有効的なCISA問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、CISA試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新CISA試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com CISA試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここでCISA問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
CISA問題集最新版のアクセス
「1435問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
次のうち、TCP / IPモデルのアプリケーション層で動作しないプロトコルはどれですか?
正解:D
説明/参照:
質問にNOTキーワードが使用されています。アプリケーション層では動作しないプロトコルを見つける必要があります。 TCPプロトコルは、TCP / IPモデルのトランスポート層で機能します。
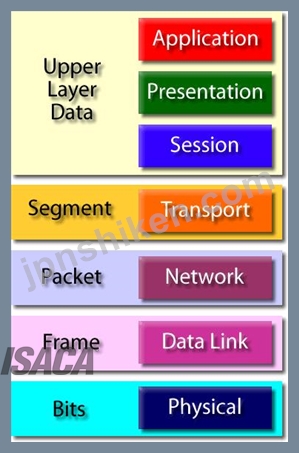
あなたの試験では、TCP / IPモデルに関する以下の情報を知っておくべきです:
ネットワークモデル

レイヤー4.アプリケーションレイヤー
アプリケーション層は、4層のTCP / IPモデルの最上位層です。アプリケーションレイヤーは、トランスポートレイヤーの上部にあります。アプリケーション層は、TCP / IPアプリケーションプロトコル、およびホストプログラムがネットワークを使用するためにトランスポート層サービスとどのようにインタフェースするかを定義します。
アプリケーション層には、DNS(Domain Name System)、HTTP(Hypertext Transfer Protocol)、Telnet、SSH、FTP(File Transfer Protocol)、TFTP(Trivial File Transfer Protocol)、SNMP(Simple Network Management Protocol) 、SMTP(簡易メール転送プロトコル)、DHCP(動的ホスト構成プロトコル)、X Windows、RDP(リモートデスクトッププロトコル)など
レイヤ3。トランスポートレイヤ
トランスポート層は、4層のTCP / IPモデルの3番目の層です。トランスポート層の位置は、アプリケーション層とインターネット層の間にあります。トランスポート層の目的は、送信元ホストと宛先ホスト上のデバイスが会話を継続できるようにすることです。トランスポート層は、データの転送時に使用される接続のレベルとサービスのレベルを定義します。
トランスポート層に含まれる主要なプロトコルは、TCP(伝送制御プロトコル)およびUDP(ユーザデータグラムプロトコル)である。
第2層インターネット層
インターネット層は、4層TCP / IPモデルの第2層である。インターネット層の位置は、ネットワークアクセス層とトランスポート層の間です。インターネット層パックデータをIPデータグラムとして知られているデータパケットに変換します。このパケットには、ホスト間およびネットワーク間でデータグラムを転送するための送信元および宛先アドレス(論理アドレスまたはIPアドレス)情報が含まれています。インターネット層はまた、IPデータグラムのルーティングを担当します。
パケット交換ネットワークは、コネクションレスなインターネットワーク層に依存します。この層はインターネット層と呼ばれます。その役割は、ホストが任意のネットワークにパケットを挿入して宛先に独立して配信させることです。宛先側では、データパケットは送信された順序とは異なる順序で現れることがある。アプリケーション層で動作する適切なネットワークアプリケーションにそれらを配信するためには、上位レイヤーがそれらを再配置するのが仕事です。
The main protocols included at Internet layer are IP (Internet Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), ARP (Address Resolution Protocol), RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol) and IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol).
Layer 1. Network Access Layer
Network Access Layer is the first layer of the four layer TCP/IP model. Network Access Layer defines details of how data is physically sent through the network, including how bits are electrically or optically signaled by hardware devices that interface directly with a network medium, such as coaxial cable, optical fiber, or twisted pair copper wire.
The protocols included in Network Access Layer are Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, X.25, Frame Relay etc.
The most popular LAN architecture among those listed above is Ethernet. Ethernet uses an Access Method called CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection) to access the media, when Ethernet operates in a shared media. An Access Method determines how a host will place data on the medium.
IN CSMA/CD Access Method, every host has equal access to the medium and can place data on the wire when the wire is free from network traffic. When a host wants to place data on the wire, it will check the wire to find whether another host is already using the medium. If there is traffic already in the medium, the host will wait and if there is no traffic, it will place the data in the medium. But, if two systems place data on the medium at the same instance, they will collide with each other, destroying the data. If the data is destroyed during transmission, the data will need to be retransmitted. After collision, each host will wait for a small interval of time and again the data will be retransmitted.
Protocol Data Unit (PDU):
Protocol Data Unit - PDU
The following answers are incorrect:
HTTP, FTP and NTP protocols works at application layer in TCP/IP model.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 page number 272
質問にNOTキーワードが使用されています。アプリケーション層では動作しないプロトコルを見つける必要があります。 TCPプロトコルは、TCP / IPモデルのトランスポート層で機能します。
あなたの試験では、TCP / IPモデルに関する以下の情報を知っておくべきです:
ネットワークモデル

レイヤー4.アプリケーションレイヤー
アプリケーション層は、4層のTCP / IPモデルの最上位層です。アプリケーションレイヤーは、トランスポートレイヤーの上部にあります。アプリケーション層は、TCP / IPアプリケーションプロトコル、およびホストプログラムがネットワークを使用するためにトランスポート層サービスとどのようにインタフェースするかを定義します。
アプリケーション層には、DNS(Domain Name System)、HTTP(Hypertext Transfer Protocol)、Telnet、SSH、FTP(File Transfer Protocol)、TFTP(Trivial File Transfer Protocol)、SNMP(Simple Network Management Protocol) 、SMTP(簡易メール転送プロトコル)、DHCP(動的ホスト構成プロトコル)、X Windows、RDP(リモートデスクトッププロトコル)など
レイヤ3。トランスポートレイヤ
トランスポート層は、4層のTCP / IPモデルの3番目の層です。トランスポート層の位置は、アプリケーション層とインターネット層の間にあります。トランスポート層の目的は、送信元ホストと宛先ホスト上のデバイスが会話を継続できるようにすることです。トランスポート層は、データの転送時に使用される接続のレベルとサービスのレベルを定義します。
トランスポート層に含まれる主要なプロトコルは、TCP(伝送制御プロトコル)およびUDP(ユーザデータグラムプロトコル)である。
第2層インターネット層
インターネット層は、4層TCP / IPモデルの第2層である。インターネット層の位置は、ネットワークアクセス層とトランスポート層の間です。インターネット層パックデータをIPデータグラムとして知られているデータパケットに変換します。このパケットには、ホスト間およびネットワーク間でデータグラムを転送するための送信元および宛先アドレス(論理アドレスまたはIPアドレス)情報が含まれています。インターネット層はまた、IPデータグラムのルーティングを担当します。
パケット交換ネットワークは、コネクションレスなインターネットワーク層に依存します。この層はインターネット層と呼ばれます。その役割は、ホストが任意のネットワークにパケットを挿入して宛先に独立して配信させることです。宛先側では、データパケットは送信された順序とは異なる順序で現れることがある。アプリケーション層で動作する適切なネットワークアプリケーションにそれらを配信するためには、上位レイヤーがそれらを再配置するのが仕事です。
The main protocols included at Internet layer are IP (Internet Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), ARP (Address Resolution Protocol), RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol) and IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol).
Layer 1. Network Access Layer
Network Access Layer is the first layer of the four layer TCP/IP model. Network Access Layer defines details of how data is physically sent through the network, including how bits are electrically or optically signaled by hardware devices that interface directly with a network medium, such as coaxial cable, optical fiber, or twisted pair copper wire.
The protocols included in Network Access Layer are Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, X.25, Frame Relay etc.
The most popular LAN architecture among those listed above is Ethernet. Ethernet uses an Access Method called CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection) to access the media, when Ethernet operates in a shared media. An Access Method determines how a host will place data on the medium.
IN CSMA/CD Access Method, every host has equal access to the medium and can place data on the wire when the wire is free from network traffic. When a host wants to place data on the wire, it will check the wire to find whether another host is already using the medium. If there is traffic already in the medium, the host will wait and if there is no traffic, it will place the data in the medium. But, if two systems place data on the medium at the same instance, they will collide with each other, destroying the data. If the data is destroyed during transmission, the data will need to be retransmitted. After collision, each host will wait for a small interval of time and again the data will be retransmitted.
Protocol Data Unit (PDU):
Protocol Data Unit - PDU

The following answers are incorrect:
HTTP, FTP and NTP protocols works at application layer in TCP/IP model.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 page number 272
- 質問一覧「802問」
- 質問1 次のどれが、あるデバイスが別のデバイス用のパケットをキャプチ
- 質問2 適切な復旧/再開手順が存在するかどうかを判断するには、次のど
- 質問3 IS監査人は、毎週同期される異なる独立した部門データベースから...
- 質問4 通常の勤務時間中にデータベースに加えられた変更は、標準的な一
- 質問5 コンポーネントベースの開発アプローチのメリットは次のとおりで
- 質問6 パスワードが文字と数字の組み合わせであることを要求するセキュ
- 質問7 秘密鍵システムのセキュリティレベルは、以下の数に依存します。
- 質問8 ネットワークパフォーマンスに関連する次の用語のどれが、情報の
- 質問9 次のうちインターネット経由で送信される情報の機密性を保証する
- 質問10 以下のネットワークパフォーマンスに関連するINCORRECTステート...
- 質問11 アプリケーションシステムの監査証跡の信頼性は、次の場合に疑わ
- 質問12 ディザスター・リカバリー計画がない場合と比較して、ディザスタ
- 質問13 情報システム監査人が実施した以下のテストのどれが、組織の変更
- 質問14 会社は、毎週の給与計算を処理するために銀行を使用します。タイ
- 質問15 ある組織が多数のラップトップコンピュータを処分しています。次
- 質問16 IPSecプロトコルのトンネルモードとトランスポートモードの違い...
