- ホーム
- Microsoft
- DP-203J - Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure (DP-203日本語版)
- Microsoft.DP-203J.v2024-08-05.q162
- 質問90
有効的なDP-203J問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、DP-203J試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新DP-203J試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com DP-203J試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここでDP-203J問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
DP-203J問題集最新版のアクセス
「365問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 コンテナーがあります。
データはコンテナーに取り込まれ、データ統合アプリケーションによって変換されます。その後、データは変更されません。ユーザーはコンテナー内のファイルを読み取ることができますが、ファイルを変更することはできません。
次の要件を満たすデータ アーカイブ ソリューションを設計する必要があります。
新しいデータは頻繁にアクセスされ、できるだけ早く利用できるようにする必要があります。
5 年以上前のデータにアクセスする頻度は低くなりますが、要求されたときに 1 秒以内に利用できるようにする必要があります。
7 年以上前のデータにはアクセスしません。 7 年後、データは可能な限り低いコストで永続化する必要があります。
必要な可用性を維持しながら、コストを最小限に抑える必要があります。
データをどのように管理する必要がありますか?答えるには、答えで適切なオプションを選択します。
注: 正しい選択ごとに 1 ポイントの価値があります。

データはコンテナーに取り込まれ、データ統合アプリケーションによって変換されます。その後、データは変更されません。ユーザーはコンテナー内のファイルを読み取ることができますが、ファイルを変更することはできません。
次の要件を満たすデータ アーカイブ ソリューションを設計する必要があります。
新しいデータは頻繁にアクセスされ、できるだけ早く利用できるようにする必要があります。
5 年以上前のデータにアクセスする頻度は低くなりますが、要求されたときに 1 秒以内に利用できるようにする必要があります。
7 年以上前のデータにはアクセスしません。 7 年後、データは可能な限り低いコストで永続化する必要があります。
必要な可用性を維持しながら、コストを最小限に抑える必要があります。
データをどのように管理する必要がありますか?答えるには、答えで適切なオプションを選択します。
注: 正しい選択ごとに 1 ポイントの価値があります。

正解:

Explanation:
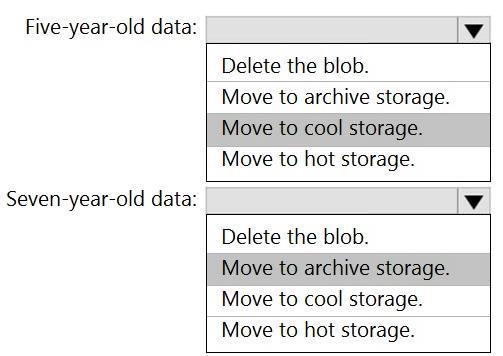
Box 1: Move to cool storage
Box 2: Move to archive storage
Archive - Optimized for storing data that is rarely accessed and stored for at least 180 days with flexible latency requirements, on the order of hours.
The following table shows a comparison of premium performance block blob storage, and the hot, cool, and archive access tiers.
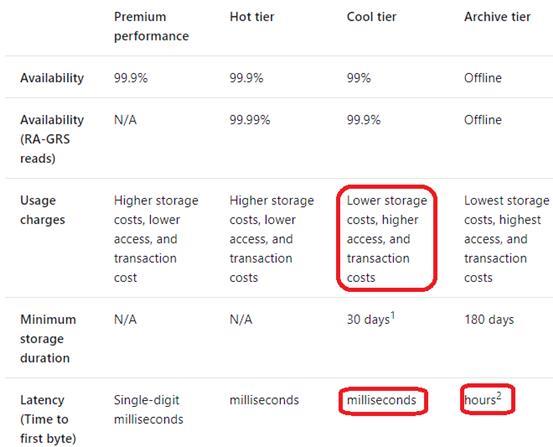
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/storage-blob-storage-tiers Explanation:
Box 1: Replicated
Replicated tables are ideal for small star-schema dimension tables, because the fact table is often distributed on a column that is not compatible with the connected dimension tables. If this case applies to your schema, consider changing small dimension tables currently implemented as round-robin to replicated.
Box 2: Replicated
Box 3: Replicated
Box 4: Hash-distributed
For Fact tables use hash-distribution with clustered columnstore index. Performance improves when two hash tables are joined on the same distribution column.
Reference:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/updates/reduce-data-movement-and-make-your-queries-more-efficient-with-th
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/replicated-tables-now-generally-available-in-azure-sql-data-warehouse/
- 質問一覧「162問」
- 質問1 次の要件を満たす Azure Synapse Analytics 専用の SQL プールを...
