有効的な300-101問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、300-101試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新300-101試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com 300-101試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここで300-101問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
300-101問題集最新版のアクセス
「225問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
Which two functionalities are specific to stateless NAT64? (Choose two.)
正解:A,E
Explanation/Reference:
Explanation:
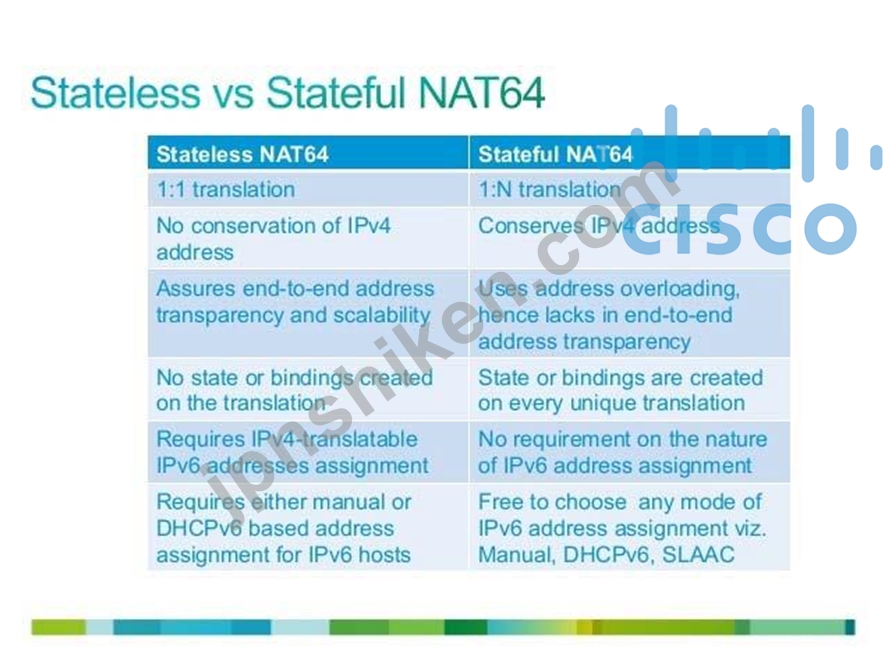
Comparison Between Stateless and Stateful NAT64
Stateless NAT64
Stateful NAT64
1:1 translation, hence applicable for limited number of endpoints
1: N translation, hence no constraint on thenumber of end points therefore, also applicable for carrier grade NAT (CGN) No conservation of IPv4 address Conserves IPv4 address Helps ensure end-to-end address transparency and scalability Uses address overloading; hence lacks end-to-end address transparency No state or bindings created on the translation State or bindings created on every unique translation Requires IPv4-translatable IPv6 address assignment (mandatory requirement) No requirement for the characteristics of IPv6 address assignment Requires either manual or Domain Host Configuration Protocol Version 6 (DHCPv6)-based address assignment for IPv6 hosts Capability to choose any mode of IPv6 address assignment: manual, DHCPv6, or stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC)
Explanation:
Comparison Between Stateless and Stateful NAT64
Stateless NAT64
Stateful NAT64
1:1 translation, hence applicable for limited number of endpoints
1: N translation, hence no constraint on thenumber of end points therefore, also applicable for carrier grade NAT (CGN) No conservation of IPv4 address Conserves IPv4 address Helps ensure end-to-end address transparency and scalability Uses address overloading; hence lacks end-to-end address transparency No state or bindings created on the translation State or bindings created on every unique translation Requires IPv4-translatable IPv6 address assignment (mandatory requirement) No requirement for the characteristics of IPv6 address assignment Requires either manual or Domain Host Configuration Protocol Version 6 (DHCPv6)-based address assignment for IPv6 hosts Capability to choose any mode of IPv6 address assignment: manual, DHCPv6, or stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC)

- 質問一覧「477問」
- 質問1 A network engineer is troubleshooting connectivity issues wi...
- 質問2 Refer to the Exhibit. (Exhibit) Which statement about the co...
- 質問3 Which statement about the split-horizon rule for distance ve...
- 質問4 By default, which statement is correct regarding the redistr...
- 質問5 Which two protocols are required for DMVPN? (Choose two.)...
- 質問6 What is the default OSPF hello interval on a Frame Relay poi...
- 質問7 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) After configuring the rotes,...
- 質問8 A network administrator is troubleshooting a redistribution ...
- 質問9 Which statement is true about IPv6? Choose the best response...
- 質問10 Which NetFlow component is applied to an interface and colle...
- 質問11 Which SNMP security level is available across all versions o...