- 質問17 IS監査人は、コントロールを確認するためにオペレーティングシス...
- 質問18 ライングラブ技術によって引き起こされる可能性のある露出はどれ
- 質問19 世界中のサプライパートナーを持つ大規模な企業ネットワークでは
- 質問20 マルウェアからの保護に使用されるスキャナの主な2つのタイプは
- 質問21 次のエンタープライズデータフローアーキテクチャのレイヤのうち
- 質問22 送信者が後でメッセージの生成と送信を拒否できないようにするデ
- 質問23 事業継続計画の見直しの頻度
- 質問24 次のうち、パケットスイッチング技術について不確実な記述はどれ
- 質問25 デジタル署名では、送信者は、送信者の公開鍵でデータを暗号化し
- 質問26 SSL(Secure Sockets Layer)プロトコルは、次の方法でメッセー...
- 質問27 IS管理者は、第4世代言語(4GL)を使用して従来の顧客関係システ...
- 質問28 システム監査者がシステムのパラメータを検討する際には、IS監査...
- 質問29 TCP / IPモデルのアプリケーション層のプロトコルデータユニット...
- 質問30 次のロックのタイプは、数字キーパッドまたはダイヤルを使用して
- 質問31 制御自己評価(CSA)技術を採用している組織から得られる主な利...
- 質問32 次のタイプのコンピュータネットワークは、都市、地域、国または
- 質問33 次のどのタイプのファイアウォールの中で、最大の程度と制御の細
- 質問34 インターネットアプリケーションでのアプレットの使用に関するも
- 質問35 新規または変更されたアプリケーションシステムでロジックをテス
- 質問36 リレーショナル・データベースのメンテナンス中に、リレーショナ
- 質問37 ファイアウォールが組織のセキュリティポリシーに準拠して構成さ
- 質問38 リグレッションテストでは、プログラムの変更や修正の影響につい
- 質問39 IS監査人は、DBAが本番データへの読み書きアクセス権を持ってい...
- 質問40 IS監査人は、アクセス制御の妥当性、アクセスポリシーの妥当性、...
- 質問41 ディザスタリカバリテスト中、IS監査人は、ディザスタリカバリサ...
- 質問42 ISプログラム、データ、機器に十分な物理的および論理的セキュリ...
- 質問43 情報システムの目標は、ネットワークを介して送信される情報の完
- 質問44 IS戦略の中心的なテナントは、
- 質問45 IS監査人は、データベースの一部のテーブルで範囲外のデータを検...
- 質問46 市場にはさまざまなタイプの監査ログ分析ツールが用意されていま
- 質問47 ネットワークパフォーマンスに関する次の用語のうち、ネットワー
- 質問48 制御自己評価(CSA)におけるIS監査人の伝統的な役割は、(n)の...
- 質問49 インターネット接続の監査中に侵入テストを行っているIS監査人は...
- 質問50 オフサイト・ロケーションに保管されたメディア・バックアップを
- 質問51 ウイルスの攻撃を防ぐ最も基本的なステップは次のどれですか?
- 質問52 次のタイプのコンピュータのうち、何千もの社内外のユーザーと処
- 質問53 毎日何百万件もの取引を処理する金融機関には、ATM(自動預け払...
- 質問54 最終的にソフトウェア開発チームに要件仕様を提供する責任は誰に
- 質問55 以下のデータベースモデルのうち、チュールで表現され、関係にグ
- 質問56 主に使用される侵入検知システム(IDS)とは何ですか?
- 質問57 次のうち、ネットワークパフォーマンスを低下させる可能性のある
- 質問58 IT災害復旧テストを見直す際に、IS監査人に最も重大な懸念事項と...
- 質問59 次のうち、組織のシステムが分散型サービス拒否(DDoS)攻撃に参...
- 質問60 組織がすべての重要業務のビジネスプロセスリエンジニアリング(
- 質問61 エンタープライズリソース管理システムの実施後のレビューでは、
- 質問62 リカバリポイント目標(RPO)で定義されているように、組織がき...
- 質問63 セキュリティ担当者の助けを借りて、データへのアクセスを許可す
- 質問64 公開鍵インフラストラクチャ(PKI)を効率的に使用することで、...
- 質問65 次のうち深刻なセキュリティの原則の一例はどれですか?
- 質問66 組織は最近、運用サーバーをクラッシュさせたセキュリティパッチ
- 質問67 組織は、バックアップファイル内の現在および重要な情報を______...
- 質問68 IS監査人は、新しいビジネスインテリジェンスプロジェクトにおけ...
- 質問69 ビジネス継続計画(BCP)のテスト中に、次の結果分析方法のどれ...
- 質問70 事後レビューを行うための主な目的は、次のような機会を提供する
- 質問71 コンピュータネットワークのうち、家庭、オフィス、キャンパスな
- 質問72 入力、出力、インターフェース、および問合せの数と複雑さに基づ
- 質問73 トロイの木馬のプログラムとは何ですか?
- 質問74 IPスプーフィング攻撃を防止するには、次の場合にファイアウォー...
- 質問75 バイオメトリック制御装置の性能の最良の総合的な定量的尺度は、
- 質問76 IS監査人は、アジャイルソフトウェア開発アプローチを使用してい...
- 質問77 暑い場所、暖かい場所または寒い場所の契約では、契約上の条項は
- 質問78 主要なプロジェクトに取り組んでいたテクニカルリーダーが、この
- 質問79 機密データをオフサイトに転送するためにユニバーサル・ストレー
- 質問80 システムリソースの命名規則は、以下の理由からアクセス制御にと
- 質問81 IS監査人は、無線顧客のためにショッピングモールにインターネッ...
- 質問82 次のどれがメッセージの信頼性を最大限に保証していますか?
- 質問83 セキュリティ管理手順には、次のものへの読み取り専用アクセスが
- 質問84 次のどのメディアをタップするのが最も難しいですか?
- 質問85 次のACIDプロパティのうち、トランザクションによって確実に1つ...
- 質問86 コンピュータのマシンルームの上げ床によって、次のうちどれが最
- 質問87 テストの範囲、目的、性質に応じていくつかのタイプの侵入テスト
- 質問88 Secure Sockets Layer(SSL)の主な目的は、次のことを保証する...
- 質問89 重要なビジネスエリアの災害復旧計画を監査するとき、IS監査人は...
- 質問90 長期にわたって、以下のうちどれがセキュリティインシデント対応
- 質問91 アプリケーションベンダー契約のソースコードエスクローを重要と
- 質問92 効果的なビジネス継続計画(BCP)にMOSTが貢献するのは次のどれ...
- 質問93 DBMS内の次のACIDプロパティのどれが、トランザクションの並行実...
- 質問94 データベースがイメージより前のダンプを使用してリストアされて
- 質問95 次のタイプのテストのどれが、既存のシステムに悪影響を及ぼすこ
- 質問96 IS監査員として、すべてのストレージメディアが確実に保護されて...
- 質問97 情報システム監査人は、異なるネットワーク伝送媒体に関する情報
- 質問98 図の2c領域には、3つのハブが互いに接続されています。これはど...
- 質問99 次のうち、データセンターへの訪問者のアクセスを効果的に制御す
- 質問100 戦略的に重要なシステムを迅速に開発し、開発コストを削減し、高
- 質問101 IS監査人は、システム開発プロジェクトの機能要件を注意深く見直...
- 質問102 送信者の秘密鍵で暗号化されたメッセージとメッセージハッシュを
- 質問103 次のうちデータベースにタプルが絡まってしまうのを防ぎますか?
- 質問104 買掛金システムをレビューするIS監査人は、監査ログが審査されて...
- 質問105 企業のWAN上でVoIPシステムの実装を検討する場合、情報システム...
- 質問106 IS監査人は、ソフトウェアベースの構成を検討しています。次のう...
- 質問107 誰がデータユーザーのアクセスを制限し、監視する責任があります
- 質問108 侵入検知システム(IDS)のデータ収集には、次のコンポーネント...
- 質問109 コールバックシステムとは何ですか?
- 質問110 不適切に実装された侵入防止システム(IPS)によってもたらされ...
- 質問111 ソフトウェア開発のテストフェーズの終わりに、IS監査人は断続的...
- 質問112 IS監査人として、ソフトウェアリリース管理プロセスを理解するこ...
- 質問113 EFTシステムの監査を行う際に、IS監査人にとって最も関心のある...
- 質問114 TCP / IPモデルのトランスポート層のプロトコルデータユニット(...
- 質問115 極めて時間に敏感なトランザクション処理のための許容可能なメカ
- 質問116 ソーシャルエンジニアリング攻撃の成功例としては、
- 質問117 次のコンピュータのうち、処理速度が最も高いものはどれですか?
- 質問118 オンライントランザクション処理システムでは、トランザクション
- 質問119 IPSecに関する次の文のうち、どちらが間違っていますか?
- 質問120 コンピュータフォレンジックでは、複数の分析が実行される場合、
- 質問121 次のうち、TCP / IPモデルのアプリケーション層で動作しないプロ...
- 質問122 論理的アクセス制御を評価している間、情報システム監査人は下記
- 質問123 フレームリレーWAN技術における次のデバイスのうち、自社のネッ...
- 質問124 PBX(Private Branch Exchange)環境には多くのセキュリティリス...
- 質問125 職務の適切な分離は、品質管理責任者が変更管理と問題管理の責任
- 質問126 次のうちVoice over IP(VoIP)について真実ではないものはどれ...
