- ホーム
- Lpi
- 101-500J - LPIC-1 Exam 101, Part 1 of 2, version 5.0 (101-500日本語版)
- Lpi.101-500J.v2024-02-15.q121
- 質問72
有効的な101-500J問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、101-500J試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新101-500J試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com 101-500J試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここで101-500J問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
101-500J問題集最新版のアクセス
「510問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
ユーザーが / ファイルシステムをいっぱいにできないようにするには、誰でも書き込み可能なディレクトリのうち、別のパーティションに配置する必要があるのはどれですか? (ディレクトリはフルパスで指定してください。)
正解:E
Explanation
The world-writable directory that should be placed on a separate partition in order to prevent users from being able to fill up the / filesystem is /tmp. This directory is used by applications and users to store temporary files, and it is world-writable by default. By creating a separate partition for /tmp, the amount ofspace available to users is limited, and the root filesystem is protected from being filled up by temporary files1.
To create a separate partition for /tmp, you can use the fdisk or parted command to create a new partition on the disk. Once the partition is created, you can format it with a filesystem such as ext4, and then mount it to the /tmp directory using the mount command. Finally, you can modify the /etc/fstab file to ensure that the partition is mounted automatically at boot time1. Here is an example of the steps to create a separate partition for /tmp:
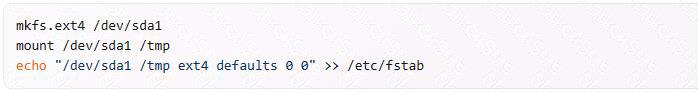
After completing these steps, the /tmp directory will be mounted on a separate partition, and users will be limited in the amount of space they can use for temporary files.
References:
* LFCS: Linux World-Writable Directory Partitioning
The world-writable directory that should be placed on a separate partition in order to prevent users from being able to fill up the / filesystem is /tmp. This directory is used by applications and users to store temporary files, and it is world-writable by default. By creating a separate partition for /tmp, the amount ofspace available to users is limited, and the root filesystem is protected from being filled up by temporary files1.
To create a separate partition for /tmp, you can use the fdisk or parted command to create a new partition on the disk. Once the partition is created, you can format it with a filesystem such as ext4, and then mount it to the /tmp directory using the mount command. Finally, you can modify the /etc/fstab file to ensure that the partition is mounted automatically at boot time1. Here is an example of the steps to create a separate partition for /tmp:

After completing these steps, the /tmp directory will be mounted on a separate partition, and users will be limited in the amount of space they can use for temporary files.
References:
* LFCS: Linux World-Writable Directory Partitioning
- 質問一覧「121問」
- 質問1 ユーザーがホームディレクトリにサブディレクトリ\ dirを誤って...
- 質問2 Debianシステムで利用可能なすべてのパッケージで全文検索を実行...
- 質問3 次のコマンドのうち、SysV initを実行しているシステムをメンテ...
- 質問4 次の環境変数のうち、共有ライブラリを保持するディレクトリのリ
- 質問5 パッケージをアンインストールするが、パッケージが再インストー
- 質問6 パッケージが初めてインストールされたかのように、どのDebianパ...
- 質問7 コマンドに関して正しいのはどれか ls > ファイル ファイルが...
- 質問8 SysV initを使用しているときに、Linuxカーネルによって通常ブー...
- 質問9 次のコマンドのうち、インストール済みのRPMパッケージrpmnameを...
- 質問10 コマンドについて: nice -5 / usr / bin / prog 次のうち正しい...
- 質問11 文字列fooで終わる名前を持つすべてのパッケージをインストール...
- 質問12 どのプログラムが特定の間隔でコマンドを実行し、プログラムの出
- 質問13 次のコマンドのうち、ファイル管理用の一般的なLinuxコマンドは...
- 質問14 ファイル/tmp/myfile.txtの変更タイムスタンプを更新しないコマ...
- 質問15 SysV initベースのシステムのinitプロセスのプロセスID番号は何...
- 質問16 次のカーネルパラメーターのどれがカーネルにほとんどのブートメ
- 質問17 次のコマンドのうち、プログラムmyappの出力を標準出力(stdout...
- 質問18 yum にリポジトリを追加するには、定義ファイルをどのディレクト...
- 質問19 lspciコマンドは、システムハードウェアについてどのような情報...
- 質問20 Linuxルートパーティションで使用できるファイルシステムは次の...
