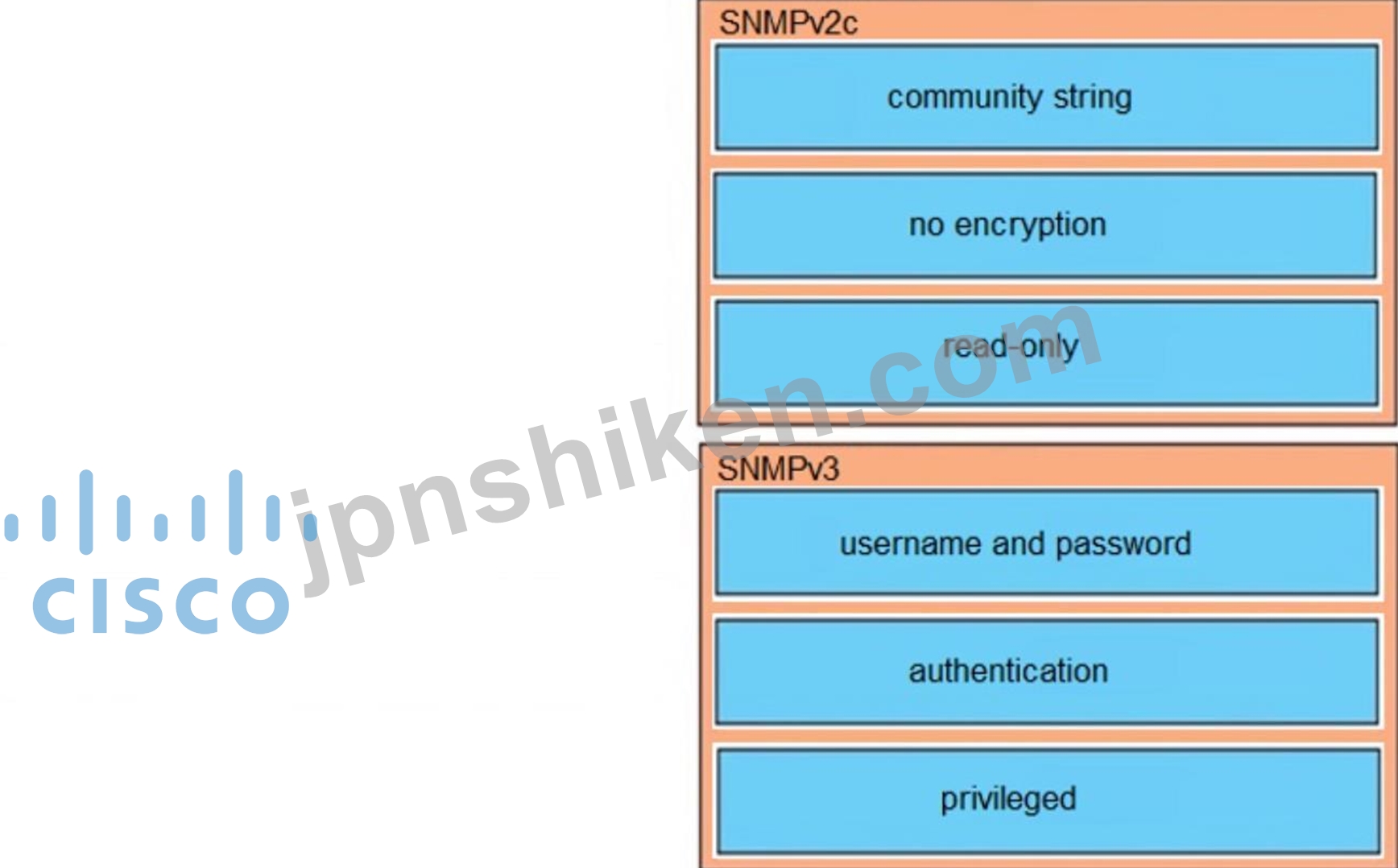
Explanation:
Both SNMPv1 and v2 did not focus much on security and they provide security based on community string only. Community string is really just a clear text password (without encryption).
Any data sent in clear text over a network is vulnerable to packet sniffing and interception. There are two types of community strings in SNMPv2c:
+ Read-only (RO): gives read-only access to the MIB objects which is safer and preferred to other method.