- 質問127 認証局(CA)は以下のプロセスを委任できます。
- 質問128 IS監査人は、事業継続監査を実施する際に、審査する上で最も重要...
- 質問129 最後のシステムイメージの前にバックアップされた情報からデータ
- 質問130 アプリケーションデータへのアクセスを許可する責任は、次のとお
- 質問131 書記官は、マスターファイルのローンの金利を変更しました。入力
- 質問132 次の暗号化/復号化のステップのうち、送信者または受信者のいず
- 質問133 オンライントランザクション処理システムのデータベースにトラン
- 質問134 デジタル証明書の検証プロセスを検討する際に、以下の知見のうち
- 質問135 次の公開鍵インフラストラクチャ(PKI)要素のどれが、侵害され...
- 質問136 特定のアクションが発生したという最も強い証拠を提供する次のメ
- 質問137 次の対称鍵暗号化のどの側面が非対称暗号化の開発に影響しました
- 質問138 災害発生時にトランザクションの可用性を確保するには、次のうち
- 質問139 IS監査人はネットワーク監査を完了しました。次の中で、最も重要...
- 質問140 エンタープライズデータフローアーキテクチャの次のレイヤのうち
- 質問141 論理アクセス制御のレビュー中、IS監査人は、ユーザアカウントが...
- 質問142 TCP / IPモデルのLANまたはWANインタフェースレイヤのデータのプ...
- 質問143 ゆるやかに結合された独立コンポーネントをシステムに定義、実装
- 質問144 IS監査人は、バックアップとリカバリの監査とオフサイト保管庫の...
- 質問145 事業継続計画と災害復旧計画の目的は以下のとおりです。
- 質問146 セキュリティと制御ポリシーがビジネスとITの目的をサポートする...
- 質問147 ビジネス継続性の次の用語のどれが、災害発生後にすべての重要な
- 質問148 データベース管理者(DBA)の主要な役割と責任を見直したIS監査...
- 質問149 仮想プライベートネットワーク(VPN)によって実行される次の機...
- 質問150 次のうち、ネットワーキング管理の重要な要素の1つとして広く受
- 質問151 次のうちTCP / IPモデルのアプリケーション層で実行されない機能...
- 質問152 ITの変更により、大規模組織の災害復旧計画が変更されました。新...
- 質問153 サインオン手順には、一意のユーザーIDとパスワードの作成が含ま...
- 質問154 情報システム監査人は、初期検証制御をクレジットカードのトラン
- 質問155 オフサイトのデータのバックアップと保存は、ハリケーンや地震な
- 質問156 データ分類の最初のステップは次のとおりです。
- 質問157 IS管理者は、組織の活動が計画レベルまたは期待レベルと異なるか...
- 質問158 WAN技術における2台のコンピュータ間の通信にシリアルインタフェ...
- 質問159 サービスレベル管理(SLM)の主目的は次のとおりです。
- 質問160 構造化プログラミングは、
- 質問161 組織は、レガシーシステムからエンタープライズリソースプランニ
- 質問162 コンピュータ間のダイアログを制御するOSIモデルの次の層はどれ...
- 質問163 病院では、医療従事者は、患者の健康データを含むハンドヘルドコ
- 質問164 データユーザーのアクセスレベルを承認する責任は誰にありますか
- 質問165 外部攻撃から最高レベルの保護を提供するために実装できるものは
- 質問166 電気配線、空調、フローリングを備えたオフサイトの情報処理施設
- 質問167 どのタイプの防火システムが、主バルブから放出される水を介して
- 質問168 MOSTが違法ソフトウェアパッケージのネットワークへのロードを効...
- 質問169 ベストプラクティスに従って、新しい情報システムの実施のための
- 質問170 組織のコンピュータセキュリティインシデント対応チーム(CSIRT...
- 質問171 ビジネス継続性における次の用語のどれが、システムおよび/また
- 質問172 従来のシステム開発ライフサイクル(SDLC)に比べて迅速なアプリ...
- 質問173 送信されるメッセージのデジタル署名を作成するために、メッセー
- 質問174 次の中で、最も信頼性の高い送信者認証方式はどれですか?
- 質問175 IS監査人は、組織の事業継続計画を見直しながら、組織のデータフ...
- 質問176 組織の方針の策定に対するどのようなアプローチがリスクアセスメ
- 質問177 ディザスタリカバリ手順のテスト計画に組み込まれるべきプラクテ
- 質問178 次の中でEDI環境における潜在的なリスクが最も大きいのはどれで...
- 質問179 ダイヤルアップ、高速応答システムで維持されているデータへの不
- 質問180 次の中で最も安全なファイアウォールシステムはどれですか?
- 質問181 最も冗長性の高いシステムおよびデータ変換戦略はどれですか?
- 質問182 位置3a、1dおよび3dの場合、この図は、開いてアクティブであるよ...
- 質問183 IPSecプロトコルとSSHプロトコルの違いを正しく説明する次の文は...
- 質問184 実稼働にデータファイルの正しいバージョンが使用されたことを確
- 質問185 パスワードは次のとおりです。
- 質問186 ビジネスアプリケーションシステムへのアクセスを許可する責任は
- 質問187 組織は、レガシーシステムを置き換える新しいシステムを実装して
- 質問188 データベース審査を実行するとき、IS監査人は、データベース内の...
- 質問189 Webと電子メールのフィルタリングツールは、組織にとって非常に...
- 質問190 次のうち、サーバーのログに保存されている情報の不正な変更を防
- 質問191 アプリケーションプログラマーがプロダクションプログラムのコー
- 質問192 適切なネットワークキャパシティ管理とサービスの可用性を測定し
- 質問193 LANの実装を検討するとき、IS監査人は最初に以下を検討すべきで...
- 質問194 「パスワードの表示を隠す必要がある」という情報セキュリティポ
- 質問195 オブジェクト指向設計と開発技術の使用は、おそらく最も可能性が
- 質問196 オフサイトの情報処理施設:
- 質問197 サービス中断事件の重大度を判断するためのMAIN基準は次のとおり...
- 質問198 インターネットを介して送信された電子メールを保護するために使
- 質問199 容易な識別がより円滑な回復を助けるので、オフサイト処理施設は
- 質問200 ジョンは、有名な金融機関の1つで新しい地位を占めるために雇わ
- 質問201 オンライン販売をサポートするデータを持つ大規模データベースの
- 質問202 IS監査人は、入力管理を見直す際に、企業方針に従って、データ検...
- 質問203 ネットワークコンピュータが、デフォルトゲートウェイ、サブネッ
- 質問204 デジタル封筒はどのように機能しますか?どのような正しい手順に
- 質問205 ビジネス継続計画(BCP)に適用する適切なテスト方法はどれです...
- 質問206 監査人はパスワードファイルの監査時に常に何を確認する必要があ
- 質問207 クライアント/サーバー環境でセキュリティを検討する際にIS監査...
- 質問208 CSOは、セキュリティポリシーで説明したように、SMIMEを使用して...
- 質問209 リスク管理の観点から、大規模で複雑なITインフラストラクチャを...
- 質問210 この図が内部機能を表し、組織がファイアウォール保護プログラム
- 質問211 IS監査人は、組織によって使用されているオペレーティングシステ...
- 質問212 他のほとんどの懸念のなかで、新しいアプリケーションソフトウェ
- 質問213 カード所有者と商人のためにクレジットカード取引に関与するすべ
- 質問214 主にデータの保存と保護を担当するのは誰ですか?
- 質問215 事業継続計画(BCP)のための大部分の努力は、
- 質問216 次の伝送媒体のうち、ネットワークを介して移動する情報を変更す
- 質問217 電子商取引に専念する企業の監査中、ISマネージャーは、顧客から...
- 質問218 OSIモデルの次のレイヤーのうち、パケットをフレームにカプセル...
- 質問219 次のうち、品質保証チームの独立性を損なうものはどれですか?
- 質問220 次の中で、MOSTがユニバーサルストレージバス(USB)ストレージ...
- 質問221 無線LANで送信されるデータの機密性は、セッションが次の場合に...
- 質問222 審査員として、機密性、完全性、真正性、可用性が情報システムに
- 質問223 次の物理アクセス制御のどれがピギーバックのリスクを効果的に軽
- 質問224 次のうち、変化するユーザーまたはビジネス要件を満たすために継
- 質問225 潜在的なセキュリティ脆弱性を特定した後、IS監査人の次のステッ...
- 質問226 特定のビジネスユニットまたはビジネスラインのニーズを満たすた
- 質問227 次の攻撃のうち、クライアントから送信されたメッセージをクライ
- 質問228 組織は、電子料金収受システム(ETCS)のターンキーソリューショ...
- 質問229 ホスティングサーバー用の秘密鍵が1つあり、公開鍵が顧客に広く
- 質問230 災害復旧計画の実施後、組織の災害前および災害後の運用コストは
- 質問231 次のうち最も信頼性が高く、誤認率(FAR)が最も低いバイオメト...
- 質問232 処理が突然停止すると、オンラインバンキング取引がデータベース
- 質問233 次のどのコントロールが侵入を検出するのに最適でしょうか?
- 質問234 以下のうち、実行されたアクションに対する説明責任を防止し、否
- 質問235 新しいシステムを短期間で実装するには、次のことが重要です。
- 質問236 財務処理組織の災害復旧計画(DRP)のレビューを実施しているIS...
- 質問237 プログラマがプロダクションプログラムを悪意を持って変更してデ
- 質問238 災害復旧計画を作成する際には、まず最初に実行する必要があるタ
- 質問239 データベースアプリケーションの要件定義フェーズでは、パフォー
- 質問240 次のオプションのどれがPBXの機能を不正確に記述していますか?...
