- ホーム
- CompTIA
- SY0-701-JPN - CompTIA Security+ Certification Exam (SY0-701日本語版)
- CompTIA.SY0-701-JPN.v2025-08-23.q252
- 質問168
有効的なSY0-701-JPN問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、SY0-701-JPN試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新SY0-701-JPN試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com SY0-701-JPN試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここでSY0-701-JPN問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
SY0-701-JPN問題集最新版のアクセス
「645問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
ある組織は、自社のデータがダークウェブ上でやり取りされていることを知りました。CIO(最高情報責任者)は、従業員アカウントを保護するための最も安全なソリューションを調査し、導入するよう依頼しました。
説明書
データをレビューして、セキュリティの弱い部分を特定し、CIO の要件を満たす最も適切なセキュリティ ソリューションを提供します。

説明書
データをレビューして、セキュリティの弱い部分を特定し、CIO の要件を満たす最も適切なセキュリティ ソリューションを提供します。

正解:
See the Explanation for complete solution for this task.
Explanation:
A screenshot of a computer AI-generated content may be incorrect.
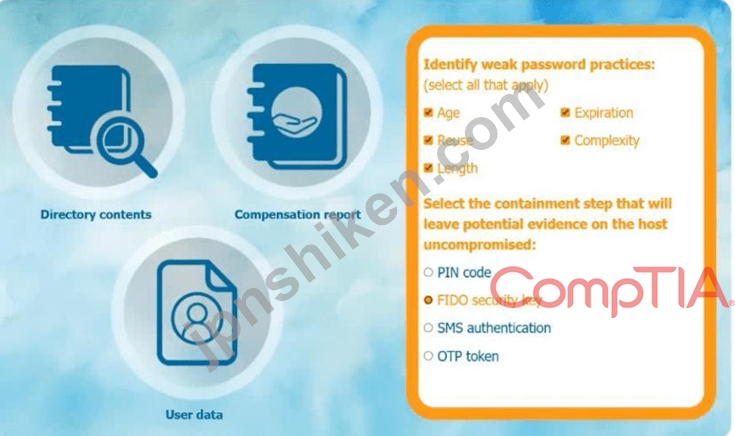
Step 1: Analyze the Data and Question
Scenario:
* Company data (directory, compensation report, user data) is found on the dark web.
* CIO asks you to investigate and implement the most secure protection for employee accounts.
* Task:
* Identify weak password practices.
* Choose the best containment step that keeps evidence on the host uncompromised.
Step 2: Identify Weak Password Practices
Prompt: Select all weak password practices from the list:
* Age
* Reuse
* Length
* Expiration
* Complexity
Let's analyze each:
* Age: If passwords are used for a long time without change, it's a weak practice (passwords become easier to compromise over time).
* Reuse: Reusing passwords across accounts is a serious weak practice (if one gets leaked, all accounts are at risk).
* Length: Short passwords are weak; password length matters. If passwords are too short, that's a weak practice.
* Expiration: Forcing frequent expiration can lead to weaker passwords (users pick simple ones), but not expiring passwords at all is also risky. (For most exams, "expiration" by itself isn't usually called a weak practice unless the policy is poorly set.)
* Complexity: Lack of complexity (not requiring numbers, symbols, etc.) is a weak practice.
So, select all that are truly weak practices:
Answer for weak password practices (check all that apply):
* ## Age
* ## Reuse
* ## Length
* ## Complexity
(Expiration is more controversial; on the exam, the main focus is usually on Age, Reuse, Length, and Complexity.) Step 3: Choose the Best Containment Step Prompt:
Select the containment step that will leave potential evidence on the host uncompromised:
* PIN code
* FIDO security key
* SMS authentication
* OTP token
* Containment step means "what security solution can you implement to protect employee accounts going forward, while preserving digital evidence on potentially compromised systems?"
* The most secure solution for account protection among these, that also doesn't interfere with host evidence, is FIDO security key.
Why?
* PIN code: Not strong enough; also may be stored locally.
* SMS authentication: Can be intercepted; often leaves traces on the host (like SMS logs).
* OTP token: Similar risks, some implementations might log to the host.