- 質問21 どのユーティリティを使用して、ext2ファイルシステムに保存され...
- 質問22 ハードリンクファイルに当てはまるのは次のうちどれですか? (3...
- 質問23 GNU GRUBの構成ファイルを変更した後、変更を有効にするにはどの...
- 質問24 バイナリファイルがコマンドとして実行される場合、パーミッショ
- 質問25 dpkgベースのパッケージ管理を使用する場合、使用可能なパッケー...
- 質問26 viエディターの次のシーケンスのうち、開いているドキュメントを...
- 質問27 64ビットLinuxシステム上の次のディレクトリのうち、通常共有ラ...
- 質問28 ハードディスクドライブをパーティション分割するときに、Linux...
- 質問29 BIOSを使用したPCのブートシーケンスについて正しいものは次のう...
- 質問30 デフォルトでkillコマンドによって送信されるシグナルはどれです...
- 質問31 ブロックデバイス名のみで追加パラメータなしで実行された場合、
- 質問32 次のコマンドのうち、lsの出力を標準エラーにリダイレクトするの...
- 質問33 追加パラメーターなしでniceコマンドを使用してプログラムを開始...
- 質問34 -vオプションを使用した場合のegrepコマンドの効果は何ですか?...
- 質問35 次のapt-getサブコマンドのうち、現在インストールされているす...
- 質問36 Bashファイルのグロビングの次の例のうち、そのファイルを保持す...
- 質問37 / etc / passwdファイルからユーザー名のリスト(最初の列)とそ...
- 質問38 インポートされたテキストファイルuserlist.txtのすべてのCR-LF...
- 質問39 カーネルリングバッファーの内容はいつリセットされますか? (2...
- 質問40 Linuxシステムで電源管理イベントを処理するデーモンはどれです...
- 質問41 カーネルのコマンドラインの次のオプションのうち、systemdブー...
- 質問42 teeコマンドのどのオプションを使用すると、既存のファイルの内...
- 質問43 システムブートプロセスのコンポーネントが開始される正しい順序
- 質問44 コマンドmount -aは何をしますか?
- 質問45 次のコマンドのうち、ユーザーrootが所有する/ tmpディレクトリ...
- 質問46 ハードリンクの使用を検討する場合、ハードリンクを使用しない正
- 質問47 次のコマンドラインを指定した場合。 echo "foo bar" |ティーバ...
- 質問48 findの出力をxargsコマンドにリダイレクトするときに、ファイル...
- 質問49 System V initを使用しているときにLinuxカーネルがブート時に開...
- 質問50 FHSに準拠して、ドキュメントファイルは次のディレクトリのどれ...
- 質問51 Debianインストールパッケージファイルのロード元のネットワーク...
- 質問52 サイズが100kBの新しいファイルを作成するために使用できるコマ...
- 質問53 中断されたコマンドのバックグラウンド実行を継続するために使用
- 質問54 dpkg -____コマンドは、パッケージが初めてインストールされたか...
- 質問55 既存のファイルの次の情報のうち、そのファイルを指すハードリン
- 質問56 次のコマンドのうち、ユーザーrootが所有する/ tmp /ディレクト...
- 質問57 viエディターのモードは次のうちどれですか? (2つ選択してくだ...
- 質問58 _______という名前のシステム構成ファイルは、通常、デフォルト...
- 質問59 次の説明のうち、シェルのバックグラウンドでコマンドを実行する
- 質問60 通常のファイルfooへのbarと呼ばれるハードリンクを正常に作成し...
- 質問61 パッケージファイルapache-xml.i386.rpmがインストールする前に...
- 質問62 バイナリ実行可能ファイルまたは別の共有ライブラリに必要なすべ
- 質問63 コマンドラインにカーネルリングバッファーの内容を表示するコマ
- 質問64 次のコマンドのうち、/ dev / sdb1にext3ファイルシステムを作成...
- 質問65 コマンドdbmaint&は、dbmaintをバックグラウンドで実行するため...
- 質問66 / etc / fstabの構文的に正しい行にはいくつのフィールドがあり...
- 質問67 Filesystem Hierarchy Standard(FHS)に従って、システムのすべ...
- 質問68 新しいプロセスを実行するときに、通常のユーザーがniceコマンド...
- 質問69 ディスクパーティションに問題があり、このパーティションでメン
- 質問70 コマンドmount -aは何をしますか?
- 質問71 ctrl-alt-deleteキーの組み合わせを無効にするには、どのSysV in...