- 質問241 情報システム監査人は、次のような合理的な保証を提供するために
- 質問242 ほとんどのアクセス違反は次のとおりです。
- 質問243 IS管理者は、最近、既存の有線LAN(Local Area Network)を無線...
- 質問244 相互接続された企業ネットワークで最も効果的なアンチウイルスソ
- 質問245 TCP / IPモデルのネットワークインタフェース層のプロトコルデー...
- 質問246 IS監査人がBCPを審査するのに、最も関心のある事項はどれですか...
- 質問247 SSLプロトコルでサポートされていない次の機能はどれですか?
- 質問248 次の場合、バックアップにネットワークデータ管理プロトコル(ND...
- 質問249 印刷システムスプーリングを検討するとき、IS監査人は、次の脆弱...
- 質問250 次のうちどれが最小の特性の実際的な応用に基づいているか 光の
- 質問251 ISO 9126は、製品の品質を評価するのに役立つ標準です。次のうち...
- 質問252 経営陣は、事業継続計画の2つの見通しを考慮した。 Aを2ヶ月間回...
- 質問253 システム開発ライフサイクル(SDLC)モデルの設計段階で実行され...
- 質問254 コールバックデバイスを使用する利点はどれですか?
- 質問255 自動化されたシステムを監査するときは、責任と報告のラインを常
- 質問256 小規模グループ内の安全な通信に最適なのはどれですか?
- 質問257 重要なシステムでは、リカバリ時間目標(RTO)はゼロに、リカバ...
- 質問258 オフサイト設備を定期的にテストするための主な目的は、
- 質問259 規制要件のために長期間保持しなければならない機密データのバッ
- 質問260 外部機関が情報処理施設(IPF)に物理的にアクセスする前に、組...
- 質問261 IS監査人として、ソフトウェアリリース管理プロセスを理解するこ...
- 質問262 モデム(変調/復調)は、アナログ伝送を容易にしてデジタルネッ
- 質問263 IS監査人は、プロジェクト承認手続きが存在しないと判断した場合...
- 質問264 コンピュータフォレンジックでの証拠の取り扱いに関して、一連の
- 質問265 電気通信アクセス制御審査を実施している情報システム監査人は、
- 質問266 ワイヤレスネットワークでWi-Fi Protected Access(WPA)の機能...
- 質問267 地域内に複数のオフィスを持ち、回復基盤が限られているビジネス
- 質問268 リカバリ時間目標(RTO)が向上した場合:
- 質問269 次のうち、一般的なオペレーティングシステムのアクセス制御機能
- 質問270 特定のシステムコールを実行するためにオペレーティングシステム
- 質問271 次のうちシングルサインオン(SSO)の欠点ではないものはどれで...
- 質問272 IS監査人は、Webサーバーを監査する際に、次の方法で個人が機密...
- 質問273 次のうち、電子メールサービスに使用されるプロトコルはどれです
- 質問274 次のうち、ソーシャルエンジニアリング、リンク操作、またはWeb...
- 質問275 次のうち、送信ホストがセキュリティパラメータを参照して適用す
- 質問276 ハッカーは、コンピュータツールやプログラムを使わずにパスワー
- 質問277 侵入検知システム(IDS)には、多くの既知の弱点があります。次...
- 質問278 以下に示す下の図からLANトポロジを特定します。 (Exhibit) バス...
- 質問279 組織の災害復旧計画では、
- 質問280 次のうちインターネットを介して開始された受動的攻撃の例はどれ
- 質問281 監査証跡の主目的は次のとおりです。
- 質問282 In the event of a data center disaster, which of the followi...
- 質問283 組織がエンタープライズリソース管理(ERP)アプリケーションを...
- 質問284 社会工学事件を効果的に削減するには、次のうちどれが効果的でし
- 質問285 次の文のうち、クライアント(例: ブラウザ)とサーバ(Webサー...
- 質問286 IS監査員として、ジョブスケジューリングの重要性を理解すること...
- 質問287 次のデータ検証編集のうち転位および転写エラーの検出に有効なも
- 質問288 情報システム監査人は、許可されたハニーポットのどの側面に最も
- 質問289 IS監査人にとって最大の懸念事項は次のうちどれですか?
- 質問290 TCP / IPモデルのLANレイヤーまたはWANレイヤーのレイヤー機能を...
- 質問291 磁気カードまたは埋め込みチップをベースにしたプラスチックカー
- 質問292 次のWANメッセージ送信テクニックメッセージのうちのどれが、送...
- 質問293 クライアント/サーバー環境でアクセス制御レビューを実施してい
- 質問294 能力成熟度モデル(CMM)に対してアプリケーション開発プロジェ...
- 質問295 次のうち、意思決定支援システムのプロセスにおける実装リスクは
- 質問296 両方のファイアウォール技術がネットワークトラフィックの7つのO...
- 質問297 ビジネスインパクト分析(BIA)のPRIMARY目的は以下のとおりです...
- 質問298 次のうちTCP / IPモデル内の不正な「レイヤー・プロトコル」マッ...
- 質問299 事業継続計画プロセスの一環として、以下のうちどれをビジネス影
- 質問300 次のどの消火方法が最も環境に優しいと考えられていますか?
- 質問301 次の文のうち、パケットフィルタリングファイアウォールとステー
- 質問302 次のRFIDリスクのうち、競合者がRFID生成情報への不正アクセスを...
- 質問303 IS監査人は、ハードウェア保守プログラムを検討する際に、
- 質問304 次のうち、IS監査人がワイヤレスネットワークを審査する上で懸念...
- 質問305 次のうち、データベースの整合性を最大限に保証するコントロール
- 質問306 DoS攻撃を可能にする一般的な脆弱性は何ですか?
- 質問307 次のうちTCP / IPモデル内の不正な「レイヤー・プロトコル・デー...
- 質問308 問題を解決しようとするときに多数の変数を考慮する能力があるた
- 質問309 ウェブベースのアプリケーションで機密性を提供するためにプライ
- 質問310 次の攻撃のうち、チェックの時間(TOC)/使用時間(TOU)とも呼...
- 質問311 アプリケーションコントロールをシステム開発プロセスの中でいつ
- 質問312 ネットワーク内を移動するデータにデジタル署名を適用すると、次
- 質問313 データベース管理システムのディレクトリシステムでは、次のこと
- 質問314 小規模な組織では、従業員はコンピュータの操作を行い、状況に応
- 質問315 投資顧問は定期的なニュースレターを顧客に電子メールで送信し、
- 質問316 組織は、ユーザーがアクセスを禁止されているWebサイトの種類を...
- 質問317 情報システム監査人がソフトウェアリリースのベースラインの記録
- 質問318 IS監査人が最も深刻であると考えられる場合、オフライン印刷の機...
- 質問319 支払命令を送信するとき、次のうちどれが命令が重複していないこ
- 質問320 次の伝送メディアのうち、少なくともどれがクロストークに弱いの
- 質問321 ネットワークセキュリティの評価の一環として実行される侵入テス
- 質問322 ISとエンドユーザの間の適切な職務分担を保証するために、アプリ...
- 質問323 COBIT 5は、情報目標を3つのサブ次元の品質に分ける。 COBIT 5の...
- 質問324 インターネット攻撃からネットワークを保護する最も優れたファイ
- 質問325 従業員がポータブルメディア(MP3プレーヤー、フラッシュドライ...
- 質問326 組織が承認したソフトウェア製品リストを確認する際に、以下のう
- 質問327 次のうち、エンドユーザーコンピューティング(EUC)アプリケー...
- 質問328 ソースとオブジェクトのバージョンが同じかどうかを判断するため
- 質問329 DBMS内の次のACIDプロパティのうち、トランザクションがコミット...
- 質問330 ISバックアップファイルのオフサイト保管場所の場所を選択する際...
- 質問331 次のうちネットワークに対する受動的な攻撃はどれですか?
- 質問332 ビジネス継続性における次の用語のどれが、許容できない結果を招
- 質問333 復旧時間目標(RTO)がより低いと、次の結果が得られます。
- 質問334 重要な情報にアクセスするデータベースユーザーのアカウンタビリ
- 質問335 次のファイアウォールタイプのどれを再構成して、ファイル転送プ
- 質問336 公開鍵インフラストラクチャでは、登録機関:
- 質問337 データセンターにはバッジ入力システムがあります。次の中で、コ
- 質問338 クライアント - サーバシステムでは、既知のユーザまたは未知の...
- 質問339 ユーザーは、企業仮想プライベートネットワーク(VPN)にアクセ...
- 質問340 コード署名の目的は、以下を保証することです。
- 質問341 組織のIT戦略計画の見直しに関して、監査クライアントのビジネス...
- 質問342 システム管理者は、最初にアプリケーションやシステムのパッチの
- 質問343 災害復旧計画を策定する場合、許容可能なダウンタイムを決定する
- 質問344 電気通信システムの監査中に、IS監査人は、リモートサイトとの間...
- 質問345 IS監査人は、システムにリモートでアクセスするために使用された...
- 質問346 次のタイプのデータ検証編集チェックは、フィールドにデータが含
- 質問347 次のうちどれを無効にすると、ワイヤレスローカルエリアネットワ
- 質問348 次のエンタープライズデータフローアーキテクチャのレイヤは、さ
- 質問349 次の中で最も効果的なウイルス対策ソフトウェアの種類はどれです
- 質問350 バックアップの代替手段としてホットサイトを使用する利点は次の
- 質問351 異機種混在環境で異なるプラットフォーム間でデータにアクセスす
- 質問352 重複する情報処理施設の実行可能性を保証するためには、次のうち
- 質問353 複数の多様なサブシステムを持つリモートアクセスネットワークで
- 質問354 情報資産に対する適切なセキュリティ対策を維持する責任は誰にあ
- 質問355 フレームリレークラウドで実際のデータ送信とスイッチングを行う
- 質問356 Flashメモリ(USBリムーバブルディスクなど)を使用する際のセキ...