+ Read-write (RW): gives read and write access to the MIB objects. This method allows SNMP Manager to change the configuration of the managed router/switch so be careful with this type.
The community string defined on the SNMP Manager must match one of the community strings on the Agents in order for the Manager to access the Agents.
SNMPv3 provides significant enhancements to address the security weaknesses existing in the earlier versions. The concept of community string does not exist in this version. SNMPv3 provides a far more secure communication using entities, users and groups. This is achieved by implementing three new major features:
+ Message integrity: ensuring that a packet has not been modified in transit.
+ Authentication: by using password hashing (based on the HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA algorithms) to ensure the message is from a valid source on the network.
+ Privacy (Encryption): by using encryption (56-bit DES encryption, for example) to encrypt the contents of a packet.
- 質問一覧「336問」
- 質問1 図を参照してください。どのサブネットが EIGRP から OSPF ルー...
- 質問2 IPv6 ファーストホップ セキュリティ バインディング テーブルは...
- 質問3 ラボシミュレーション4 ガイドライン これは、仮想デバイス上で...
- 質問4 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、R9 と R10 で OSPF を設...
- 質問5 図を参照してください。ルーティング プロトコル間の再配布が有
- 質問6 図を参照してください。どのアクションによって、ルート 192.168...
- 質問7 図を参照してください。R2 には 192.168.13.0/24 に到達するため...
- 質問8 図を参照してください。ISP ルータは、VRF-Lite 機能を使用して...
- 質問9 図を参照してください。R1 と R2 間のプライマリ リンクがダウン...
- 質問10 MPLS クラウド内の転送パスでLDPによって使用される機能はどれで...
- 質問11 どの BGP 属性を使用して、AS から他の自律システムへの送信トラ...
- 質問12 ネットワーク管理者は、Cisco Catalyst 6509 スイッチでコンパク...
- 質問13 ネットワーク エンジニアは、接続ルートとサマリー ルートのみを...
- 質問14 図を参照してください。ネットワークは EIGRP 等コスト ロード ...
- 質問15 悪意のあるトラフィックからルータを保護するためにルータ上でコ
- 質問16 図を参照してください。198A:0:200C::1/64 からルータ 2 への Te...
- 質問17 新しくインストールされたルータは、直接接続されていない別の M...
- 質問18 図を参照してください。ルーター R1 (本社) は、すべてのユーザ...
- 質問19 図を参照してください。R1 は SP1 をプライマリ パスとして使用...
- 質問20 信頼性の高いトランスポート接続を提供するために LDP が使用す...
- 質問21 図を参照してください。ルータ R4 はデフォルトの OSPF 値で正し...
- 質問22 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、OSPF ネットワークで 2 つ...
- 質問23 図を参照してください。192.168.200.0 へのルートは、R1 と R2 ...
- 質問24 ドラッグアンドドロップの質問 左側のパケット タイプを右側の正...
- 質問25 図を参照してください。R6 は、R5>R2>R1 を経由して R1 に...
- 質問26 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、EIGRP を使用し...
- 質問27 MPLS はトラフィック エンジニアリングをサポートするためにどの...
- 質問28 図を参照してください。R1 は、R6 の背後にあるサーバーの可用性...
- 質問29 ネットワーク エンジニアは、過剰なトラフィックを示すインター
- 質問30 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、セキュリティを強化し、
- 質問31 新しくインストールされたスポーク ルータは、ip mtu 1400 コマ...
- 質問32 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク操作では、操作サブネット
- 質問33 展示を参照してください。R1 と R2 の構成は次のとおりです。 (E...
- 質問34 図を参照してください。OSPFのエリア0ルーターは、より具体的な...
- 質問35 図を参照してください。ルータ R1 と R2 は、OSPF を介して互い...
- 質問36 MPLS レイヤ 3 VPN サービスはどのように展開されますか?...
- 質問37 エンジニアは、あらゆるイベントに関する信頼性の高い暗号化され
- 質問38 展示を参照してください。エンジニアが UserSW2 スイッチで SNMP...