- 質問2 WS1 という名前の Azure Synapse Analytics ワークスペースがあ...
- 質問3 AzureDatabricksワークスペースを含むAzureサブスクリプションが...
- 質問4 ジオゾーン冗長ストレージ(GZRS)を導入する高可用性Azure Data...
- 質問5 Pool1という名前のAzureSynapse Analytics専用SQLプールと、DB1...
- 質問6 Azure Stream Analyticsを使用して、Azure Event HubsからTwitte...
- 質問7 FlightとWeatherという名前の2つのファクトテーブルがあります。...
- 質問8 MP1 という名前の Microsoft Purview アカウント、DF1 という名...
- 質問9 次の図に示すように、Git リポジトリ設定を持つ Azure データ フ...
- 質問10 製品販売トランザクションのパーティションを設計する必要があり
- 質問11 次のリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります。 Group1...
- 質問12 ある企業は、製造機械を監視するために IoT デバイスを購入しま...
- 質問13 あなたは、会社の人事 (HR) 部門と運用部門のデータを保存するた...
- 質問14 Trigger1 というタンブリング ウィンドウ トリガーによって呼び...
- 質問15 複数の会社をサポートするAzureSynapseAnalytics専用SQLプールの...
- 質問16 次の Azure Stream Analytics クエリがあります。 (Exhibit) 次...
- 質問17 Azure Data Factory には、太平洋時間でスケジュールされたスケ...
- 質問18 AzureStorageアカウントに格納されているデータのクエリインター...
- 質問19 Azure Synapse Analytics 専用の SQL プールがあります。 PDW_SH...
- 質問20 Azure サブスクリプションがあります。 ステージング テーブルと...
- 質問21 ステージングゾーンを含むAzureData LakeStorageアカウントがあ...
- 質問22 Azure Cosmos DB 分析ストアと WS 1 という名前の Azure Synapse...
- 質問23 Table1 という名前のテーブルを含む Azure Synapse Analytics 専...
- 質問24 Dataflow1 という名前のデータ フロー アクティビティを含む Pip...
- 質問25 Azure Event Hubからのストリーミングデータを処理し、そのデー...
- 質問26 Azure Data Factory を使用して、Azure Synapse Analytics サー...
- 質問27 SQLPool1 という名前の Azure Synapse Analytics 専用 SQL プー...
- 質問28 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問29 Azure Stream Analytics にストリーミングするソリューションを...
- 質問30 Sales.Orders という名前のテーブルを含む Azure Synapse Analyt...
- 質問31 分析ワークロードで使用するために raw JSON ファイルを変換する...
- 質問32 Server1 という名前の論理 Microsoft SQL サーバーを含む Azure ...
- 質問33 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 を使用します。 データがディスク...
- 質問34 会社の人材(MR)部門向けのデータマートを設計しています。デー...
- 質問35 次の種類のアクティビティが混在する Azure Data Factory パイプ...
- 質問36 あなたは、Dataflow1 という名前のマッピング データ フローを含...
- 質問37 AzureSynapseにSQLプールがあります。 AzureBlobストレージから...
- 質問38 Azure Synapse Analytics 専用の SQL プールがあります。 データ...
- 質問39 次のファクト テーブルを含むオンプレミスのデータ ウェアハウス...
- 質問40 温度という名前の Apache Spark DataFrame があります。データの...
- 質問41 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 ステージングテーブルを含...
- 質問42 会社の次の 3 つの部門のデータを処理するための Azure Data Fac...
- 質問43 Azure Synapse Analytics 専用の SQL プールがあります。 過去 3...
- 質問44 Pipeline1とPipeline2という名前の2つのパイプラインを含むAzure...
- 質問45 次の表に示すリソースを含む Azure サブスクリプションがありま...
- 質問46 Azure Databricks テーブルを設計しています。テーブルは、1 日...
- 質問47 Df1 という名前の Azure Data Factory バージョン 2 (V2) リソー...
- 質問48 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 アカウントへのソース データの増...
- 質問49 workspace1 という名前の Azure Synapse Analytics ワークスペー...
- 質問50 100 TB のデータを含む Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 コンテナ...
- 質問51 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen 2 アカウントを使用して、料金所の...
- 質問52 Azure Databricksを使用して、DBTBL1という名前のデータセットを...
- 質問53 ユーザーが Web ページの機能を操作するために費やす時間を特定...
- 質問54 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2を使用するアプリケーションを開発...
- 質問55 Azure Stream Analytics ジョブがあります。 ジョブに十分なスト...