- 質問357 次のうち、送信者の信頼性と電子メールの機密性を保証するものは
- 質問358 ホスト名をIPアドレスからホスト名に変換する分散データベースは...
- 質問359 ビジネス継続計画(BCP)を策定する場合、組織のビジネスプロセ...
- 質問360 浸透テスターにターゲットの情報システムに関する知識が限られて
- 質問361 短期間の電力削減からコンピュータ機器を保護するのに適している
- 質問362 侵入検知システム(IDS)の特徴は次のうちどれですか?
- 質問363 サイバー攻撃のリスクを管理するための最初のステップは次のとお
- 質問364 ビジネスアプリケーションシステムは、プログラムに埋め込まれた
- 質問365 論理アクセス制御の設計と開発の枠組みは次のどれですか?
- 質問366 IS監査人は、一部のパラメータがテープヘッダーレコードをバイパ...
- 質問367 中小規模の組織でプライベートネットワークをインターネット経由
- 質問368 職務の適切な分離は、コンピュータオペレータ(ユーザ)がセキュ
- 質問369 事業継続計画(BCP)は、以下を促進するための準備として定義さ...
- 質問370 クライアント/サーバー環境のアクセス制御をレビューするIS監査...
- 質問371 OSIモデルの次の層のどれが、ビットストリームを適切な媒体また...
- 質問372 フロッピーディスクからファイルをコピーする際に、ユーザーがウ
- 質問373 IS監査人は、特定のリソースに対して許可されたユーザー権限を判...
- 質問374 単一障害点や共通災害の脆弱性を最小限に抑えるにはどうすればよ
- 質問375 パスワード盗聴を使用したインターネットベースの攻撃は、
- 質問376 公開鍵インフラストラクチャ(PKI)におけるディレクトリサーバ...
- 質問377 どのようにしてWebサーバでよく使用される共通ゲートウェイイン...
- 質問378 情報システム監査人は、電話交換機とネットワーク機器と文書バイ
- 質問379 バルクデータ暗号化やスマートカードなどの小型デバイスに最適な
- 質問380 クレジットカードの取引がクレジットカードの所有者よりも盗難さ
- 質問381 ビジネスプロセスリエンジニアリング(BPR)プロジェクトに起因...
- 質問382 次のうち、トランザクションの発信者を効果的に検証するものはど
- 質問383 財務処理組織の災害復旧計画(DRP)のレビューを実施しているIS...
- 質問384 24/7の可用性を最も良くサポートするのは次のどれですか?
- 質問385 災害復旧計画に関しては、情報システム監査人の役割には、以下が
- 質問386 組織のデータファイル管理手順をレビューするIS監査人は、最新の...
- 質問387 EDIプロセスを実装するプロジェクトのフィージビリティスタディ...
- 質問388 以下の状況のうち、回復戦略としてデータミラーリングを実装する
- 質問389 以前に収集された証拠から組織のITプロセスを理解するのと比較し...
- 質問390 着信コールが次の使用可能なエージェントに配信されるように、ま
- 質問391 ネットワークパフォーマンスに関連する次の用語のどれが、パケッ
- 質問392 IS監査人は、開発者が欠陥修正を実装したため、新しいシステムの...
- 質問393 データセンターのセキュリティを監査する場合、IS監査人は次のこ...
- 質問394 第三者のサービスプロバイダーを監査する場合、情報システム監査
- 質問395 次のタイプのコンピュータネットワークはLANのバリエーションで...
- 質問396 IPSEC内では、暗号アルゴリズム、鍵初期化ベクトル、鍵の寿命な...
- 質問397 次のうちどれが計算能力が低く、ビットあたりのセキュリティが向
- 質問398 特定のシステムリソースを使用する許可を与えられた人物を特定す
- 質問399 機能は、ライフサイクルを通じてソフトウェア製品の品質を評価す
- 質問400 次のうち、対称鍵暗号システムを上回る非対称暗号システムの利点
- 質問401 ファイアウォールログの整合性を維持するには、次のうちどれがベ
- 質問402 ITインフラストラクチャをレビューする際、IS監査人はストレージ...
- 質問403 ネットワークトラフィックの高速化と管理の簡素化のために使用さ
- 質問404 ソフトウェア開発プロジェクトの要件定義段階では、対処すべきソ
- 質問405 次のうち、ルータと相互接続性デバイス監視システムの実装に関係
- 質問406 チェックポイント再開手順の使用に関連する論理的な露出は次のと
- 質問407 トランスポンダを使用して情報を送信する次の伝送メディアのどれ
- 質問408 災害復旧計画(DRP)は、
- 質問409 次の火災抑制システムのどれが、データセンター環境で使用するの
- 質問410 標準のセキュア電子メール保護プロトコルはどれですか?
- 質問411 メッセージの認証、機密性、および完全性を保証するために、送信
- 質問412 次のうちどれが自分の職務を遂行するために必要な機能をユーザー
- 質問413 ネットワークパフォーマンス監視ツールによって直接影響を受ける
- 質問414 テスト環境からプロダクション環境へのアプリケーションプログラ
- 質問415 アクティブラジオ周波数ID(RFID)タグは、次のいずれの露出の対...
- 質問416 IS管理者は、オフサイトバックアップの排除を補うために、すべて...
- 質問417 マスターレコードの重要なフィールドが正しく更新されたことを確
- 質問418 情報システム監査人が不十分なテスト手順を使用し、実際にエラー
- 質問419 データ保護の最も重要な目的はどれですか?
- 質問420 組織の内部ネットワークの侵入テストを実施する場合、以下のアプ
- 質問421 成功したビジネス継続計画を策定するには、エンドユーザーの関与
- 質問422 組織の金融システムの災害復旧計画では、リカバリポイント目標(
- 質問423 「各個人は、制御されたすべてのドアでバッジを読み取らなければ
- 質問424 ネットワーク設定の監査を計画する場合、IS監査人は、以下のネッ...
- 質問425 パケット交換広域ネットワーク通信のためのITU-T標準プロトコル...
- 質問426 システム開発における次のフェーズのうち、ユーザー受入れテスト
- 質問427 ネットワークをインストールした後、組織は脆弱性評価ツールまた
- 質問428 ネットワークを拡張し、フレームを格納し、ストレージおよび転送
- 質問429 ネットワークデバイスの構成を検討するとき、情報システム監査人
- 質問430 データベースシステムの同時実行制御の目的は、次のとおりです。
- 質問431 小規模な組織では、開発者は緊急の変更を直接プロダクションにリ
- 質問432 組織のビジネス継続計画(BCP)の複雑さによっては、このような...
- 質問433 次のどのバイオメトリック方法が最も高い精度を提供し、ユーザー
- 質問434 クライアントリレーションシップマネジメント(CRM)システム移...
- 質問435 以下のうち識別可能な予防制御がない固有のリスクはどれですか?
- 質問436 デジタル著作権管理(DRM)アプリケーションを審査するIS監査人...
- 質問437 データベースシステムを実装する際に不適切なファイルアクセスの
- 質問438 コールバックシステムでは、IDとパスワードを持つユーザがダイヤ...
- 質問439 侵入テストを計画する上で最も重要な成功要因は次のとおりです。
- 質問440 アプリケーション開発プロジェクトのシステムテストフェーズでは
- 質問441 誰がデータにアクセスできるか、機密レベル、アクセスの種類、企
- 質問442 次のうちWorld Wide Webに関連する懸念事項のうちファイアウォー...
- 質問443 監査中に、IS監査人は、組織の事業継続計画(BCP)が、復旧プロ...
- 質問444 データベースサーバーの監査中に、以下のうちどれが最大のエクス
- 質問445 次の災害復旧/継続計画コンポーネントのどれが、災害発生後の復
- 質問446 高度に重み付けされたスパムキーワードを含む有効な可変長の電子
- 質問447 次のどのソフトウェア開発方法論の中で、最小限の計画を使用して
- 質問448 コンピュータ施設へのアクセスを制御するデッドマン・ドアの目的
- 質問449 BCPとDRPの主な目的は次のどれですか?
- 質問450 プロダクションコードに不正な変更が加えられたかどうかを判断す
- 質問451 仮想プライベートネットワーク(VPN)のセキュリティを確保する...
- 質問452 次の文のうち、対称鍵の暗号化と非対称鍵の暗号化の違いを正しく
- 質問453 プログラムの緊急時の変更手順を見直す際、情報システム監査人は
- 質問454 攻撃者が、クレジットカード番号やパスワードなどのユーザーの身
- 質問455 職務の適切な分離は、通常、LAN管理者がプログラミング責任を持...
- 質問456 次のうち、送信者がSymmetric Key暗号を使用して大部分のデータ...
- 質問457 情報システム監査人は、アプリケーションのユーザに対する認可プ
- 質問458 ファイアウォールの製造元が提供する多くのファイアウォール実装
- 質問459 次の中でMOSTにとって重大であり、データウェアハウスのデータ品...
- 質問460 コンピュータ、電話、携帯情報端末などのデバイス間でのデータ伝
- 質問461 次の声明のうち、洪水総量とローカルアプリケーション消火剤の違
- 質問462 積極的にセキュリティ設定を強化するためのMOST関連の情報は、次...
- 質問463 大規模な組織のIT運用はアウトソーシングされています。アウトソ...