- 質問39 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、特定のプレフィックスの
- 質問40 図を参照してください。サイト 1 は、サイト 2 とサイト 3 の背...
- 質問41 図を参照してください。ルータへの認証試行の失敗を解決するには
- 質問42 図を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、ハブと 2 つのス...
- 質問43 エンジニアは、TFTP サーバから設定をダウンロードするように Ci...
- 質問44 展示を参照してください。FastEthernet0/1がダウンすると、172.2...
- 質問45 図を参照してください。ルータ R1 は、インターネットにアクセス...
- 質問46 DHCP メッセージに対する IPv6 DHCP ガード機能の機能は何ですか...
- 質問47 図を参照してください。ネットワーク エンジニアが、R2 と R3 間...
- 質問48 展示を参照してください。顧客は、アプリケーション サーバー (1...
- 質問49 エンジニアがインストール中に Cisco DNA Center エンタープライ...
- 質問50 DMVPN ネットワークでは、Spoke1 ユーザは、音声トラフィックが...
- 質問51 MPLS ラベルの 2 つの特性とは何ですか? (2つお選びください。)...
- 質問52 展示を参照してください。HostA と HostB は DHCP サーバーから ...
- 質問53 図を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、ブランチ ルータ
- 質問54 IP/VPN ハブ アンド スポークの展開シナリオで AS_PATH ループ防...
- 質問55 EIGRP は可能な場合にどの宛先アドレスを使用しますか? (2 つ選...
- 質問56 ネットワーク管理者は、OSPF トラフィックを 1 Mbps に制限する...
- 質問57 図を参照してください。R3 は、EIGRP ではなく OSPF を介して 1....
- 質問58 ラボシミュレーション8 ガイドライン これは、仮想デバイス上で...
- 質問59 図を参照してください。ある企業は、エンドツーエンドの通信を提
- 質問60 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、プレフィックス 10.10.10....
- 質問61 展示を参照してください。 展示を参照してください。 ネットワー...
- 質問62 MPLS ネットワークでは、LDP はどのように動作しますか?...
- 質問63 添付資料を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、Cisco Cata...
- 質問64 VRF インスタンスの 2 つの特性は何ですか? (2 つ選択してくださ...
- 質問65 ラベルエッジルーターによって実行されるラベル操作はどれですか
- 質問66 IPv6 RA ガードの特徴は何ですか?
- 質問67 MPLS L3VPN トポロジではデバイスはどのように動作しますか?...
- 質問68 送信元アドレスがスヌーピング テーブルに見つからない場合にパ
- 質問69 複数の顧客 VPN ネットワークをサポートするために、ルータ R1 ...
- 質問70 図を参照してください。バンコクは ECMP を使用して 172.20.2.0/...
- 質問71 BFD の 2 つの機能は何ですか? (2 つ選択してください)...
- 質問72 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、R2 Loopback0 を除くす...
- 質問73 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは最近、インターフェイスgi...
- 質問74 メンテナンス期間中に、金曜日から日曜日の夜の時間帯にのみ、内
- 質問75 管理者は会社のルーターにセキュリティを実装したいと考えていま
- 質問76 FastEthernet0/0 で「inet」というラベルの付いた VRF を有効に...
- 質問77 ドラッグアンドドロップの質問 左側の MPLS VPN デバイス タイプ...
- 質問78 エンジニアは 2 つのルーター間の動的ルーティングを必要として...
- 質問79 再配布ネットワークでのルート選択問題を解決するには、EIGRP ま...
- 質問80 ドラッグアンドドロップの質問 Cisco IOS ルータで BGP を設定す...
- 質問81 DMVPN ネットワークで論理 IP アドレスを物理 IP アドレスにマッ...
- 質問82 図を参照してください。ルータ R1 に IP SLA が設定されており、...
- 質問83 図を参照してください。ルータ DHCP は、ALS1 および ALS2 上の...
- 質問84 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、Cisco DNA Assurance Ce...
- 質問85 図を参照してください。管理者は、リモート ルータへの EIGRP ネ...
- 質問86 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、ポーリング間隔で ICMP パ...
- 質問87 図を参照してください。IPv6 ACL を適用して、PC1 と PC2 の通信...
