- ホーム
- Microsoft
- DP-200J - Implementing an Azure Data Solution (DP-200日本語版)
- Microsoft.DP-200J.v2021-08-16.q80
- 質問27
有効的なDP-200J問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、DP-200J試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新DP-200J試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com DP-200J試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここでDP-200J問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
DP-200J問題集最新版のアクセス
「242問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
会社は、カスタムソリューションを使用して、オンプレミスのMicrosoft SQL Serverパイプラインを管理します。
データエンジニアリングチームは、SQL Serverからデータを取得してAzure Blobストレージに移行するプロセスを実装する必要があります。プロセスは、データのライフサイクルを調整および管理する必要があります。
オンプレミスのSQL Serverデータベースに接続するようにAzure Data Factoryを構成する必要があります。
順番に実行する必要がある3つのアクションはどれですか?回答するには、適切なアクションをアクションのリストから回答エリアに移動し、正しい順序に並べます。
データエンジニアリングチームは、SQL Serverからデータを取得してAzure Blobストレージに移行するプロセスを実装する必要があります。プロセスは、データのライフサイクルを調整および管理する必要があります。
オンプレミスのSQL Serverデータベースに接続するようにAzure Data Factoryを構成する必要があります。
順番に実行する必要がある3つのアクションはどれですか?回答するには、適切なアクションをアクションのリストから回答エリアに移動し、正しい順序に並べます。

正解:
Explanation
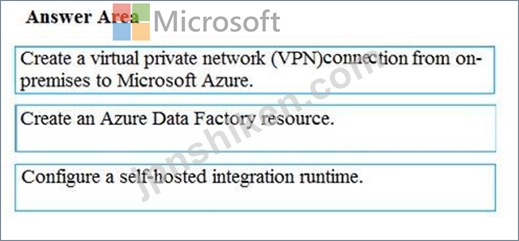
Step 1: Create a virtual private network (VPN) connection from on-premises to Microsoft Azure.
You can also use IPSec VPN or Azure ExpressRoute to further secure the communication channel between your on-premises network and Azure.
Azure Virtual Network is a logical representation of your network in the cloud. You can connect an on-premises network to your virtual network by setting up IPSec VPN (site-to-site) or ExpressRoute (private peering).
Step 2: Create an Azure Data Factory resource.
Step 3: Configure a self-hosted integration runtime.
You create a self-hosted integration runtime and associate it with an on-premises machine with the SQL Server database. The self-hosted integration runtime is the component that copies data from the SQL Server database on your machine to Azure Blob storage.
Note: A self-hosted integration runtime can run copy activities between a cloud data store and a data store in a private network, and it can dispatch transform activities against compute resources in an on-premises network or an Azure virtual network. The installation of a self-hosted integration runtime needs on an on-premises machine or a virtual machine (VM) inside a private network.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-factory/tutorial-hybrid-copy-powershell

Step 1: Create a virtual private network (VPN) connection from on-premises to Microsoft Azure.
You can also use IPSec VPN or Azure ExpressRoute to further secure the communication channel between your on-premises network and Azure.
Azure Virtual Network is a logical representation of your network in the cloud. You can connect an on-premises network to your virtual network by setting up IPSec VPN (site-to-site) or ExpressRoute (private peering).
Step 2: Create an Azure Data Factory resource.
Step 3: Configure a self-hosted integration runtime.
You create a self-hosted integration runtime and associate it with an on-premises machine with the SQL Server database. The self-hosted integration runtime is the component that copies data from the SQL Server database on your machine to Azure Blob storage.
Note: A self-hosted integration runtime can run copy activities between a cloud data store and a data store in a private network, and it can dispatch transform activities against compute resources in an on-premises network or an Azure virtual network. The installation of a self-hosted integration runtime needs on an on-premises machine or a virtual machine (VM) inside a private network.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-factory/tutorial-hybrid-copy-powershell
- 質問一覧「80問」
- 質問1 Group1という名前のセキュリティグループを含むAzureActive Dire...
- 質問2 会社のデータエンジニアリングソリューションを開発します。 Mic...
- 質問3 Mechanical Workflowのデータストアソリューションを構築してい...
- 質問4 料金所を通過する車両からのストリーミングデータを処理していま
- 質問5 Microsoft Azure SQL Data Warehouse Gen 2を管理します。 一般...
- 質問6 Azure Stream Analytics機能を実装しています。 各要件に対して...
- 質問7 (Exhibit) 必要に応じて、次のログイン資格情報を使用します。 A...
- 質問8 Azureイベントハブからクリックストリームデータを受信するAzure...
- 質問9 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問10 次の図に示すように、Azureストレージアカウントの診断設定があ...
- 質問11 必要に応じて、次のログイン資格情報を使用します。 Azureユーザ...
- 質問12 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問13 Azure Databricks環境とAzure Storageアカウントを含むAzureサブ...
- 質問14 企業のデータエンジニアリングソリューションを開発します。 プ
- 質問15 Azure IoT Hubから入力データを受信し、その結果をAzureBlobスト...