- 質問464 ソフトウェア開発プロジェクトで遭遇する欠陥の数を減らすための
- 質問465 内部構造を覗き込むことなく、または内部構造の詳細を知ることな
- 質問466 プロトコルの脆弱性を悪用するネットワークワームの拡散に対処す
- 質問467 サイバー攻撃から回復するのに最も重要なのは次のうちどれですか
- 質問468 どのプロセスがサブジェクトの身元を確認するために使用されます
- 質問469 クライアント - サーバーアーキテクチャでは、ドメインネームサ...
- 質問470 古い磁気テープを処分する前に、それを処理する最良の方法はどれ
- 質問471 どの2つのホストマシン間に直接リンクを含むネットワーク構成オ
- 質問472 データファイルの不正使用を防ぐ最も効果的な方法は何ですか?
- 質問473 IS監査人は、コンピュータ予防保守プログラムの有効性と妥当性を...
- 質問474 プロセス内の予防的、捜査的、または是正的な統制の集団的効果を
- 質問475 詳細なネットワーク評価とアクセス制御レビューを実行するIS監査...
- 質問476 次のアプレットの侵入に関する問題のうち、組織にとっての中断の
- 質問477 次のどれがBESTシングルファクタ認証を提供しますか?
- 質問478 TCP / IPベースの環境はインターネットに公開されています。次の...
- 質問479 電子商取引に関連する電子署名アプリケーションに適切なセキュリ
- 質問480 MOSTがネットワーク伝送のエラーバーストの存在を効果的に検出す...
- 質問481 下記の選択肢からビジネスプロセスリエンジニアリング(BPR)ア...
- 質問482 ISセキュリティポリシーの策定に最終的に責任があるのは誰ですか...
- 質問483 承認されたプログラム出口(トラップドア)にはどのような種類の
- 質問484 継続的な監査アプローチの利点は、多数のトランザクションを処理
- 質問485 組織全体のすべてのコンピュータクロックを同期させる必要がある
- 質問486 参照整合性のあるリレーショナル・データベースでは、次のキーを
- 質問487 次のうち、コンポーネントの通信エラー/エラーに対する制御はど
- 質問488 IS監査の間、監査人は、認証ステップと認可ステップが2つの機能...
- 質問489 IS監査人は、ポートスキャンに関連するIDSログエントリが分析さ...
- 質問490 事業継続性監査中、IS監査人は、事業継続計画(BCP)が重大なプ...
- 質問491 インターネットサイト上の分散型サービス拒否(DDoS)攻撃は、通...
- 質問492 以下に示す下の図からネットワークトポロジを特定します。 (Exhi...
- 質問493 従業員の非自発的な解雇中に、以下のうち最も重要なものはどれで
- 質問494 オフサイトの情報処理施設に関する以下の記述のどれがTRUEである...
- 質問495 次のうち、暴風雨や騒々しい電気設備による環境問題、またコンピ
- 質問496 次のうち、e-コマース取引に否認防止サービスを提供するのはどれ...
- 質問497 コントロールの観点からは、情報資産を分類するための主な目的は
- 質問498 統合されたテスト機能は、処理出力を独立して計算されたデータと
- 質問499 情報システム監査人は、本番データおよびシステムへのアクセス権
- 質問500 次のうちどれがデバイスとTCP / IPモデル内のどこに記述されてい...
- 質問501 フィッシングに関連するリスクを軽減するための効果的な最も効果
- 質問502 Which of the following technique is NOT used by a preacher a...
- 質問503 ウェブサイトの認証を提供するために使用されるものと、データ暗
- 質問504 次のうち、本質的に組織内の小さな社内電話会社と考えることがで
- 質問505 重要なファイルサーバーのストレージの増加が適切に管理されてい
- 質問506 次の侵入検知システム(IDS)のうち、ネットワーク上のアクティ...
- 質問507 次のうち、侵入者がサーバーのシステムログに加えた変更を検出す
- 質問508 「コンピュータは犯罪の標的」であり、「コンピュータは犯罪の道
- 質問509 次のうちコンピュータセキュリティインシデント対応チームの有効
- 質問510 次のうち、電力会社が許容範囲内で電力を供給できないことはどれ
- 質問511 オープンソースソフトウェアを使用している組織のアプリケーショ
- 質問512 次のタイプのIDSのうち、自己学習機能を備えていて、ある期間に...
- 質問513 次のうち、組織の災害復旧の準備状況を示す最も良い証拠はどれで
- 質問514 機密情報を含む磁気媒体を処分するための最も堅牢な方法はどれで
- 質問515 いくつかの外部システムと接続するサードパーティアプリケーショ
- 質問516 オンラインバンキングアプリケーションでは、以下のうちどれがID...
- 質問517 以下に示す説明から、使用されているWANメッセージスイッチング...
- 質問518 論理アクセス制御レビューの主目的は、次のとおりです。
- 質問519 ホワイトボックステストの具体的な利点は、次のとおりです。
- 質問520 次のハニーポットのタイプのどれがハッカーに本質的な攻撃環境を
- 質問521 提案されたアプリケーションソフトウェアの取得を検討しているIS...
- 質問522 大企業では、ビジネスプロセスをレビューした後、VoIPテクノロジ...
- 質問523 侵入検知システム(IDS)の実装をレビューするIS監査人は、
- 質問524 分散環境におけるサーバー障害の影響を次のどれかで制限していま
- 質問525 デジタル署名には、次のようなメッセージダイジェストが含まれて
- 質問526 オフサイトのデータストレージは、次のような時間に敏感なデータ
- 質問527 2つの当事者間のメッセージの完全性、機密性および否認防止を確
- 質問528 次のうち、ルータなどのネットワークデバイスを不当に記述してい
- 質問529 次のうち、非同期転送モード(ATM)のテクニックを記述している...
- 質問530 サービス品質(QoS)の利点は、次のとおりです。
- 質問531 次のデータベースモデルのうち、ツリー状の構造に編成されたデー
- 質問532 IS監査員が稼働時間のSLA(Service Level Agreement)要件への準...
- 質問533 インターネットからの電子メールトラフィックは、ファイアウォー
- 質問534 なぜIS監査人は組織図を見直すのですか?
- 質問535 ソフトウェアの成果物を比較的短期間で一定の期間内に定義し、展
- 質問536 組織のバックアップ機能が暖かいサイトにあるときに、最も重大な
- 質問537 監査人は、マルウェアからコンピュータを保護するために使用され
- 質問538 次のエンタープライズ・データ・フロー・アーキテクチャーのうち
- 質問539 組織が対称暗号化を使用しています。次のうち、非対称暗号化に移
- 質問540 IS監査員は、特定の時刻にデータウェアハウスのクエリのパフォー...
- 質問541 OSIモデルの次のレイヤーのうち、ネットワークパケットのルーテ...
- 質問542 ワイヤレスネットワークセキュリティを検討しているIS監査人は、...
- 質問543 次のどのタイプのネットワークサービスがドメイン名をネットワー
- 質問544 カードキーやロックを使用してコンピュータルームなどの機密領域
- 質問545 次のエンタープライズデータフローアーキテクチャのレイヤは、コ
- 質問546 次のエンタープライズデータフローアーキテクチャの層は、データ
- 質問547 ビジネス継続性における次の用語のうち、時間内に測定される最大
- 質問548 次のタイプのIDSは、データベース、重要なサーバーなどの重要な...
- 質問549 次のうちどれが時間に敏感なシステムやトランザクション処理のた
- 質問550 ネットワークを介して送信される暗号化されたデータにアクセスし
- 質問551 公開鍵インフラストラクチャ(PKI)では、オンライン取引が特定...
- 質問552 次のうち、ネットワークユーザーのパスワードを取得できるのはど
- 質問553 バックアップ処理施設の見直しを行っている情報システム監査人は
- 質問554 自己組織化チーム間のコラボレーションによって要件とソリューシ
- 質問555 IPSecのコンポーネントではないものはどれですか?
- 質問556 ピーク生産時間中に次のうちどれかを実行すると、予期しないダウ
- 質問557 ビジネス継続性における次の用語のどれが、許容できない結果を招
- 質問558 以下のうち、外部のITサービスプロバイダの管理をレビューする情...
- 質問559 プライマリ情報処理施設でハードウェアを交換した後、ビジネス継
- 質問560 IS監査人は、組織の物理的セキュリティ対策を見直しています。ア...
- 質問561 プログラマーは、アプリケーションやシステムに変更を加えた後、
- 質問562 デジタル署名を使用する場合、メッセージダイジェストが計算され
- 質問563 ネットワークの中央データベースにさまざまなリソースに関する情
- 質問564 プロキシベースのファイアウォールを監査する場合、IS監査人は次...
- 質問565 コンピュータフォレンジックでは、抽出された情報を調査者が理解
- 質問566 組織はヘルプデスクをアウトソーシングしています。 SLAに含める...
- 質問567 トランスポートモードでは、カプセル化セキュリティペイロード(
- 質問568 このような観点から、組織は近年縮小され、IS監査人は論理アクセ...
- 質問569 以下の選択肢から、BPR(Business Process Reengineering)ベン...
- 質問570 システムの独立した分類を行っている情報システム監査人は、次の
- 質問571 最小のパスワードの長さとパスワードの複雑さの検証は、次の例で
- 質問572 トレーディングパートナのサーバーで実装されているSSL(Secure ...
- 質問573 組織は、従業員からの電子メールの受信者が次の方法で送信者の身
- 質問574 以下のうち、IS監査人が仮想プライベートネットワーク(VPN)の...
- 質問575 IS戦略監査を実施する場合、IS監査人は、短期(1年)および長期...