* FIDO security key: Hardware-based, phishing-resistant, no codes sent to the host, and doesn't alter host evidence-authentication happens off the device.
So, the best answer is:
* FIDO security key
Step 4: Solution Recap and Justification
Detailed Solution Recap:
* Identify weak password practices:
* Weaknesses: passwords are reused, not long enough, lack complexity, and used for a long time.
* Select the best security solution:
* Implement FIDO security keys for employees.
* Most secure among listed options.
* Hardware-based; resistant to phishing, interception, and does not leave evidence on the compromised host (which is important for forensics).
Explanation:
A screenshot of a computer AI-generated content may be incorrect.

Step 1: Analyze the Data and Question
Scenario:
* Company data (directory, compensation report, user data) is found on the dark web.
* CIO asks you to investigate and implement the most secure protection for employee accounts.
* Task:
* Identify weak password practices.
* Choose the best containment step that keeps evidence on the host uncompromised.
Step 2: Identify Weak Password Practices
Prompt: Select all weak password practices from the list:
* Age
* Reuse
* Length
* Expiration
* Complexity
Let's analyze each:
* Age: If passwords are used for a long time without change, it's a weak practice (passwords become easier to compromise over time).
* Reuse: Reusing passwords across accounts is a serious weak practice (if one gets leaked, all accounts are at risk).
* Length: Short passwords are weak; password length matters. If passwords are too short, that's a weak practice.
* Expiration: Forcing frequent expiration can lead to weaker passwords (users pick simple ones), but not expiring passwords at all is also risky. (For most exams, "expiration" by itself isn't usually called a weak practice unless the policy is poorly set.)
* Complexity: Lack of complexity (not requiring numbers, symbols, etc.) is a weak practice.
So, select all that are truly weak practices:
Answer for weak password practices (check all that apply):
* ## Age
* ## Reuse
* ## Length
* ## Complexity
(Expiration is more controversial; on the exam, the main focus is usually on Age, Reuse, Length, and Complexity.) Step 3: Choose the Best Containment Step Prompt:
Select the containment step that will leave potential evidence on the host uncompromised:
* PIN code
* FIDO security key
* SMS authentication
* OTP token
* Containment step means "what security solution can you implement to protect employee accounts going forward, while preserving digital evidence on potentially compromised systems?"
* The most secure solution for account protection among these, that also doesn't interfere with host evidence, is FIDO security key.
Why?
* PIN code: Not strong enough; also may be stored locally.
* SMS authentication: Can be intercepted; often leaves traces on the host (like SMS logs).
* OTP token: Similar risks, some implementations might log to the host.
* FIDO security key: Hardware-based, phishing-resistant, no codes sent to the host, and doesn't alter host evidence-authentication happens off the device.
So, the best answer is:
* FIDO security key
Step 4: Solution Recap and Justification
Detailed Solution Recap:
* Identify weak password practices:
* Weaknesses: passwords are reused, not long enough, lack complexity, and used for a long time.
* Select the best security solution:
* Implement FIDO security keys for employees.
* Most secure among listed options.
* Hardware-based; resistant to phishing, interception, and does not leave evidence on the compromised host (which is important for forensics).
- 質問一覧「252問」
- 質問1 不明なプログラムの実行をブロックする最善の方法は次のどれです
- 質問2 ある会社がクラウドにベンダーのセキュリティ ツールを実装して
- 質問3 管理者は期限切れの SSL 証明書を置き換える必要があります。管...
- 質問4 次のシナリオのうち、ビジネス メール詐欺攻撃の可能性を説明し
- 質問5 大企業の顧客が、その企業に勤めていると主張する人物から電話を
- 質問6 銀行環境で監査を完了する最も適切な理由はどれですか?
- 質問7 セキュリティアナリストが役割と責任を確認するインシデント対応
- 質問8 デバイスがネットワークに接続されたリソースにアクセスできない
- 質問9 証拠の完全性を確保する必要がある場合、企業はデジタルフォレン
- 質問10 ある企業は、悪意のある内部関係者が組織に危害を加える可能性が
- 質問11 最近、会社のシステムがランサムウェア攻撃を受けた後、管理者が
- 質問12 ある企業は、社内ネットワークへの安全なリモート アクセスを確
- 質問13 会社のウェブサイトは www. Company. com です。攻撃者はドメイ...