- 質問56 オンプレミスのデータ ソースと Azure Synapse Analytics を統合...
- 質問57 Microsoft Purview アカウントに接続する Azure データ ファクト...
- 質問58 Sales という名前の外部テーブルを含む、Pool1 という名前の Azu...
- 質問59 顧客用の JSON ファイルを含む Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 ア...
- 質問60 Azure SynapseAnalytics専用のSQLプールにテーブルを作成するこ...
- 質問61 ストレージ アカウント コンテナー ビューは、Refdata の展示に...
- 質問62 ある企業は、製造機械を監視するために IoT デバイスを購入しま...
- 質問63 Azure SynapseAnalyticsにエンタープライズデータウェアハウスが...
- 質問64 Microsoft Purview アカウントに接続する Azure データ ファクト...
- 質問65 SQL1 という名前の Azure Synapse Analytics 専用 SQL プールが...
- 質問66 Azure Synapse Analytics 専用 SQL プールでディメンション テー...
- 質問67 統合パイプラインにバージョン管理された変更を実装する必要があ
- 質問68 AzureSynapseAnalyticsで1GB未満のディメンションテーブルを作成...
- 質問69 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを示す一連の質問の一部です。この...
- 質問70 Pool1という名前のAzureSynapse Analytics専用SQLプールと、DB1...
- 質問71 ハイブリッドAzureActive Directory(Azure AD)テナントにリン...
- 質問72 企業全体の Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 アカウントを持ってい...
- 質問73 ADF1 という名前の Azure データ ファクトリがあります。 現在、...
- 質問74 CSV ファイルを含む Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 コンテナーを...
- 質問75 Job1 という名前の Azure Stream Analytics ジョブがあります。 ...
- 質問76 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。...
- 質問77 Azure Stream Analytics ジョブを監視しています。 過去 1 時間...
- 質問78 Pool1という名前のApacheSparkプールを含むWS1という名前のAzure...
- 質問79 7つの主要な地理的地域に分散された2500万台のデバイスからのテ...
- 質問80 Azure Synapse Analytics 専用 SQL プールのテーブルにデータを...
- 質問81 storage1という名前のAzureBlobStorageアカウントとPool1という...
- 質問82 Azure Blob Storage アカウントに保存されている Parquet ファイ...
- 質問83 Azure DataFactoryパイプラインにアクティビティがあります。こ...
- 質問84 AzureDatabricksワークスペースとstorageという名前のAzureDataL...
- 質問85 Azure Synapse Analytics 専用の SQL プール 1 があります。 Poo...
- 質問86 データ フローを含む Azure Data Factory パイプラインがありま...
- 質問87 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。...
- 質問88 ユーザー定義のローカル プロセスを実行する Azure Databricks ...
- 質問89 リアルタイム データ処理ソリューションの高可用性を向上させる
- 質問90 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 コンテナーがあります。 データは...
- 質問91 次の図に示すように、Azure Synapse ワークスペースの Azure Dat...
- 質問92 Microsoft Azure SQL データ ウェアハウスの実装の監視を構成し...
- 質問93 毎日200,000個の新しいファイルを生成するAzureStorageアカウン...
- 質問94 次の展示に示すように、Azure DataFactoryインスタンスのバージ...
- 質問95 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問96 Azure イベント ハブからインスタント メッセージング データを...
- 質問97 ファイルがAzureData Lake Storage Gen2コンテナーに到着したと...
- 質問98 あなたは、Microsoft Azure で Lambda アーキテクチャを使用して...
- 質問99 Azure Synapse Analytics 専用の SQL プールで販売トランザクシ...
- 質問100 storage1 という名前の Azure Data Lake Storage Gen 2 アカウン...
- 質問101 Azure イベント ハブからデータを読み取る Azure Stream Analyti...
- 質問102 ある会社は、侵入検知データを分析するために Apache Spark 分析...
- 質問103 Azure データ ファクトリがあります。 パイプライン実行データが...
- 質問104 次のコードセグメントは、AzureDatabricksクラスターを作成する...
- 質問105 Twitterフィード用のデータ取り込みおよびストレージソリューシ...
- 質問106 Azure Synapse Analyticsに、FactOnlineSalesという名前のテーブ...
- 質問107 2020年上半期のトランザクションのファクトテーブルを含むAzureS...
- 質問108 Azure Databricks 対話型クラスターを設計しています。クラスタ...
- 質問109 Azure Synapse Analytics でエンタープライズ データ ウェアハウ...
- 質問110 CSV ファイルからデータを取り込み、指定された種類のデータに列...