- 質問576 組織の施設内の端末またはワークステーションによる不正なシステ
- 質問577 次のうち、ネットワークユーザーのパスワードを取得するために使
- 質問578 多国籍企業のIS管理者は、既存の仮想プライベートネットワーク(...
- 質問579 既存のシステムは、設計およびプログラムのコンポーネントを抽出
- 質問580 エキスパートシステムを実装する際の最大の利点は、次のとおりで
- 質問581 ある会社が最近、購入システムをアップグレードしてEDI伝送を組...
- 質問582 バイオメトリックシステムでの識別と認証に使用される次の比較は
- 質問583 情報資産に対する適切なセキュリティ対策を維持する責任は、
- 質問584 不十分であれば、サービス拒否攻撃の可能性が最も高いのは次のう
- 質問585 インターネットに接続されたコンピュータのハッキングに対する最
- 質問586 侵入検知システム(IDS)を見直す際、情報システム監査人は、次...
- 質問587 IS監査を実施する上で最も重視されるのは次のうちどれですか?
- 質問588 テーブルリンクの検証と参照チェックで何が保証されるのですか?
- 質問589 企業のコンピュータシステムの災害復旧計画(DRP)は、通常、次...
- 質問590 リカバリポイント目標(RPO)を定義する上で、最も重要なのは次...
- 質問591 IS監査では、監査人のうちの1人が、共有/共通のユーザー名とパス...
- 質問592 情報システム監査人が、セキュリティ管理者に業務機能を実行させ
- 質問593 エラーの検出と修正を容易にするために、各文字またはフレームに
- 質問594 対称鍵暗号システム内の秘密鍵の強さを決めるのは何ですか?
- 質問595 変更管理手順は、IS管理者によって以下の目的で確立されます。
- 質問596 次のマルウェアの技術的な愚か者のマルウェアは、ファイルにマル
- 質問597 データ・ウェアハウス(DW)形式および品質管理におけるデータの...
- 質問598 テスト環境と開発環境は分離する必要があります。正しいか間違っ
- 質問599 ビジネスインパクト分析(BIA)を完了した後、ビジネス継続性計...
- 質問600 情報システムがユーザーのニーズを満たすことができない最も一般
- 質問601 次の攻撃のいずれによって、2要素認証が迂回される可能性があり
- 質問602 組織は、重要なPCベースのシステムをインターネットに接続するこ...
- 質問603 次の暗号化技術のどれが中間者攻撃からワイヤレスネットワークを
- 質問604 機密データの不正な開示から適切に保護するために、ハードディス
- 質問605 以前に検出されたエラーに対する修正が受入れテストのために再提
- 質問606 WAPゲートウェイは、メッセージの機密性を強制するコントロール...
- 質問607 組織には、幅広い地理的領域に亘る多数の支店があります。災害復
- 質問608 重要ではないシステムを回復するための最も合理的なオプションは
- 質問609 情報システム監査人は、事業継続計画(BCP)を監査しています。...
- 質問610 電子署名をメッセージに付加するには、送信者はまず次のものに対
- 質問611 次に挙げるのは、情報処理施設内のソフトウェアとデータを保護す
- 質問612 プログラマーが稼働中のシステムへの更新アクセス権を持っている
- 質問613 IS監査人は、データウェアハウスに格納されている特定の機密情報...
- 質問614 ラップトップコンピュータの機密情報漏洩を防止するための最良の
- 質問615 次のどのDBMSのACIDプロパティの中で、各トランザクションが「す...
- 質問616 エンタープライズデータフローアーキテクチャの次の層のどれがエ
- 質問617 次のうち二要素ユーザー認証を満たすものはどれですか?
- 質問618 バッチ制御の調整は、不適切な職務分離のリスクを軽減するための
- 質問619 テープバックアップを現在使用している組織では、毎週1回の完全
- 質問620 ビジネス継続性と災害復旧計画の主な目的は、次のとおりです。
- 質問621 組織の災害復旧要件に対処するには、バックアップ間隔は以下を超
- 質問622 ファイアウォールが認識できない攻撃の試みを検出するには、情報
- 質問623 スプリットケーブル設備またはケーブル設備の二重化によるデータ
- 質問624 アクセス許可がまだ有効であることを確認するベストプラクティス
- 質問625 侵入検知システム(IDS)をインストールする場合、以下のうちど...
- 質問626 職務の適切な分離は、システムアナリストが品質保証機能を実行す
- 質問627 JavaアプレットとActiveXコントロールは、Webブラウザクライアン...
- 質問628 情報システム監査人は、IPアドレスとメディアアクセス制御(MAC...
- 質問629 IS管理者は、通信コストを削減するためにVoIP(Voice over Inter...
- 質問630 EDI取引の見直し中に不正取引を発見したIS監査人は、以下を改善...
- 質問631 次の攻撃のうち、コンピュータネットワークに対するもので、断片
- 質問632 次のどのラインメディアが電気通信ネットワークに最高のセキュリ
- 質問633 電気配線、エアコン、フローリングを備えたオフサイトの情報処理
- 質問634 組織は災害復旧計画を実施しています。次のステップのどれを次に
- 質問635 システム開発プロジェクトの全体的な方向性、コスト、タイムテー
- 質問636 IS監査人は、インターネットを介した企業間取引のデジタル証明書...
- 質問637 ソフトウェアモジュールをテストするための動的解析ツールはどれ
- 質問638 ソフトウェアテストのボトムアップとトップダウンのアプローチを
- 質問639 EDIプロセスでは、電子ドキュメントを送受信するデバイスは次の...
- 質問640 EDIアプリケーションのコントロールを評価する場合、情報システ...
- 質問641 ホットサイトは、次の場合に復旧戦略として実装する必要がありま
- 質問642 ソフトウェア開発のウォーターフォールライフサイクルモデルは、
- 質問643 データベース管理システム(DBMS)の監査ログを分析するIS監査人...
- 質問644 ファイアウォールの実装時に発生する可能性が最も高いエラーは次
- 質問645 脆弱性評価と侵入テストの違いは、脆弱性評価:
- 質問646 統計的サンプリング手順を使用することで、
- 質問647 データベースアプリケーションをレビューしているIS監査人は、現...
- 質問648 ソフトウェアテストのトップダウンアプローチの利点はどれですか
- 質問649 次のうち、2要素ユーザー認証を満たすための最良の方法はどれで
- 質問650 バイオメトリクスシステム運用の見直し中、IS監査人はFIRSTが次...
- 質問651 高可用性ネットワークの復元力を評価するIS監査人は、
- 質問652 どのようなアンケートを使用して、結論に至る一連の選択肢を通じ
- 質問653 次の暗号化オプションのどれがオーバーヘッド/コストを増加させ
- 質問654 災害復旧計画の構造化ウォークスルーテストには、次のものが含ま
- 質問655 複数の親を許可する木構造の多対多リレーションシップを可能にす
- 質問656 次のうち、コンピューターフォレンジックの画像データセットから
- 質問657 アプリケーションの開発中に、品質保証テストとユーザー受け入れ
- 質問658 ディスクレスワークステーションは、次のような例です。
- 質問659 以下の代替案のうち、災害復旧戦略を策定するための第一のアプロ
- 質問660 ニューラルネットワークは、以下を行うことができるため、詐欺の
- 質問661 ルータのアクセス制御リストをどのプロセスで確認する必要があり
- 質問662 次のうち、電子クレジットカード決済に使用されるSecure Digital...
- 質問663 コンピュータの廃棄手順を見直す際には、以下のうちどれが情報シ
- 質問664 企業は、顧客に対する新しいダイレクト・マーケティング・アプロ
- 質問665 誰がネットワークセキュリティ運用を担当する必要がありますか?
- 質問666 第三者としての認証局(CA)の役割は次のとおりです。
- 質問667 EDIシステム間でデータを送受信するための認証技術は、次のいず...
- 質問668 組織内のセキュリティ意識を高め、すべての従業員に適切なセキュ
- 質問669 データの機密性、信頼性、整合性を求めているインターネットビジ
- 質問670 ハードウェアで実装できるウイルス防止技術はどれですか?
- 質問671 次のうち、アクティブなインターネット攻撃を検出するためのデコ
- 質問672 データセンター内の火災を抑制する以下の方法のどれが効果的かつ
- 質問673 組織のさまざまなログおよびイベントファイルを集約し、相互に関
- 質問674 次の機密性、完全性、可用性(CIA)属性のどれが、認可されたユ...
- 質問675 すべてのシステムのバックアップに関する考慮事項に加えて、オン
- 質問676 エンタープライズデータフローアーキテクチャのコア日付倉庫レイ
- 質問677 次のうち、ネットワーク管理システムの必須機能と見なされるのは
- 質問678 仮想プライベートネットワーク(VPN)は、以下を使用してデータ...
- 質問679 IS監査人は、組織がプロセスごとに適切なBCP(ビジネス継続計画...
- 質問680 組織は、エクストラネットインフラストラクチャを通じてサプライ
- 質問681 次のどのタイプの伝送媒体が不正アクセスに対して最高のセキュリ
- 質問682 次のリスクのうち、RFID以外のネットワーク化されたシステム、資...
- 質問683 デジタル署名には次のものが必要です。
- 質問684 不適切なプログラミングとコーディングの慣習は、以下のリスクを
- 質問685 保存日をファイルに適用すると、次のことが保証されます。
- 質問686 災害復旧計画(DRP)の継続的な有効性を維持するためには、次の...