- 質問14 組織の最高情報セキュリティ責任者は、ランサムウェアからの復旧
- 質問15 攻撃者がバッファ オーバーフローを悪用したため、組織のインタ
- 質問16 会社のハードウェア攻撃対象領域を減らすために、システム管理者
- 質問17 パッチ適用の優先順位付けに最も役立つのは次のどれですか?
- 質問18 内部監査チームは、ソフトウェア アプリケーションが外部レポー
- 質問19 ある顧客がセキュリティ会社に、プロジェクトの概要、コスト、完
- 質問20 RTOS を実行しているシステムを侵害するために使用できるのは次...
- 質問21 システム管理者がベンダーの Web サイトに掲載されているインス...
- 質問22 セキュリティ エンジニアは、SIEM 内での自動化とオーケストレー...
- 質問23 組織のセキュリティ監査により、ほとんどの IT スタッフがドメイ...
- 質問24 組織のルーターのファームウェアをアップグレードする場合、シス
- 質問25 ある企業が自社のシステムで機密データを処理および保存していま
- 質問26 実行時にデプロイされたアプリケーションで実行できる識別方法の
- 質問27 最高経営責任者を装った攻撃者が従業員に電話をかけ、ギフトカー
- 質問28 ユーザーに証明書が提示されたときに、証明書を検証するために使
- 質問29 会社の VPN アプライアンスのローカル管理者アカウントが予期せ...
- 質問30 IoT 管理にクラウドベースのプラットフォームを使用する場合、次...
- 質問31 ある企業が事業継続戦略を策定しており、混乱が発生した場合に事
- 質問32 システム管理者は、クラウド コンピューティング インスタンス内...
- 質問33 次のシナリオのうち、トークン化がプライバシー技術として最も適
- 質問34 攻撃者は XSS を使用して Web サーバーを侵害しました。この攻撃...
- 質問35 IT 管理者は、エンタープライズ アプリケーションにデータ保持標...
- 質問36 データ センターのセキュリティ管理は、データが適切に保護され
- 質問37 管理者は、多数のアカウントのアカウント権限の更新を自動化した
- 質問38 従業員が電子メール内の悪意のあるリンクをクリックし、会社のコ
- 質問39 ある会社は最近、従業員にリモートワークを許可することを決定し
- 質問40 様々なプライバシー規則および規制に基づき、ユーザーは自身に関
- 質問41 保留中の調査で法的要請に応じる際に、セキュリティ チームが実
- 質問42 組織内の誠実性と倫理的行動に関連する期待を確立し、伝達するた
- 質問43 金融機関は、顧客データをクラウドに保存したいが、暗号化された
- 質問44 医療機関は、個人が健康上の緊急事態をデジタルで報告できる Web...
- 質問45 災害復旧サイトの整合性と可用性を検証する最良の方法はどれです
- 質問46 セキュリティアナリストは、セキュリティ侵害により 15,000 ドル...
- 質問47 会社 A は、別の国に所在する会社 B と共同で製品を開発していま...
- 質問48 新入社員が初めてメール システムにログインすると、人事部から
- 質問49 セキュリティ アナリストは、人事部門が実装しようとしている Sa...
- 質問50 DPO がデータ インベントリを開発する最も適切な理由はどれです...
- 質問51 セキュリティ担当者が会社のネットワークの脆弱性評価を完了し、
- 質問52 ユーザーが重要なシステムにパッチを適用しようとしましたが、パ
- 質問53 承認されていないソフトウェアの導入によって企業ネットワークに
- 質問54 組織は保護したい知的財産を保持しています。次の概念のうち、会
- 質問55 システム管理者は、組織のプライベート クラウド内で機密データ
- 質問56 フォレンジックエンジニアは、侵害の根本原因がSQLインジェクシ...
- 質問57 管理者は、ネットワークに接続するすべてのゲストデバイスに対し
- 質問58 ある会社のオンラインショッピングサイトが、2023 年 1 月 30 日...
- 質問59 セキュリティ アナリストは、オンプレミス ネットワーク内の侵害...