- 質問12 Which two statements about VRRP object tracking are true? (C...
- 質問13 Which statement about stateless and stateful IPv6 autoconfig...
- 質問14 Which two statement about GRE tunnel interface are true? (Ch...
- 質問15 Which option is the best for protecting CPU utilization on a...
- 質問16 An IPv6 overlay tunnel is required to communicate with isola...
- 質問17 Refer to the exhibit. Which interoperability technique imple...
- 質問18 How can you mitigate fragmentation issues between endpoints ...
- 質問19 A network engineer executes the show ip cache flow command. ...
- 質問20 Refer to the exhibit. You notice that traffic from R1 to the...
- 質問21 Which three characteristics are shared by subinterfaces and ...
- 質問22 A customer asks its service provider for VPN support IPv4 an...
- 質問23 Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output from the show comm...
- 質問24 Which two methods of deployment can you use when implementin...
- 質問25 Which type of handshake does CHAP authentication use to esta...
- 質問26 Which traffic does the following configuration allow? Ipv6 a...
- 質問27 A router with an interface that is configured with ipv6 addr...
- 質問28 What is the minimum level that displays a log message when a...
- 質問29 Frame Relay LMI autosense. Which statements are true? (Choos...
- 質問30 Which IPv6 address type is seen as the next-hop address in t...
- 質問31 Which two options are requirements for EIGRP authentication?...
- 質問32 A network engineer configured an IOS router to send syslog m...
- 質問33 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which one statement is true?...
- 質問34 Users were moved from the local DHCP server to the remote co...
- 質問35 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) How would you confirm on R1 ...
- 質問36 (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer has confi...
- 質問37 Which command denies the default route?...
- 質問38 Which IP SLA deployment cycle reduces the deployment time fo...
- 質問39 Which authentication methods are EIGRP uses?...
- 質問40 A policy needs to be implemented on Router B so that any tra...
- 質問41 Which two statements about EVN are true? (Choose two.)...
- 質問42 Which option describes why the EIGRP neighbors of this route...
- 質問43 Which two LSA types were introduced to support OSPF for IPv6...
- 質問44 Which two debug commands can you use to view issues with CHA...
- 質問45 Which two statements about NHRP in a DMVPN environment are t...
- 質問46 Which routing protocol does DMVPN support? (Choose three.)...
- 質問47 To configure 6to4 on a dual-stack edge router. Which three o...
- 質問48 Which option is one way to mitigate symmetric routing on an ...
- 質問49 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) A network administrator chec...
- 質問50 Case study. (Exhibit) Some notices from above configuration:...
- 質問51 To enable BGP tunneling over an IPv4 backbone, the IPv4 addr...
- 質問52 What are 2 protocols used for user with authentication on ne...
- 質問53 A network administrator is troubleshooting a DMVPN setup bet...
- 質問54 What does the command show ip vrf purple TOPOLOGY shows?...
- 質問55 Which option is a prerequisite for stateful NAT64?...
- 質問56 Which values identifies VPNs in an EVN environment?...
- 質問57 Which statement about local policy routing is true?...
- 質問58 Which command do you enter to display log messages with a ti...
- 質問59 Which keyword of the aaa authentication ppp command supports...
- 質問60 Which command must be globally enabled on a Cisco router to ...
- 質問61 What is the administrative distance for EBGP?...
- 質問62 Which LSA type on OSPFv3 is used for link-local updates?...
- 質問63 Which two functionalities are specific to stateless NAT64? (...
- 質問64 Which two statements about AAA with the local database are t...
- 質問65 What is the viable successor of NAT_PT?...
- 質問66 On which two types of interface is Frame Relay switching sup...
- 質問67 What are three key concepts that apply when configuring the ...
- 質問68 Refer to the exhibit. configure terminal ip flow-export dest...
- 質問69 Which two packet types can an EIGRP router send when a route...
- 質問70 (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. Which effect of this configu...
- 質問71 Instructions: - Enter IOS commands on the device to verify n...
- 質問72 Which three configuration parameters can a DHCPV6 pool conta...
- 質問73 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which two statements are cor...
- 質問74 What does the following access list, which is applied on the...
- 質問75 In a comparison of an IPv4 header with an IPv6 header, which...
- 質問76 Refer to the exhibit. Which statement about the command outp...
- 質問77 What from the following can cause an issue for uRPF?...
- 質問78 Which problem can be caused by latency on a UDP stream?...
- 質問79 What does the following access list, which is applied on the...
- 質問80 Which two technologies can encapsulate an IPv6 payload in an...
- 質問81 Refer to Exhibit. (Exhibit) Which two reasons for IP SLA tra...