- 質問88 図を参照してください。エンジニアは R1 に NetFlow を設定しま...
- 質問89 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、TCP リターン ...
- 質問90 IPsec 事前フラグメンテーション (先読みフラグメンテーション) ...
- 質問91 展示を参照してください。エンジニアが IPv6 プレフィックス 200...
- 質問92 図を参照してください。 図を参照してください。 ルータ間で EIG...
- 質問93 ネットワーク エンジニアは、NTP サーバーに同期されているコア ...
- 質問94 展示を参照してください。R1 と R2 は認証を使用して EIGRP ピア...
- 質問95 2 つの MPLS ルータ (R1 と R2) は直接接続されておらず、それら...
- 質問96 展示を参照してください。エンジニアが debug ip packet コマン...
- 質問97 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、ルーターの構成に表示さ
- 質問98 展示品を参照してください。自律システム番号 AS65401 を持つ会...
- 質問99 MPLS レイヤー 3 VPN はどのように機能しますか?
- 質問100 エンタープライズ クラスのネットワークを監視するために使用で
- 質問101 以下のオプションから、MPLS ネットワークを設定することによる...
- 質問102 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、移行プロジェクトのために
- 質問103 ネットワーク管理者は、Cisco Prime からのすべての SNMP トラフ...
- 質問104 展示を参照してください。IT スタッフが通常の勤務時間中にオフ...
- 質問105 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、SNMP サーバーに設定を...
- 質問106 展示を参照してください。エンジニアはネットワーク上のルーティ
- 質問107 EIGRP を OSPF に再配布することに関する 2 つの記述のうち、正...
- 質問108 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、PC から DHCP サーバー...
- 質問109 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク上の問題のトラブルシュー
- 質問110 図を参照してください。エンジニアがルーターに静的ルートを設定
- 質問111 ユーザーはローカル DHCP サーバーからリモートの企業 DHCP サー...
- 質問112 Cisco デバイスでコントロール プレーン ポリシング (CoPP) を設...
- 質問113 図を参照してください。R1 はすべてのループバック インターフェ...
- 質問114 展示を参照してください。プライマリがダウンしたときにバックア
- 質問115 VRF-Lite セットアップ実装によるルート識別子の役割は何ですか?...
- 質問116 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、ルーターのログ メッセ
- 質問117 レイヤー 3 MPLS VPN ネットワーク内の PE ルータ間のハブアンド...
- 質問118 ドラッグアンドドロップの質問 DNA Center クライアント ヘルス ...
- 質問119 図を参照してください。R2 は、AS300 の外部から発信されたルー...
- 質問120 BFD を構成するための前提条件は何ですか?
- 質問121 展示を参照してください。エンジニアが OSPF を BGP に再配布し...
- 質問122 図を参照してください。スポーク B ルータとの動的 DMVPN トンネ...
- 質問123 展示を参照してください。NTP は、ネットワーク インフラストラ...
- 質問124 図を参照してください。ネットワーク エンジニアは、スイッチ S1...
- 質問125 BFD を実装する利点は何ですか?
- 質問126 ネットワーク管理者がルーターをリロードしているときに、起動中
- 質問127 ドラッグアンドドロップの質問 推奨される手順に従って以下を調
- 質問128 MPLS レイヤ 3 VPN の 2 つの機能は何ですか? (2つお選びくださ...
- 質問129 BFDの機能は何ですか?
- 質問130 図を参照してください。RADIUS サーバーが AAA 認証に失敗した後...
- 質問131 ネットワーク エンジニアは、過剰なトラフィックを示すインター
- 質問132 展示を参照してください。PC は IP アドレスを自動的に取得する...
- 質問133 DHCPv6 ガードが設定されたエンドデバイスの機能は何ですか?...
- 質問134 展示を参照してください。ある企業が複数のネットワーク管理シス
- 質問135 ドラッグアンドドロップの質問 左側の DHCP メッセージを右側の...
- 質問136 展示を参照してください。Cisco DNA Center Assurance ダッシュ...
- 質問137 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、DNA Assurance ...
- 質問138 どのアクセス リスト エントリがパケット ヘッダー内の ACK をチ...