- 質問60 一連のアカウント侵害と認証情報の不正使用が発生した後、企業は
- 質問61 経理部門の従業員が、ベンダーが実行したサービスに対する支払い
- 質問62 セキュリティアナリストは、既知のマルウェアのダウンロード試行
- 質問63 従業員は、給与部門から送信されたと思われる、資格情報の確認を
- 質問64 セキュリティ アナリストが会社のパブリック ネットワークをスキ...
- 質問65 ウェブサイトのユーザーが、電子メールのリンクをクリックして別
- 質問66 高可用性ネットワークを設計する際に考慮する必要があるのは次の
- 質問67 セキュリティ アナリストは、最近のインシデントで使用された攻
- 質問68 システム管理者は、クラウドベースの低コストのアプリケーション
- 質問69 ある組織は、サードパーティベンダーに特定のデバイスを対象とし
- 質問70 暗号化された接続を確立するために、外部向けの Web サーバーに...
- 質問71 企業が HIPS を導入して実装しているセキュリティ制御は次のどれ...
- 質問72 サイト信頼性エンジニアは、プライマリ施設がダウンした場合に同
- 質問73 ソフトウェア開発マネージャーは、会社が作成したコードの信頼性
- 質問74 ベンダーの多様性の利点は次のどれですか?
- 質問75 ある会社は、サービス プロバイダーと毎年契約を結んでいます。
- 質問76 小売業者が PCI DSS に準拠していない場合、小売チェーンが顧客...
- 質問77 セキュリティ アナリストは、コマンド アンド コントロール サー...
- 質問78 最高情報セキュリティ責任者は、業務をできるだけ早く再開できる
- 質問79 次のどれがメッセージを個人に帰属させることを可能にしますか?
- 質問80 ある企業が、社内ネットワークから発信される DNS トラフィック...
- 質問81 ある企業は、顧客が使用するソフトウェアを構築するためにオープ
- 質問82 セキュリティ アナリストは、業務時間外に短時間に大量の異常な ...
- 質問83 セキュリティ アナリストが企業のすべてのエンドポイントで毎日
- 質問84 次の脅威アクターのうち、巨額の資金を使って他国にある重要なシ
- 質問85 管理者がインシデントを調査しているときに、共有されたファイル
- 質問86 公式アプリケーション ストア以外の手段でデバイスにアプリケー
- 質問87 数人の従業員が、最高経営責任者(CEO)を名乗る人物から詐欺の...
- 質問88 IT マネージャーは、世界的なインシデントが発生した場合に組織...
- 質問89 最近の侵入テストでは、攻撃者がネットワーク スイッチの MAC ア...
- 質問90 ハードウェアとインターネット アクセスを含む低コストのスタン
- 質問91 リモートで作業していた従業員が、会社のデータを含むモバイル
- 質問92 最高情報セキュリティ責任者は、コンプライアンス目標を追跡する
- 質問93 ある企業は、次の方法でシステムを保護することを計画しています
- 質問94 レガシー IoT デバイスの OS に、新たに特定されたネットワーク ...
- 質問95 レガシー デバイスが廃止され、更新やパッチを受信しなくなりま
- 質問96 従来のインフラストラクチャ モデルよりも、Infrastructure as C...
- 質問97 ウェブサイトの秘密鍵が盗まれ、新しい証明書が発行されました。
- 質問98 従業員が新しいシステム管理者に悪意のある Web リンクを電子メ...
- 質問99 セキュリティ エンジニアは、環境内でシグネチャベースの攻撃を
- 質問100 ある企業は、従業員が就業時間中に仮想デスクトップからファイル
- 質問101 ハードドライブから機密データを繰り返し消去したいが、ハードド
- 質問102 サイドローディング時に導入される可能性のあるものはどれですか
- 質問103 パスワードを強化し、ハッカーによる解読を防ぐために、36 文字...
- 質問104 ある中小企業では、販売フロアのキオスクを使用して顧客に製品情
- 質問105 ある企業がベンダーと協力して侵入テストを実施しています。次の
- 質問106 従業員は退職時に特定の行為を制限する契約書に署名します。この
- 質問107 セキュリティ アナリストは、ネットワークに接続されている現在
- 質問108 IT 請負業者との契約を作成した後、人事部門はいくつかの条項を...