- 質問111 Table1 という名前のテーブルを含む Azure Synapse Analytics 専...
- 質問112 あなたは、小売環境のセンサーからの受信イベントを処理する Azu...
- 質問113 Azure Synapse Analytics 専用 SQL プールにスター スキーマを実...
- 質問114 Microsoft Visual Studio の Stream Analytics プロジェクト ソ...
- 質問115 Pool1 という名前の Azure Synapse Analytics 専用 SQL プールを...
- 質問116 あなたは、500 台の車両の監視ソリューションを設計しています。...
- 質問117 Twitterのティードデータレコードのデータ保持ソリューションを...
- 質問118 DB1 と DB2 という名前の 2 つの Azure SQL データベースがあり...
- 質問119 container1 という名前のコンテナーを含む Azure Data Lake Stor...
- 質問120 Database1 という名前の Azure SQL データベースと、HubA と Hub...
- 質問121 ユーザーがAzureSynapseAnalyticsサーバーレスSQLプールからAzur...
- 質問122 Folder と Folder2 という名前の 2 つのフォルダーを含む Azure ...
- 質問123 企業全体の Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 アカウントを持ってい...
- 質問124 databricks1 という名前の Azure Databricks ワークスペースと s...
- 質問125 R を主要言語としてサポートするが、Scale と SOL もサポートす...
- 質問126 次の Azure Stream Analytics クエリがあります。 (Exhibit) 次...
- 質問127 account1 と account2 という名前の 2 つの Azure Blob Storage ...
- 質問128 さまざまな量のデータを取り込むストリーミングデータソリューシ
- 質問129 pool1 という名前の Azure Synapse Analytics 専用 SQL プールが...
- 質問130 会社はAzureStreamAnalyticsを使用してデバイスを監視しています...
- 質問131 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 Azure Data Lake Storage ...
- 質問132 CSV ファイルを含む Azure Data Lake Storage アカウントがあり...
- 質問133 pool1という名前のAzureSynapseAnalytics専用SQLプールがありま...
- 質問134 Azure Data Factory にセルフホステッド統合ランタイムがありま...
- 質問135 Storage1とStorage2という名前の2つのAzureStorageアカウントが...
- 質問136 次の展示に示すアクティビティを備えたものです。 (Exhibit) ド...
- 質問137 AzureSynapseにSQLプールがあります。 一部のクエリが失敗するか...
- 質問138 Azure Synapse Analytics にエンタープライズ データ ウェアハウ...
- 質問139 Litware オンプレミス ネットワークの外部のユーザーが分析デー...
- 質問140 Microsoft Entra テナントがあります。 テナントには、storage ...
- 質問141 Azure Synapse Analytics 専用の SQL プールで FactPurchase と...
- 質問142 Azure Synapse Analyticsに、Server1という名前のサーバー上のDW...
- 質問143 Pool1 という Azure Synapse Analytics サーバーレス SQL プール...
- 質問144 仮想ネットワーク サービス エンドポイントが構成されている Azu...
- 質問145 Tablet という名前の Delta Lake ディメンション テーブルを含む...
- 質問146 Pcol1 という名前の Azure Synapse Analytics 専用 SQL プールが...
- 質問147 Azure IoT ハブからのデータを処理し、複雑な変換を実行する C# ...
- 質問148 Standard 価格レベルに、workspace1 という名前の Azure Databri...
- 質問149 Azure Synapse Analytics ワークスペースがあります。 Azure Syn...
- 質問150 ゲームデータを取得するためのAzureStreamAnalyticsジョブを構築...
- 質問151 Pool1 という名前の Azure Synapse Analytics 専用 SQL プールが...
- 質問152 Azure Synapse Analytics 専用の SQL プールにパーティション分...
- 質問153 次の図に示されている Azure Data Factory パイプラインがありま...
- 質問154 ある企業は、Platform-as-a-Service(PaaS)を使用して新しいデ...
- 質問155 Azure データ ファクトリがあります。 過去 60 日間のパイプライ...
- 質問156 英国南部リージョンの Azure Synapse Analytics に Azure ストレ...
- 質問157 ws1 という名前の Azure Synapse Analytics ワークスペースと Co...
- 質問158 storage1 という名前の Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 アカウン...
- 質問159 オンライン注文のレコードを含むデータセットのスタースキーマを
- 質問160 Azure Databricks クラスターを作成し、インストールする追加の...
- 質問161 Azure Synapse Analytics サーバーレス SQL プール、Azure Synap...
- 質問162 Sales という名前のテーブルを含む、Pool1 という名前の Azure S...