- 質問139 次のどれが IPv6 トラフィックのソースを検証するために使用され...
- 質問140 展示品を参照してください。 (Exhibit) ルータは、フィルタリン...
- 質問141 展示を参照してください。 ネットワーク エンジニアは、BANK SIT...
- 質問142 DMVPN トンネルを設定するための 2 つの前提条件は何ですか? (2 ...
- 質問143 2 つの PE ルータ間で LSP が切断される原因として考えられるの...
- 質問144 BFDの機能とは何ですか?
- 質問145 MPLS におけるダウンストリーム非請求配信方式とは何ですか?...
- 質問146 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、着信アクセス
- 質問147 展示を参照してください。Copp ポリシーが適用された後、BGP が...
- 質問148 展示を参照してください。SNMP トラップ パケットで観察される断...
- 質問149 展示を参照してください。サーバーにアクセスするには、どの 2 ...
- 質問150 図を参照してください。コール センターのユーザーから、土曜日
- 質問151 パケットが MPLS ラベル (内部 MPLS ラベルにある VPN 情報を含...
- 質問152 2 つの EIGRP ルータがネイバーになる場合の次の記述のうち正し...
- 質問153 展示を参照してください。転送エントリは、プレフィックスの次の
- 質問154 図を参照してください。ブランチ B のサービスが停止しています...
- 質問155 エンジニアは、TFTP を使用して、あるルータから別のルータに IO...
- 質問156 図を参照してください。エンジニアがスポーク ルータに DMVPN を...
- 質問157 展示を参照してください。この構成を適用すると、どのような結果
- 質問158 展示を参照してください。クライアントは、show archive log con...
- 質問159 図を参照してください。ネットワーク セキュリティを強化するた
- 質問160 展示を参照してください。この会社は、スプーフィング対策攻撃に
- 質問161 P ルータから RD タグを削除した後、PE ルータが再配布または静...
- 質問162 ドラッグアンドドロップの質問 Cisco IOS デバイスの SNMP 属性...
- 質問163 図を参照してください。ネットワーク エンジニアは、R5 上の OSP...
- 質問164 デバイスは MPLS L3VPN トポロジでどのように動作しますか?...
- 質問165 Cisco IP SLA 操作に専用ルートを使用する場合、ネットワーク内...
- 質問166 MPLS レイヤー 3 VPN で RD アドレスと VPNv4 アドレスを使用す...
- 質問167 BFD プロトコルはどのように機能しますか?
- 質問168 図を参照してください。トラブルシューティングを行い、ブランチ
- 質問169 展示を参照してください。R5 からネットワーク 10.1.1.0/24 への...
- 質問170 顧客は、内部ネットワークを隠すためにループバックを使用して、
- 質問171 GRE over IPsec を使用する DMVPN で構成されているすべてのリモ...
- 質問172 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、HQ_R1 をプライマリ デフ...
- 質問173 デバイスの CPU 使用率を保護するにはどのオプションが最適です...
- 質問174 ネットワーク接続の問題をトラブルシューティングするために IP ...
- 質問175 展示を参照してください。コンソールに接続している管理者には、
- 質問176 図を参照してください。192.168.12.1 から R2 へのアクセスを制...
- 質問177 MPLS レイヤ 3 VPN は、各 VPN 間で使用される IP アドレス空間...
- 質問178 展示を参照してください。R2 はサーバー上のコンテンツに正常に...
- 質問179 次のどれが有効な IPv6 ルータ アドバタイズメント (RA) ガード ...
- 質問180 図を参照してください。R1 は GigabitEthernet0/0 経由で R2 に...
- 質問181 MPLS LDP ルータ ID に関する次の記述のうち正しいものはどれで...
- 質問182 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは Router2 を設定して Rout...
- 質問183 IPv6 ネットワーク上で DoS 攻撃を最小限に抑える機能はどれです...
- 質問184 LSR で LDP は何に使用されますか?
- 質問185 ドラッグアンドドロップの質問 展示品を参照してください。 (Exh...
- 質問186 展示を参照してください。OSPF ネイバー関係が確立されていませ...
- 質問187 図を参照してください。セキュリティ監査の後、管理者はルート
- 質問188 展示品を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、ホストからの
- 質問189 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、サーバーから I...