- 質問687 インターネット上のサーバーであり、意図的に侵入から保護するた
- 質問688 ビジネスユニットは、新しく実装されたシステムのパフォーマンス
- 質問689 ベンダーや外部サポート担当者に一時的にアクセスできるようにす
- 質問690 次の実装モードのうち、インターネットに接続するアウトバウンド
- 質問691 ネットワーク攻撃の証拠を収集するために使用できるものは何です
- 質問692 ベンダーは、ソフトウェアのセキュリティ上の欠陥を修正するパッ
- 質問693 2つ以上のシステムが統合されている場合、入力/出力制御は以下の...
- 質問694 CMMIモデルの次のレベルは、プロセス定義とプロセス展開に重点を...
- 質問695 統合テスト施設(ITF)を使用する場合、情報システム監査人は次...
- 質問696 次のうち、回線交換技術について不確実な記述はどれですか?
- 質問697 ハッシュと暗号化の最も重要な違いはハッシングです。
- 質問698 電子商取引環境における通信障害のリスクを最小限に抑える最良の
- 質問699 次の攻撃のどれが、ゲートウェイの背後にあるコンピュータからの
- 質問700 DoS攻撃の結果はどれですか?
- 質問701 機密データを含むハードディスクが修復を超えて破損しました。ハ
- 質問702 OSIモデルの次のレイヤのどれが、アプリケーションがネットワー...
- 質問703 データベース管理者は、次のことを担当します。
- 質問704 情報システム監査人が脅威と潜在的な影響を特定した後、監査人は
- 質問705 デジタル署名を使用する主な理由は、データを保証することです。
- 質問706 次のうち、RSA暗号化よりも楕円曲線暗号化の方が最大の利点はど...
- 質問707 次のうち、内部構造やアプリケーションの動作を調べるテスト方法
- 質問708 任意のアクセス制御を有効にするには、以下の条件を満たす必要が
- 質問709 最初に署名されたデジタル証明書を受け取ると、ユーザーは以下の
- 質問710 電気通信の継続性を提供する次の方法のどれに代替メディアの使用
- 質問711 アプリケーションの購入者がアプリケーションベンダーが業務を終
- 質問712 端末からの電磁放射は、次の理由から露出を表します。
- 質問713 OSIモデルの次の層のどれが、エラーがなく、順番に、かつ損失や...
- 質問714 通常、プロジェクトの開始段階には次のステークホルダーのいずれ
- 質問715 組織には、より強力なセキュリティにアップグレードすることがで
- 質問716 全面的な緊急事態テストの後、IS監査人は回復手順のレビューを実...
- 質問717 ワイドエリアネットワーク(WAN)の使用状況を見直すと、マスタ...
- 質問718 オンライン注文入力システムの更新が処理されると、更新はトラン
- 質問719 次の中でチャレンジレスポンス認証システムのセキュリティを効果
- 質問720 セキュリティ要件が非常に高い組織では、バイオメトリックシステ
- 質問721 ネットワークパフォーマンスに関連する次の用語のうち、情報がネ
- 質問722 MOSTの効果的なバイオメトリックコントロールシステムは、
- 質問723 災害やビジネス中断のリスクと影響を軽減することは、通常、保険
- 質問724 次のうち、監査を計画する上で最も重要なステップはどれですか?
- 質問725 アプリケーション保守監査を行っているIS監査人は、次の場合のプ...
- 質問726 次のうち、SSLとS / HTTPの違いを正しく説明しているのはどれで...
- 質問727 磁気メディア上の機密データを永久に消去するためにセキュリティ
- 質問728 次のうち煙探知器について真実ではないものはどれですか?
- 質問729 ファイルサーバーでRAIDレベル1のRedundant Array of Arrayを実...
- 質問730 重要なシステムで認証および認定プロセスが実行される理由は、次
- 質問731 システム監査のプロセスは、リスクベースのアプローチを監査計画
- 質問732 電子メールソフトウェアアプリケーションで検証されたデジタル署
- 質問733 パリティビットは、検証するために使用されるコントロールです。
- 質問734 航空会社予約システムのビジネス継続計画(BCP)を設計する際に...
- 質問735 内部アプリケーションのインタフェースエラーができるだけ早く確
- 質問736 非武装地帯(DMZ)のサーバー上でファイル転送プロトコル(FTP)...
- 質問737 バイオメトリックシステムの精度の測定値は次のとおりです。
- 質問738 2つのシステム間で情報を交換するためにWebサービスを使用するこ...
- 質問739 ITサービスの可用性と継続性に関するITベストプラクティスは、...
- 質問740 不正なアクセスを得るための残存生体情報の使用は、以下の攻撃の
- 質問741 以下のWANメッセージ伝送技術のうち、2つのネットワークノードは...
- 質問742 アクセス権の監査を行う場合、情報システム監査人は、コンピュー
- 質問743 次の中で最も信頼性の高い単一因子の個人識別情報ですか?
- 質問744 バイオメトリックユーザ認証システムを検査するIS監査人は、バイ...
- 質問745 費用対効果の高いコントロールを自動システムで実装する責任は誰
- 質問746 ERP金融システムの論理アクセス制御の監査中、IS監査人は複数の...
- 質問747 審査員が組織のバイオメトリクスシステムをよりよく理解するのに
- 質問748 公開鍵暗号化を使用して、ネットワーク上でデータが送信されるよ
- 質問749 次のPBX機能のうち、重要なメッセージを他のユーザーに知らせる...
- 質問750 FIRSTのアクセス制御の実装には、次のものが必要です。
- 質問751 ネットワークパフォーマンスに関連する次の用語のどれが、送信さ
- 質問752 ピギーバックのリスクに対処するための最も効果的なコントロール
- 質問753 組織の災害復旧計画は、
- 質問754 電子メールのメッセージの信頼性と機密性は、以下を使用してメッ
- 質問755 UTP(Unshielded Twisted Pair)ネットワークで動作するイーサネ...
- 質問756 人事(HR)監査では、IS監査人は、期待されるITサービスのレベル...
- 質問757 次のうち、公開鍵インフラストラクチャ(PKI)について真実では...
- 質問758 OSI参照モデルを使用して、データを暗号化するために使用される...
- 質問759 次の場合は、Webサーバーのリバースプロキシ技術を導入する必要...
- 質問760 ブランチオフィスの場所でワイヤレスセキュリティをテストするた
- 質問761 IS監査人は、事業継続計画(BCP)の監査中に、すべての部署が同...
- 質問762 次の攻撃のうち、コンピュータ化された取引やアカウントから少額
- 質問763 次のうちどれがサーバーのオペレーティングシステムの完全性を保
- 質問764 次のPBX機能のうち、複数のデバイス間で共有拡張機能をサポート...
- 質問765 統合システム環境におけるアプリケーションの入出力制御を実装す
- 質問766 次のインターネットセキュリティの脅威のうち、整合性を損なう可
- 質問767 データベース管理者は、非正規化によって解決できるいくつかのテ
- 質問768 IS監査人は、暗号化システムを評価する際に多くの要素を考慮する...
- 質問769 販売時点管理(POS)システムを見直す際に、最も重要な監査結果...
- 質問770 潜在的なネットワークの脆弱性を判断するために侵入者が使用する
- 質問771 侵入検知システム(IDS)の中で、通常のネットワーク活動に起因...
- 質問772 企業は、重要なdatAにアクセスするすべてのPCでバイオメトリック...
- 質問773 IS監査人が継続的監視システムを導入するために推奨される最初の...
- 質問774 次のうち、アドレスフィールドの重複を検索するのに最適なのはど
- 質問775 ベスト・アクセス制御の手順はどれですか?
- 質問776 生産環境における各アプリケーションシステムの重要性を判断する
- 質問777 DOD TCP / IPモデルで使用されているINCORRECTレイヤーからプロ...
- 質問778 次のうち、TCP / IPモデル内のアプリケーション層のレイヤ機能を...
- 質問779 他の従業員によって再利用される磁気メディア上のデータを消去す
- 質問780 以下に示す下の図からネットワークトポロジを特定します。 (Exhi...
- 質問781 次のタイプのコンピュータネットワークは、WANに限定されている...
- 質問782 次のネットワークコンポーネントのどれが、ネットワークのさまざ
- 質問783 次のうち、データベースに接続されたアプリケーションの移植性を
- 質問784 次のうち、TCP / IPモデルのネットワークインターフェイスレイヤ...
- 質問785 次のうち맬웨어防止ソフトウェアを正しく記述していない声明はど
- 質問786 企業は新しいクライアント/サーバーエンタープライズリソースプ
- 質問787 CMMIモデルの次のレベルのどれがプロセス革新と継続的な最適化に...
- 質問788 企業は動的ホスト構成プロトコル(DHCP)を実装しています。以下...
- 質問789 データベース管理者(DBA)は、一部の表を非正規化することによ...
- 質問790 生産ソースコードとオブジェクトコードが同期されることを保証す
- 質問791 データ管理者は次の責任を負います。
- 質問792 EDIトランザクションを受信し、通信のインタフェースステージを...
- 質問793 組織の論理アクセスセキュリティを見直す際には、以下のうちどれ
- 質問794 いつユーザーの受け入れをテストする計画は準備する必要がありま
- 質問795 ネットワーク情報を監視して記録するネットワーク診断ツールはど
- 質問796 ビジネスユニットによる集中的な使用の4時間のテストを含む、IT...
- 質問797 Webサイト証明書の主目的は次のとおりです。
- 質問798 Webベースのソフトウェア開発プロジェクトのレビュー中、IS監査...
- 質問799 ウイルスの保護としてファイルに追加されるのは次のうちどれです
- 質問800 エンドユーザーがアプリケーションではなくシステムレベルでデー
- 質問801 エンタープライズデータフローアーキテクチャの次のレイヤのうち
- 質問802 侵入検知システム(IDS)の操作における最も一般的な問題は次の...