- 質問16 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問17 会社のデータエンジニアリングソリューションを開発しています。
- 質問18 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問19 グローバルな小売企業のデータプラットフォームを開発しています
- 質問20 基幹業務アプリケーションをサポートするデータベースのセキュリ
- 質問21 必要に応じて、次のログイン資格情報を使用します。 Azureユーザ...
- 質問22 Azure Databricksでバッチ処理を毎日1回実行する予定です。 どの...
- 質問23 Azure Data Factoryに自己ホスト型の統合ランタイムがあります。...
- 質問24 会社は、地理空間データの複数のセットのバッチ処理を実行するソ
- 質問25 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2アカウントへのアクセスを提供する...
- 質問26 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2には、数千のCSVファイルにデータ...
- 質問27 会社は、カスタムソリューションを使用して、オンプレミスのMicr...
- 質問28 24時間ごとに100,000 JSONを書き込むAzure Cosmos DBデータベー...
- 質問29 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問30 会社は、Twitterからのストリーミングデータを処理するイベント...
- 質問31 AzureSynapseにSQLプールがあります。 一部のクエリが失敗するか...
- 質問32 会社はAzure Stream Analyticsを使用してデバイスを監視していま...
- 質問33 Tier 10データのAzure Data Factory JSON定義をセットアップする...
- 質問34 次のAzure Stream Analyticsクエリがあります。 (Exhibit) 次の...
- 質問35 Azure SQL Data Warehouseインスタンスを実装します。 最大のフ...
- 質問36 会社のデータエンジニアリングソリューションを開発します。 プ
- 質問37 Azure Stream Analyticsサービス内に複雑なステートフルビジネス...
- 質問38 Microsoft Azureにラムダアーキテクチャを実装するデータエンジ...
- 質問39 AzureSynapseにSQLプールがあります。 AzureBlobストレージから...
- 質問40 Azure Stream Analyticsにストリーミングするソリューションを開...
- 質問41 財務計算データ分析プロセスを管理します。 Microsoft Azure仮想...
- 質問42 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問43 会社は、オンプレミスの仮想マシン(VM)でMicrosoft SQL Server...
- 質問44 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問45 会社は、Azure SQL Databaseを使用して販売トランザクションデー...
- 質問46 各US 2リージョンにDB1という名前のAzure SQLデータベースがあり...
- 質問47 Microsoft AzureでLambdaアーキテクチャを使用してソリューショ...
- 質問48 Race CentralのCosmos DBからSQL Databaseに実行されるData Fact...
- 質問49 SALESDBの暗号化を実装する必要があります。 どの3つのアクショ...
- 質問50 技術要件を満たすために、リアルタイム処理のためにどのカウンタ
- 質問51 Microsoft Azureで新しいLambdaアーキテクチャを設計しています...
- 質問52 企業がサービスベースのデータ環境を展開しています。このデータ
- 質問53 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問54 Microsoft Azure Stream Analyticsを使用してイベント処理ソリュ...
- 質問55 ASA1という名前のAzureStreamAnalyticsジョブがあります。 ASA1...
- 質問56 (Exhibit) 必要に応じて、次のログイン資格情報を使用します。 A...
- 質問57 Race Controlのテレメトリデータを収集するソリューションを構築...
- 質問58 会社は、データとオンプレミスのMicrosoft SQL Serverデータベー...
- 質問59 必要に応じて、次のログイン資格情報を使用します。 Azureユーザ...
- 質問60 Database1という名前のAzure SQLデータベースと、HubAおよびHubB...
- 質問61 あなたの会社は防犯カメラからの画像を分析し、異常な活動に対応
- 質問62 必要に応じて、次のログイン資格情報を使用します。 Azureユーザ...
- 質問63 Azure Monitorを使用して、AzureBlobストレージのパフォーマンス...
- 質問64 Note: This question is part of a series of questions that pr...
- 質問65 次のリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります。 Group1...
- 質問66 (Exhibit) 必要に応じて、次のログイン資格情報を使用します。 A...
- 質問67 電話ベースのポーリングデータをPollingDataデータベースで分析...
- 質問68 Azure HDInsightクラスターを使用するソリューションを管理しま...
- 質問69 会社はAzure SQL DatabaseとAzure Blobストレージを使用していま...
- 質問70 電話ベースのポーリングデータアップロードの信頼性要件が満たさ
- 質問71 データを処理するためのパイプラインを開発する必要があります。
- 質問72 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問73 マルチマスターレプリケーションをサポートするAzure Cosmos DB...
- 質問74 必要に応じて、次のログイン資格情報を使用します。 Azureユーザ...
- 質問75 Azure SQLデータベースを使用するASP.NET Webアプリがあります。...
- 質問76 Azure DataFactoryパイプラインにアクティビティがあります。こ...
- 質問77 企業は、ミッションクリティカルなアプリケーションをサポートす
- 質問78 アプリケーションは、データソリューションとしてMicrosoft Azur...
- 質問79 DB1という名前のAzure SQLデータベースを、SQL1という名前のAzur...
- 質問80 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。