- 質問109 従来の Linux システム上のホストベースのファイアウォールが特...
- 質問110 データベース サーバーによってアクティブに処理されているデー
- 質問111 新しく導入されたサーバーを保護するための最初のステップは次の
- 質問112 限られたコンピューティング リソースでの通信を保護するために
- 質問113 企業のインフラストラクチャの重要な部分であるレガシー システ
- 質問114 リスク管理プロセスにおける次のステップのうち、プロジェクトに
- 質問115 組織では単一のオペレーティング システムのバリエーションが多
- 質問116 システム管理者は、ユーザーの責任に基づいて、ユーザーがデータ
- 質問117 クライアントは、サービス プロバイダーがホストするセキュリテ
- 質問118 ある会社がモバイル デバイス ポリシーを変更しています。会社に...
- 質問119 システム管理者は、企業環境内でパスワード ポリシーを変更して
- 質問120 セキュリティ オペレーション センターは、疑わしい IP アドレス...
- 質問121 インシデント対応スペシャリストは、悪意のある攻撃が組織の他の
- 質問122 ある組織では、組織内のシステムとソフトウェアの一般的な運用に
- 質問123 特定の業界における情報セキュリティ運用に関連する法律や規制を
- 質問124 次のタスクのうち、BIA プロセスに通常含まれるものはどれですか...
- 質問125 高い可用性が求められるミッションクリティカルな運用サーバーで
- 質問126 組織のクラウド導入戦略を検討しながら、最高情報セキュリティ責
- 質問127 セキュリティ アナリストは、リスクベースのアプローチを使用し
- 質問128 企業は、セキュリティ境界を通過するトラフィックを最小限に抑え
- 質問129 セキュリティ保護された施設への訪問者は、写真付き身分証明書で
- 質問130 社内の Web サイトにアクセスしようとすると、サイトが安全でな...
- 質問131 新しい脆弱性が公開されたときに、セキュリティアナリストが組織
- 質問132 失われた場合に最も影響を受けるデータのカテゴリを説明するもの
- 質問133 企業ネットワークの攻撃対象領域を減らすための最良の方法はどれ
- 質問134 ある会社のベンダーがアナリストに BIOS アップデートを推奨する...
- 質問135 ハード ドライブを再利用できるようにしながら、ハード ドライブ...
- 質問136 組織がインシデント対応プロセスを改善するために使用すべき演習
- 質問137 組織は、その管理が適切に設計され、効果的に運用されていること
- 質問138 数日間にわたる停電でもデータセンターが稼働し続けるためには、
- 質問139 セキュリティアナリストが侵入テストのレポートを検証していたと
- 質問140 権限のないユーザーが従業員の電話ネットワーク ポートにラップ
- 質問141 セキュリティ アナリストは、サーバー上で悪意のある可能性のあ
- 質問142 ある会社では、従業員がネットワークにリモート アクセスできる
- 質問143 最近のログレビュー中に、アナリストはインジェクション攻撃が成
- 質問144 レガシー システムを使用して実稼働サービスを提供する場合に最
- 質問145 次の環境のうち、顧客データのサブセットを利用し、主要なシステ
- 質問146 重要なアプリケーション用の重要なパッチがリリースされたばかり
- 質問147 転送中のデータを保護するのに最もよく使用されるデータ保護方法
- 質問148 レガシー サーバーで実行されている重要なビジネス アプリケーシ...
- 質問149 クレジットカードの最後の 4 桁の数字のみを表示する必要がある...
- 質問150 次のチームのうち、組織の重要なシステムを保護するために、攻撃
- 質問151 セキュリティ マネージャーは MFA とパッチ管理を実装しています...
- 質問152 技術者は、本番システムに優先度の高いパッチを適用する必要があ
- 質問153 銀行は顧客の Pll を格納する新しいサーバーを設置しました。機...
- 質問154 セキュリティ ディレクターが企業の IT 環境内で脆弱性のパッチ...
- 質問155 セキュリティ オペレーション センターは、サーバー上で検出され...