- 質問82 Which three functionalities are specific to stateful NAT64? ...
- 質問83 Which criterion does BGP evaluate first when determining the...
- 質問84 Which two BGP neighbor states are valid? (Choose two.)...
- 質問85 Which PPP authentication method sends authentication informa...
- 質問86 Refer to exhibit. What is indicated by the show ip cef comma...
- 質問87 Router E is configured with the EIGRP variance 2 command. (E...
- 質問88 PPPoE requires certain signals and information to establish,...
- 質問89 The OSPF database of a router shows LSA types 1, 2, 3, and 7...
- 質問90 Refer to the exhibit. Will redistributed RIP routes from OSP...
- 質問91 Which two commands do you need to implement on the CALLING r...
- 質問92 (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. Which networking challenge i...
- 質問93 Consider this scenario. TCP traffic is blocked on port 547 b...
- 質問94 Which value determines the amount of traffic that a network ...
- 質問95 A network engineer wants an NTP client to be able to update ...
- 質問96 Which routing protocol routers traffic through the best path...
- 質問97 NPTv6 restrictions? (Choose all that apply.)...
- 質問98 What happens when two EIGRP peers have mismatched K values?...
- 質問99 Which IPV6 address type does RIPng use for next-hop addresse...
- 質問100 The company network is in the process of migrating the IP ad...
- 質問101 If routers in a single area are configured with the same pri...
- 質問102 Refer to the exhibit. Which BGP attribute can be used to inf...
- 質問103 Which two among the following are used to indicate external ...
- 質問104 Which condition can cause unicast reverse path forwarding to...
- 質問105 Which protocol is used in a DMVPN network to map physical IP...
- 質問106 What is supported RADIUS server? (Choose two)...
- 質問107 Ipv6 has just been deployed to all of the hosts within a net...
- 質問108 Refer to the exhibit. Why is the 140.140.0.0 network not use...
- 質問109 Which three statements about IPv6 EIGRP are true? (Choose th...
- 質問110 (Exhibit) Which interoperability technique implemented on th...
- 質問111 Which of the following NSAP addresses is a private, locally ...
- 質問112 A network administrator recently redistributed RIP routes in...
- 質問113 Refer to the exhibit. Based upon the configuration, you need...
- 質問114 What command would you use to set EIGRP routes to be priorit...
- 質問115 Prior to enabling PPPoE in a virtual private dialup network ...
- 質問116 You need the IP address of the devices with which the router...
- 質問117 Scenario You have been asked to evaluate an OSPF network set...
- 質問118 Which feature eliminates the need for Cisco Express Forwardi...
- 質問119 A network engineer wants to ensure an optimal end-to-end del...
- 質問120 Which the Valid range for BGP private ASNs?...
- 質問121 Study this exhibit below carefully. (Exhibit) What is the ef...
- 質問122 What are the default timers for RIPng?...
- 質問123 Which IOS commands can you use to limit the CPU impact of lo...
- 質問124 Refer to the exhibit. Which three statements accurately desc...
- 質問125 When policy-based routing (PBR) is being configured, which t...
- 質問126 Which command is needed to get the ip address assigned from ...
- 質問127 Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP is configured on all routers in ...
- 質問128 Which three statements about SNMP are true? (Choose three.)...
- 質問129 Refer to the exhibit. Which two effects of this configuratio...
- 質問130 Which next hop is going to be used for 172.17.1.0/24 ? (Exhi...
- 質問131 Which SNMP verification command shows the encryption and aut...
- 質問132 Which statement about dual stack is true?...
- 質問133 Which two statements about EVN are true? (Choose two.)...
- 質問134 Which IPv4-mapped IPv6 address is equivalent to IPv6 address...
- 質問135 Which routing protocol will continue to receive and process ...
- 質問136 Refer to the exhibit. After configuring GRE between two rout...
- 質問137 (Exhibit) The configuration of R1 to R6 are posted below for...
- 質問138 What is EIGRP Summary Route Administrative Distance?...
- 質問139 (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. Based on Cisco best practice...
- 質問140 What following parameters for the EIGRP authentication need ...
- 質問141 In SNMP v3, which security level provides encryption of the ...
- 質問142 Which feature is supported with the PPPoE client?...
- 質問143 Which protocol can you use to remotely install an IOS on a C...
- 質問144 A network engineer wants to verify the status of a recently ...
- 質問145 Which three items can you track when you use two time stamps...
- 質問146 Refer to the exhibit. The network setup is running the RIP r...
- 質問147 Which two protocols are used to deploy a single Hub-DMVPN su...
- 質問148 What is true about EIGRP's redistributed static routes and s...
