- ホーム
- Microsoft
- MB-500J - Microsoft Dynamics 365: Finance and Operations Apps Developer (MB-500日本語版)
- Microsoft.MB-500J.v2024-08-27.q123
- 質問72
有効的なMB-500J問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、MB-500J試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新MB-500J試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com MB-500J試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここでMB-500J問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
MB-500J問題集最新版のアクセス
「287問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations の開発者です。
Extensible Data Security (SDS) フレームワークを使用して、顧客グループとユーザーの役割に基づいて Sales テーブル フォームのデータに制限する必要があります。
どの 4 つのアクションを順番に実行する必要がありますか? 回答するには、アクションのリストから適切なアクションを回答領域に移動し、正しい順序で並べます。

Extensible Data Security (SDS) フレームワークを使用して、顧客グループとユーザーの役割に基づいて Sales テーブル フォームのデータに制限する必要があります。
どの 4 つのアクションを順番に実行する必要がありますか? 回答するには、アクションのリストから適切なアクションを回答領域に移動し、正しい順序で並べます。

正解:
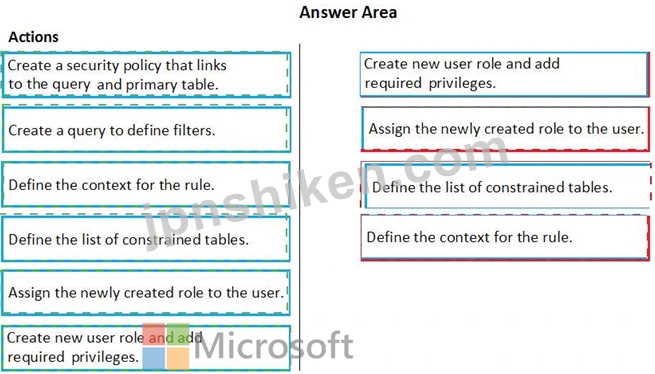
Explanation:
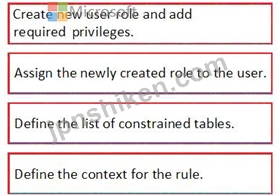
Step 1: Create a new user role and add required privileges.
Individual security permissions are combined into privileges, and privileges are combined into duties. The administrator grants security roles access to the program by assigning duties and privileges to those roles.
Step 2: Assign the newly created role to the user.
Step 3: Define the list of constrained tables.
Add the constrained tables and views.
Step 4: Define the context of the rule.
Set the context.
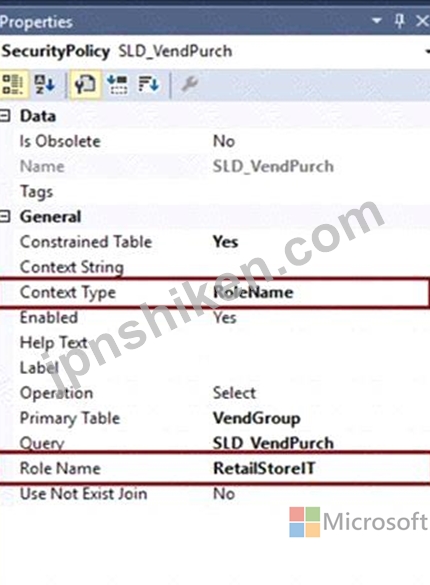
Set the ContextType property to one of the following:
* ContextString - Set the property to this value if a global context is to be used to determine whether the policy should be applied. When required, this context string needs to be set by the application using the XDS::SetContext API.
* RoleName - Set the property to this value if the policy should be applied only if a user in a specific role accesses the constrained tables.
* RoleProperty - Set the property to this value if the policy is to be applied only if the user is a member of any one of a set of roles that have the ContextString property set to the same value.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dynamics365/fin-ops-core/dev-itpro/sysadmin/security-architecture
https://community.dynamics.com/365/b/exploringdynamics365/posts/extensible-data-security-in-d365
- 質問一覧「123問」
- 質問1 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。totalSales という...
- 質問2 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。既存のカスタム ク...