- 質問190 会社の所在地 407173257 での OSPF の再コンバージェンス時間を...
- 質問191 展示を参照してください。エンジニアがエリア7の設定を変更して
- 質問192 ドラッグアンドドロップの質問 左側の用語を右側の対応する定義
- 質問193 展示を参照してください。PC-2 はターミナル サーバーへの Telne...
- 質問194 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、ホスト 192.168.1.1 を除...
- 質問195 図を参照してください。どのアクションにより、R1 と R2 間の OS...
- 質問196 図を参照してください。ブランチ ネットワークからのトラフィッ
- 質問197 展示を参照してください。ホストのパケットドロップ問題をトラブ
- 質問198 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、R3 AS64513 をプライマリ ...
- 質問199 ネットワーク操作で、外部ルートの受信が多すぎるという問題が報
- 質問200 図を参照してください。ルータ R1、R2、R3、および R4 は EIGRP ...
- 質問201 展示を参照してください。Cisco DNA Center で、ネットワーク エ...
- 質問202 図を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は顧客 A に対して VR...
- 質問203 エンジニアは、通常のルーティング動作をオーバーライドするポリ
- 質問204 展示を参照してください。エンジニアはDMVPNを設定し、ハブロケ...
- 質問205 ルーターへの接続の問題をトラブルシューティングする際に、次の
- 質問206 ドラッグアンドドロップの質問 左側の MPLS VPN の概念を右側の...
- 質問207 DMVPN トンネルを保護できるセキュリティ機能はどれですか?...
- 質問208 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、RADIUS サーバ...
- 質問209 図を参照してください。R1 は R2 と隣接関係を確立できません。...
- 質問210 VRF インスタンスの 2 つの特性は何ですか? (2 つ選択してくださ...
- 質問211 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、示されている構成を使用
- 質問212 図を参照してください。ジュニア エンジニアがブランチ ルーター...
- 質問213 インターフェイスがオプションを使用して大量のトラフィックを受
- 質問214 図を参照してください。ACLはルータの受信ギガビット0/1インター...
- 質問215 図を参照してください。ネットワーク エンジニアは、R1 と R2 が...
- 質問216 エンジニアがマルチエリア OSPF 自律システム内のエリア間のサマ...
- 質問217 図を参照してください。R4 は、R2 の背後にある 172.16.2.7 に到...
- 質問218 MPLSLDP ターゲットセッションとは何ですか?
- 質問219 図を参照してください。OSPF プロセス 5 からのどのルートが EIG...
- 質問220 IPsec を使用して支社から本社への安全な接続を提供する 2 つの...
- 質問221 VRF-Lite に関連付けられた IP ルーティング テーブル情報を表示...
- 質問222 MPLS レイヤー 3 VPN の PE ルーターでは顧客ルートはどのように...
- 質問223 あるデバイスから別のデバイスに送信された ping パケットが、宛...
- 質問224 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、ポート 2001 ~ 2011 で...
- 質問225 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、ISP リンクのフラッピング...
- 質問226 IPv6 アドレスを取得して IPv6 ネイバーを検出するためのトラフ...
- 質問227 MPLS ラベルの挿入にはどの 0S1 モデルが使用されますか?...
- 質問228 エンジニアは次のような構成でルーターを構成しました。 (Exhibi...
- 質問229 展示を参照してください。管理者は Cisco ルータを TACACS 認証...
- 質問230 図を参照してください。IT ルータは Science VRF で構成されてお...
- 質問231 展示を参照してください。R2 が DHCP サーバーから IP アドレス...
- 質問232 スプーフィングベースの攻撃から自身を保護するために、サービス
- 質問233 IPv6ソースガードとはどのような機能ですか?
- 質問234 マイクロ BFD セッションの 2 つの目標は何ですか? (2 つ選択し...
- 質問235 エリア 2 を使用して OPSF ネットワークに新しいサイトが追加さ...
- 質問236 展示を参照してください。管理者はルーターを強化する必要があり
- 質問237 エンジニアが複数の OSPF ドメイン間のルーティングを設定したと...