- 質問72 ユーザーが / ファイルシステムをいっぱいにできないようにする...
- 質問73 次の文字のうち、区切り文字列と組み合わせて現在の入力ソースか
- 質問74 EFIシステムパーティションには何が含まれていますか?
- 質問75 通常、システムの実行中に定期的に変更され、再起動までの間保持
- 質問76 次のコマンドのうち、必要な依存モジュールとともにカーネルモジ
- 質問77 システムのブートサイクル中に、BIOSがタスクを完了した後に実行...
- 質問78 / etc / fstabにリストされておらず、システムに認識されていな...
- 質問79 次のコマンドのうち、file.txtの所有権をユーザーdanとグループ...
- 質問80 パーティションテーブルまたはそれに続くデータを上書きせずに、
- 質問81 コマンドfoo 1> barに関して正しいものは次のうちどれですか...
- 質問82 / dev / sr0にすでに挿入されているCD-ROMを、root権限で発行さ...
- 質問83 / procファイルシステムのどのファイルに、現在マウントされてい...
- 質問84 正規表現を使用する場合、次の文字のうち行の先頭に一致するもの
- 質問85 次のコマンドのうち、実行可能ファイル/ bin / fooのsetuid(sui...
- 質問86 どのコマンドが、マウントされているすべてのファイルシステムの
- 質問87 コマンドを実行するとき sed -e "s/a/b/" /tmp/file >/tmp/fi...
- 質問88 通常のファイルへのハードリンクを作成すると、エラーが返されま
- 質問89 SysV initを使用する場合、どの実行レベルをデフォルトの実行レ...
- 質問90 viエディターで、カーソルの移動やバッファーへの行のコピーなど...
- 質問91 Bash内で有効なストリームリダイレクト演算子は次のうちどれです...
- 質問92 通常のファイルへのハードリンクを作成しようとしていますが、ln...
- 質問93 何が?正規表現内の記号は表しますか?
- 質問94 実行中のプロセスのナイスレベルを変更するコマンド (パスまた
- 質問95 次のシェルコマンドのうち、すでに定義されている変数TESTを新し...
- 質問96 findの出力をxargsコマンドにパイプするときに、ファイル名にス...
- 質問97 ネストされたディレクトリ構造では、特定の数のサブディレクトリ
- 質問98 ルート権限なしでファイルシステムをマウントするために、/ etc ...
- 質問99 GRUBブートプロセスのステージ1の間、画面に「ハードディスクエ...
- 質問100 BIOSに保存されている情報は次のうちどれですか? (2つの正解を...
- 質問101 コマンドがフォアグラウンドで実行されているときにキーボードの
- 質問102 どのumask値を使用すると、ファイルのデフォルトのアクセス許可...
- 質問103 すべての一般的なファイルタイプに関する情報を含む定義データベ
- 質問104 次のコマンドのどれを使用して、システムの実行時間を確認できま
- 質問105 dpkgコマンドでの--removeアクションと--purgeアクションの違い...
- 質問106 次のコマンドのうち、fooコマンドの出力を画面に表示し、/ tmp /...
- 質問107 RPMパッケージファイルapache-xml.rpmによってインストールされ...
- 質問108 コマンドmount --bindは何をしますか?
- 質問109 Debianシステムで利用可能なパッケージに関する情報を照会するた...
- 質問110 コマンドfooが呼び出されたときに実行される実行可能ファイルへ...
- 質問111 管理者は次のコマンドを発行しました。 grub-install --root-dir...
- 質問112 Linuxシステム内で使用されるinitシステムは次のうちどれですか...
- 質問113 ディスクイメージからUSBストレージメディアを作成するために使...
- 質問114 次のシェルリダイレクトのうち、filenameという名前のファイルに...
- 質問115 次のディレクトリを検討してください。 drwxrwxr-x 2ルートセー...
- 質問116 次のコマンドのどれがSysVinitに構成ファイルを再ロードするよう...
- 質問117 / procのどのファイルがさまざまなカーネルドライバーで使用され...
- 質問118 コマンドgrub-install / dev / sdaは何をしますか?...
- 質問119 ファイル内のスペースをタブ文字に変換し、結果を標準出力に出力
- 質問120 RPM --verifyを使用してRPMパッケージのインストール中に作成さ...
- 質問121 / procファイルシステムのどのファイルに、ブートローダーからカ...