- 質問3 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。 ビジネス プロセス...
- 質問4 ある企業は、販売および流通業務に Dynamics 365 Commerce を使...
- 質問5 Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者を食べました。 埋め込まれた Micro...
- 質問6 ある企業は Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management を導入してい...
- 質問7 ある企業は Dynamics 365 Unified Operations を使用しています...
- 質問8 ある企業は Dynamics 365 の財務および運用アプリを使用していま...
- 質問9 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問10 要件を満たすように CashDisc レポートを更新する必要があります...
- 質問11 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。変更を加えるには、...
- 質問12 カスタム データ エンティティのデータ管理ワークスペースでター...
- 質問13 複数のプロパティを変更する必要があるテーブルがあります。複数
- 質問14 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。 コマンドチェーン...
- 質問15 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。 埋め込まれた Micr...
- 質問16 ある会社では Dynamics 365 の財務および運用アプリを使用してい...
- 質問17 ある銀行会社は、金融取引を統合して転記するためのカスタム機能
- 質問18 発注書の新しい承認ワークフローを作成する必要があります。 何
- 質問19 ある企業は Dynamics 365 Finance を導入しています。 ベンダー...
- 質問20 企業は、Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) の基...
- 質問21 会社には、基本フォームに変更を加える拡張機能があります。 基
- 質問22 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問23 標準フォームに新しいフィールドを追加し、要件を満たすようにグ
- 質問24 会社は Dynamics 365 Finance を使用しています。 SysOperation ...
- 質問25 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations の開発者です。...
- 質問26 会社は Dynamics 365 Finance を使用しています。次の表に示す拡...
- 質問27 ある企業は Dynamics 365 財務および運用アプリを実装しています...
- 質問28 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。 次の要件を満たす...
- 質問29 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations の開発者です。 ...
- 質問30 外部システムから Dynamics 365 Finance にデータ パッケージを...
- 質問31 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations の開発者です。 ...
- 質問32 ある企業は Dynamics 365 財務および運用アプリを実装しています...
- 質問33 Visual Studio で拡張データ型を使用しています。 基本データ型...
- 質問34 ある企業は Dynamics 365 財務および運用アプリを実装しています...
- 質問35 ユーザーは、会社の Dynamics 365 Finance Web サイトが遅いと報...
- 質問36 拡張機能を使用して、SalesTable エンティティにフィールドを追...
- 質問37 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問38 会社は Dynamics 365 Finance を使用しています。 顧客グループ...
- 質問39 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問40 あなたは、Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management のワークフロ...
- 質問41 ある企業は、Dynamics 365 Finance をサードパーティ アプリケー...
- 質問42 プロジェクトのモデルを構成する必要があります。 目標を達成す
- 質問43 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。 レポートでは、sal...
- 質問44 組織には、Employee という名前のベンダー グループに属する 1,0...
- 質問45 ある企業は Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management を実装してい...
- 質問46 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問47 企業は Dynamics 365 Finance と Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Man...
- 質問48 次のコードがあります。 (Exhibit) 次の各ステートメントについ...
- 質問49 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。Visual Studio を含...
- 質問50 ユーザーから、フォームの読み込みに時間がかかると報告がありま
- 質問51 あなたは、新しい Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations 開発者...
- 質問52 CashDisc フォームのセキュリティを構成する必要があります。 ど...
- 質問53 Visual Studio で新しいフォームを作成しています。 Simple List...
- 質問54 複数のプロパティを変更する必要があるテーブルがあります。複数
- 質問55 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問56 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations の開発者です。 ...
- 質問57 あなたはアプリの新機能を開発しています。 SysTest フレームワ...
- 質問58 仕入先期限超過請求書フォームのフィルタリングを構成する必要が
- 質問59 会社は Dynamics 365 Finance を使用しています。 ユーザーは新...
- 質問60 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問61 企業は Dynamics 365 財務および運用アプリを実装しています。 O...
- 質問62 企業には、出荷リクエストに関するメモを入力するために、[すべ
- 質問63 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。 Dynamics 365 Fina...