- 質問238 展示を参照してください。R1 は uRPF で設定されており、Gigatxt...
- 質問239 VRF-Lite 設定に関する 2 つの記述のうち、正しいものはどれです...
- 質問240 VPN ルーティング情報は MPLS ネットワーク内でどのように配布さ...
- 質問241 次のコマンドの出力は次のとおりです。 IP VRF を表示
- 質問242 異なる顧客が重複する IP 範囲で同じ MPLS ネットワークに接続で...
- 質問243 管理者はオフィス間に DMVPN トンネルを設定しており、コマンド...
- 質問244 ネットワーク管理者は、登録された IP アドレスを持つだけでなく...
- 質問245 展示を参照してください。トラブルシューティング中に、安全な W...
- 質問246 展示を参照してください。問題を解決するために、エンジニアは C...
- 質問247 展示を参照してください。172.16.1.0/24ネットワークからの着信...
- 質問248 添付資料を参照してください。アクセス リストはネットワーク デ...
- 質問249 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者が IPv6 DHCP サー...
- 質問250 展示を参照してください。EIGRP ネイバー隣接関係の問題をトラブ...
- 質問251 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、R3 がエリア 1 でタイプ 1...
- 質問252 図を参照してください。ルータへの VTY アクセスを監視している...
- 質問253 図を参照してください。ハブとスポーク間の EIGRP ネイバー隣接...
- 質問254 MP-BGP を介して他のデバイスと VPNv4 ルートを交換するために、...
- 質問255 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、ルータ R1 と R2 間の接続...
- 質問256 図を参照してください。BGP と EIGRP は R3 で相互に再配布され...
- 質問257 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、ISP1 および ISP2 への...
- 質問258 MPLS ベースの VPN の 2 つの主要コンポーネントは何ですか? (2 ...
- 質問259 展示を参照してください。ハブとスポークは 2 つの DMVPN トンネ...
- 質問260 展示を参照してください。エンジニアが NetFlow を設定しました...
- 質問261 最後から2番目のホップポッピングの機能は何ですか?
- 質問262 図を参照してください。R1 は ISP1 と ISP2 にマルチホームされ...
- 質問263 BFD を使用する利点は何ですか?
- 質問264 IPv6 ND検査の機能とは何ですか?
- 質問265 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは DENVER ルーターのログを...
- 質問266 エンジニアは、10.1.1.0/24 サブネットに接続されているルータに...
- 質問267 使用されているトラフィックの種類を可視化するために、さまざま
- 質問268 レイヤー 2 の信頼できないポート上の IPv6 トラフィックをフィ...
- 質問269 展示を参照してください。エンジニアはポリシーベース ルーティ
- 質問270 展示を参照してください。R1、R2、R3間のすべてのシリアルは同じ...
- 質問271 内部 BGP では、すべてのピアが論理的に完全にメッシュ化されて...
- 質問272 ネットワーク内のリンクが共通のファイバーを介して接続されてい
- 質問273 IPv6 スヌーピングの用途は何ですか?
- 質問274 展示を参照してください。リモート サーバーが NetFlow データを...
- 質問275 パケットが隣接する LER に転送される前に、MPLS タグ付きパケッ...
- 質問276 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、R1 のコンソールに接続さ...
- 質問277 展示を参照してください。管理者は、DNS サーバー 8.8.8.8 がそ...
- 質問278 展示を参照してください。ブランチ 2 ホストは動的 IP アドレス...
- 質問279 レイヤー 3 MPLS VPN で IPv4 および VPNv4 アドレス ファミリ設...
- 質問280 RADIUS ベースの認証とアカウンティングを実装するときによく使...
- 質問281 完全にメッシュ化されたネットワークを必要とするアプリケーショ
- 質問282 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは IPv6 MP-BGP にルートを...
- 質問283 PE ルータがパケットを正しい顧客に転送するために使用するタグ...
- 質問284 図を参照してください。ISP 1 と ISP 2 はインターネットに直接...
- 質問285 ラボシミュレーション7 ガイドライン これは、仮想デバイス上で...
- 質問286 図を参照してください。R1のどのポリシー構成が、 192.168.130.0...