- 質問156 システム管理者は、会社の最高経営責任者を名乗る未知の番号から
- 質問157 特定のインシデント対応シナリオに対してセキュリティ チームを
- 質問158 セキュリティ管理者は、インシデントを調査しているときに、Web ...
- 質問159 サードパーティの侵入テスターによるテストの条件についての
- 質問160 内部者が企業の開発プロセスに悪意のあるコードを導入するのを防
- 質問161 ある企業は、自社のデータがダークウェブ上で販売されていると広
- 質問162 地理的に分散したインフラストラクチャ間で転送される機密データ
- 質問163 ある企業は、財務部門のサポートにオフショア チームを活用して
- 質問164 リスク、責任者、しきい値を文書化するために最もよく使用される
- 質問165 内部脅威アクターがデータの流出を試みる際に最もよく利用される
- 質問166 技術者は、リモート ワークからオフィス ワークに移行する既存ユ...
- 質問167 セキュリティ オペレーション センターは、疑わしい IP アドレス...
- 質問168 ある組織は、自社のデータがダークウェブ上でやり取りされている
- 質問169 レガシー システムを識別するために最もよく使用される方法はど
- 質問170 実際の外部接続に似た侵入テストを最もよく表すのは次のどれです
- 質問171 ネットワーク エンジニアは、ネットワーク デバイスの全体的なセ...
- 質問172 セキュリティアナリストが Web サーバーのログを確認すると、次...
- 質問173 複数のエンティティが必要に応じてキーにアクセスできるように、
- 質問174 ファイルの整合性を確認するために使用できるデータ保護戦略は次
- 質問175 会社のマーケティング部門は、機密性の高い顧客データを収集、変
- 質問176 オフサイトにいる従業員は、割り当てられたタスクを完了するため
- 質問177 デジタル証明書の偽装 ID が検出されました。会社のドメインで使...
- 質問178 セキュリティ エンジニアは、シャドー IT サービスが組織にもた...
- 質問179 ユーザーが電子メールを確認している間に、ホストに接続された外
- 質問180 ある企業は現在、ユーザー名とパスワードを使用しており、シーム
- 質問181 セキュリティ アナリストがアプリケーション サーバーを調査して...
- 質問182 ある企業は、ランサムウェア攻撃に対する補償を削除することで、
- 質問183 セキュリティ インシデント発生中に、セキュリティ運用チームは
- 質問184 会社の Web サーバーで見つかった脆弱性に対処するのに最適なア...
- 質問185 ベンダーの営業担当者は、ある会社の最高財務責任者(CFO)の個...
- 質問186 管理者は、組織外にこれらのファイルを電子メールで送信しようと
- 質問187 アナリストは、ユーザーがフィッシング メール内のリンクをクリ
- 質問188 次のどのタイプの脆弱性が、主に暗号化証明書の不適切な使用と管
- 質問189 エアギャップ ネットワークで最も一般的なデータ損失パスは次の
- 質問190 システム管理者は、デバイスがネットワーク認証を実行するように
- 質問191 次のどれが CVSS の使用例ですか?
- 質問192 提供される内容と、企業にリソースを提供するために必要な許容時
- 質問193 セキュリティ アナリストが、単純で繰り返し可能なタスクを自動
- 質問194 ある会社では、財務データを第三者に転送するためにレガシー FTP...
- 質問195 経理担当者は、電話で新しい口座を使用するようにという不正な指
- 質問196 次の脆弱性スキャンレポートを確認した後: サーバー:192.168.14....
- 質問197 侵入テストにより、ドメイン管理者アカウントがパスザハッシュ攻
- 質問198 ソフトウェア開発者は、ソース コードをリバース エンジニアリン...
- 質問199 従業員が誤って会社のシステムにマルウェアをインストールするの
- 質問200 次のデータ タイプのうち、データ主権に関連するものはどれです
- 質問201 海外オフィスに影響を与えるセキュリティ侵害が発生した場合に備
- 質問202 次のトピックのうち、組織の SDLC に含まれる可能性が高いのはど...
- 質問203 セキュリティ マネージャーは、さまざまな種類のセキュリティ イ...