- 質問64 次のステータスを持つ、truckStatus という名前の列挙があります...
- 質問65 会社の統合要件を実装する必要があります。 どの統合戦略を使用
- 質問66 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。 特定のプロセスの...
- 質問67 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。 地域ごとの総売上...
- 質問68 会社は Dynamics 365 Finance を使用しています。 すべてのカス...
- 質問69 Web ポータル統合ソリューションを展開する必要があります。 ど...
- 質問70 要件を満たすように CashDisc フォームを変更する必要があります...
- 質問71 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問72 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations の開発者です。 ...
- 質問73 ある企業は、サプライ チェーンの運用に Dynamics 365 を使用し...
- 質問74 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。 次のクラス定義が...
- 質問75 従業員がドキュメントのステータスを追跡するためにカスタム承認
- 質問76 会社は Dynamics 365 Finance を使用しています。 Visual Studio...
- 質問77 SFTP サイトから Dynamics 365 Finance にデータを取得するには...
- 質問78 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問79 ユーザーが送信電子レポート ドキュメントを保存しようとすると
- 質問80 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。 テーブルキャッシ...
- 質問81 ある企業が Dynamics 365 の財務および運用アプリを実装していま...
- 質問82 顧客のフィードバックを表示する Power Apps アプリを作成します...
- 質問83 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。フォームを作成しま...
- 質問84 製品名とバッチ ID を表すために、在庫ステータス フォームのテ...
- 質問85 ある企業は Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management を使用してい...
- 質問86 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。次の拡張データ型 (...
- 質問87 クラウドベースの Dynamics 365 Finance 運用環境があります。 ...
- 質問88 4 つのテーブルを含む Bring Your Own Database (BYOD) エンティ...
- 質問89 ベンダー除外リスト用の新しいテーブルを作成する必要があります
- 質問90 ソフトウェア展開可能なパッケージをテスト環境に展開する準備を
- 質問91 ある企業は従来のシステムから Dynamics 365 Unified Operations...
- 質問92 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。次の図に示すように...
- 質問93 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問94 MigrateAttachment クラスの processAttachment メソッドを設計...
- 質問95 会社は Dynamics 365 Finance を使用しています。次の表に示す拡...
- 質問96 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問97 会社は Dynamics 365 Finance を使用しています。 会社は、発注...
- 質問98 ある企業は、Dynamics 365 Unified Operations の展開を計画して...
- 質問99 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。 ユーザーは、フィ...
- 質問100 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問101 Dynamics 365 Finance でテーブルを作成します。 FMAssetld とい...
- 質問102 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問103 給与アプリケーション データ プロセスを実装する必要があります...
- 質問104 新しいフィールドのテーブルにデータを挿入するためのコマンド
- 質問105 企業は Dynamics 365 Finance と Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Man...
- 質問106 あなたは、中古車を販売する会社の Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者...
- 質問107 開発者は品質保証レビューのためにコードを送信します。コードの
- 質問108 あなたは、会社の実装のためのデータ構造に取り組んでいます。
- 質問109 あなたは、新しい Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者をトレーニングし...
- 質問110 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。次のコードがありま...
- 質問111 あなたは Dynamics 365 Finance 開発者です。 リストページ コン...
- 質問112 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問113 会社は Dynamics 365 Finance を使用しています。 クラス A に c...
- 質問114 あなたは Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management の開発者です。...
- 質問115 ベンダー除外リストのレポート要件を実装する必要があります。
- 質問116 私たちは Dynamics 365 財務開発者です。 inventQuantity という...
- 質問117 貨物処理統合をテストしてマッピングする必要があります。 貨物
- 質問118 会社は Dynamics 365 Finance を使用しています。図に示すように...
- 質問119 次のクラス定義があります。 (Exhibit) 拡張クラスを作成し、そ...
- 質問120 ある企業は Dynamics 365 Unified Operations を使用しています...
- 質問121 SalesTable フォームに新しいフィールドを追加しています。 フォ...
- 質問122 D18912E1457D5D1DDCBD40AB3BF70D5D あなたは Dynamics 365 Finan...
- 質問123 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...