- 質問287 展示を参照してください。財務部門のサーバーは、 200.30.40.0/2...
- 質問288 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは、VLANのためにトランクを...
- 質問289 エンジニアは、会社の複数エリア OSPF 本社ルータとサイト A の ...
- 質問290 MPLS ネットワークにおける LDP の役割は何ですか?
- 質問291 展示を参照してください。エンジニアはルーターの認証データベー
- 質問292 図を参照してください。管理者はネットワーク デバイスをエンド
- 質問293 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、ルータのネクストホップの
- 質問294 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、カスタマーエッ
- 質問295 CE ルーティングからの受信パケットに VPN ラベルを付けるルータ...
- 質問296 図を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、最長の要約マスク
- 質問297 Cisco DNA Center でデバイスをプロビジョニングするときに、エ...
- 質問298 IPv6 RA ガードの制限は何ですか?
- 質問299 展示を参照してください。EIGRP ピアリングが失われました。 (Ex...
- 質問300 図を参照してください。192.168.130.0/24 ネットワークから発信...
- 質問301 次の出力を参照してください。 ルーター#show ip nhrp 詳細 10.2...
- 質問302 次のどれが MPLS ヘッダーの有効なフィールドですか? (4 つ選択...
- 質問303 展示を参照してください。FTP クライアントがパッシブ FTP を使...
- 質問304 ドラッグアンドドロップの質問 左側の ICMPv6 ネイバー探索メッ...
- 質問305 エンジニアは、ルートに影響を与えるためにポリシーにアクセス
- 質問306 図を参照してください。管理者は、最近強化された別の Cisco IOS...
- 質問307 展示を参照してください。隣接関係が確立されていません。どの 2...
- 質問308 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク エンジニアは、次の要件
- 質問309 展示を参照してください。接続されたルータが OSPF ネイバーとし...
- 質問310 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者が R1 で特権 EXEC ...
- 質問311 ネットワーク管理者は、Cisco Catalyst c3560 スイッチでの AAA ...
- 質問312 ラボシミュレーション3 ガイドライン これは、仮想デバイス上で...
- 質問313 展示を参照してください。DMWN ではスポーク間フェーズ 3 トンネ...
- 質問314 Router_A で以下の設定を行った後、サマリー ルートは Router_B ...
- 質問315 図を参照してください。送信元 209.165.200.215 から到着するパ...
- 質問316 展示を参照してください。すべてのリンクが稼働しているのにこの
- 質問317 図を参照してください。デフォルト ルートが隣接ルータにアドバ
- 質問318 図を参照してください。ルータ R2 VLAN 10 ユーザーは、R1 から...
- 質問319 デバイス バインディング テーブルに格納されていないアドレスか...
- 質問320 OSPF 模造リンクの目的は何ですか?
- 質問321 図を参照してください。R2 ループバック インターフェイスは、デ...
- 質問322 同じインターフェイスから同じネクスト ホップを経由して発信さ
- 質問323 展示を参照してください。ジュニア エンジニアがネットワーク デ...
- 質問324 図を参照してください。R1のどのポリシー構成が、 192.168.130.0...
- 質問325 展示を参照してください。問題を解決するために必要な情報を管理
- 質問326 次のどれが有効な TFTP エラー コードですか? (2 つ選択してくだ...
- 質問327 MPLS LSP トンネルの特徴は何ですか?
- 質問328 展示を参照してください。ネットワーク管理者は、サービス プロ
- 質問329 展示を参照してください。エンジニアは 10.1.80.65/32 をルーテ...
- 質問330 MPLS ラベルは OSI モデルのどのレイヤーに適用されますか?...
- 質問331 図を参照してください。ネットワーク エンジニアは、PC1 がホテ...
- 質問332 セカンダリ RP が障害が発生したプライマリ RP から引き継いだと...
- 質問333 図を参照してください。エンジニアは、ルータ A の LAN ネットワ...
- 質問334 ルーティング ポリシーをいくつか変更した後、AS 45123 のルータ...
- 質問335 どのタイプのルータで MPLS 転送に必要な 2 つの機能はどれです...
- 質問336 IPv6 ソースガードの 2 つの特徴は何ですか? (2 つ選択してくだ...