- 質問204 侵入テスト中に、ベンダーはアクセス バッジを使用して許可され
- 質問205 最高情報セキュリティ責任者は、会社のサーバーを監視して SQLi ...
- 質問206 外国語を話す士官候補生が会社の電話番号を使用してパートナー組
- 質問207 ある組織は、リモート ワークが原因で、VPN コンセントレータと...
- 質問208 脆弱性評価を実施する際のリスクは次のどれですか?
- 質問209 セキュリティ管理者が新しいファイアウォール ルール セットを設...
- 質問210 システム管理者は地元の病院に勤務しており、患者データが保護さ
- 質問211 ある組織は最近、SSO を実装することを決定しました。要件は、ア...
- 質問212 モノリシック アーキテクチャと比較した場合のマイクロサービス ...
- 質問213 2 つの会社が合併中です。両社は情報セキュリティ プログラムを...
- 質問214 組織は、侵入が発生した場合に、ログイン データベースへの潜在
- 質問215 ある組織の Web サーバーはオンライン注文システムをホストして...
- 質問216 ユーザーは https://comptiatraining.com でトレーニングを完了...
- 質問217 ある会社の物理的なセキュリティ チームは、従業員がバッジを表
- 質問218 ある組織が、コストと利益を主な要件とし、RTO と RPO の値が約 ...
- 質問219 ある組織では、顧客データを、メインの企業ネットワーク上のユー
- 質問220 高可用性ネットワークを設計する際に考慮する必要があるのは次の
- 質問221 最近のログレビュー中に、アナリストはインジェクション攻撃が成
- 質問222 セキュリティ管理者はハッシュ化を用いてパスワードを保護します
- 質問223 さまざまな関係者が、セキュリティ インシデントや大規模災害な
- 質問224 次のどれがメモリインジェクションの例ですか?
- 質問225 エンジニアがネットワーク デバイスの廃止を推奨すべきケースは
- 質問226 在宅勤務中の人事部 (HR) の従業員が会社のノートパソコンを開い...
- 質問227 ある会社がカメラを設置し、訪問者に録画されていることを知らせ
- 質問228 新入社員が不正なウェブサイトにアクセスしました。調査の結果、
- 質問229 インシデント後のレビューフェーズに含まれるアクティビティは次
- 質問230 脆弱性の優先順位付けに関する決定を行う際に、組織が最も重点を
- 質問231 内部脅威のシナリオにおいて、悪意のある攻撃者の注意を引く可能
- 質問232 ある企業が、インフラストラクチャをオフプレミス ソリューショ
- 質問233 許容使用ポリシーは、次のセキュリティ制御タイプのうちどれを最
- 質問234 エンジニアは、スイッチが最新のOSを使用していること、サーバー...
- 質問235 セキュリティ レポートによると、2 週間のテスト期間中に、従業...
- 質問236 セキュリティ管理者が元従業員のラップトップを再発行しています
- 質問237 セキュリティアナリストは、サードパーティのクラウド サービス ...
- 質問238 ある企業は、コスト削減のために請負業者と社内従業員が使用する
- 質問239 使用されなくなったソーシャル メディア アカウントから個人デー...
- 質問240 ある企業がインフラストラクチャを再設計し、使用中の物理サーバ
- 質問241 ログを確認しているときに、セキュリティ管理者は次のコードを特
- 質問242 セキュリティ管理者は、会社のデータ センターの攻撃対象領域を
- 質問243 インシデント対応の次のフェーズのうち、レポートの生成が含まれ
- 質問244 次の契約タイプのうち、ベンダーが応答する必要がある時間枠を定
- 質問245 クラウド プロバイダー内でリソースを簡単に展開できるようにす
- 質問246 ある企業は、コードの導入に関連する時間と費用を削減したいと考
- 質問247 システム管理者は、次の要件を満たすソリューションに取り組んで
- 質問248 セキュリティ管理者は、機密データを第三者に転送するために暗号
- 質問249 セキュリティアナリストがログを確認したところ、次のことが分か
- 質問250 個人がコンピュータ ネットワークにログインした後にアクセスを
- 質問251 セキュリティチームは、オフィスビルの大部分で遅延が大きくなり
- 質問252 次のどれが、エクスプロイトがオペレーティング システムによっ