- 質問149 Technologies used in preparing Service Provider IPv6? (Choos...
- 質問150 Redistributing BGP into OSPF what statement is correct? rout...
- 質問151 What happens when a router receives a packet with a TTL of 0...
- 質問152 When ospf is forming an adjacency, in which state does the a...
- 質問153 Which three methods can a network engineer use to fix a metr...
- 質問154 Which task must you perform to enable a point-to-point Frame...
- 質問155 Which three causes of unicast flooding are true? (Choose thr...
- 質問156 Which command creates a manual summary on an interface when ...
- 質問157 How does an EVN provide end-to-end virtualization and separa...
- 質問158 A network engineer wants to baseline the network to determin...
- 質問159 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) How can you change this conf...
- 質問160 IP CEF load-sharing options (Choose three.)...
- 質問161 Windows Server Syslog blocked by ACL and....?...
- 質問162 A company has their headquarters located in a large city wit...
- 質問163 Which two OSPF router types can perform summarization in an ...
- 質問164 What is the default authentication in RIPv2 when authenticat...
- 質問165 Which Cisco Express Forwarding components maintains Layer 2 ...
- 質問166 Which of the following are features of Netflow version 9?...
- 質問167 Which command will display all the EIGRP feasible successor ...
- 質問168 How to set up IP SLA to monitor Bandwidth between the certai...
- 質問169 Refer to the exhibit. Which effect of this configuration is ...
- 質問170 Which two commands must you configure in the calling router ...
- 質問171 What is a valid ipv6 multicast address?...
- 質問172 Which two statements indicate a valid association mode for N...
- 質問173 Which action can you take to mitigate unicast flooding in a ...
- 質問174 After testing various dynamic IPv6 address assignment method...
- 質問175 Which type of traffic does DHCP snooping drop?...
- 質問176 Device R1 has 1 Gigabit and 10 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. ...
- 質問177 An engineer is asked to monitor the availability of the next...
- 質問178 Which set of actions does a network engineer perform to set ...
- 質問179 Using the rules for IPv6 addressing, how can the address 203...
- 質問180 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) If this configuration is app...
- 質問181 What happens when a router receives a route with an administ...
- 質問182 Which option is the minimum privilege level that allows the ...
- 質問183 Which two statements about EVNs are true? (Choose two.)...
- 質問184 Which three statements about configuring OSPF in a IPv6 netw...
- 質問185 Which value does a point-to-point GRE tunnel use to identity...
- 質問186 A user is having issues accessing file shares on a network. ...
- 質問187 (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is workin...
- 質問188 What attribute is used to influce traffic form AS200 and AS3...
- 質問189 Your Company trainee asks you, in the context of IPv6 and OS...
- 質問190 (Exhibit) A network engineer is working on the network topol...
- 質問191 Refer to the exhibit. In the network diagram, Area 1 is defi...
- 質問192 What type of IPv6 packet will indicate traffic from single h...
- 質問193 Which two statements about password-protecting device access...
- 質問194 Which adverse circumstance can the TTL feature prevent?...
- 質問195 Which three statements are true when configuring redistribut...
- 質問196 Scenario You have been asked to evaluate an OSPF network set...
- 質問197 A network engineer is disabling split horizon on a point-to-...
- 質問198 What is a key benefit of using a GRE tunnel to provide conne...
- 質問199 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Why is the default route not...
- 質問200 Which of the following is a GRE Tunnel characteristic?...
- 質問201 Which command enables NAT-PT on an IPv6 interface?...
- 質問202 Refer to exhibit. A user calls from another branch office wi...
- 質問203 What is the maximum number of hops on a router that RIPng ad...
- 質問204 A route map was configured and it was distributing OSPF exte...
- 質問205 When a packet is denied by an IPv6 traffic filter, which add...
- 質問206 Router R1, a branch router, connects to the Internet using D...
- 質問207 Which two routers can do OSPF route summarization? (Choose t...
- 質問208 Which two statements are benefits of BGP peer groups? (Choos...
- 質問209 What is show on logging console 7?...
- 質問210 Which two features does RADIUS combine? (Choose two.)...
- 質問211 Which alerts will be seen on the console when running the co...
- 質問212 Which two statements about route targets that are configured...
- 質問213 OSPF chooses routes in which order, regardless of route's ad...
- 質問214 The Dev-1 and Dev-3 routers are OSPF neighbors over the Ethe...
- 質問215 Which mode of uRPF causes a router interface to accept a pac...
- 質問216 Refer to the exhibit. Which effect of this configuration is ...
- 質問217 What is VRF-Lite?
- 質問218 How does R1 handle the route to network 10.1.80.0.0/24? (Exh...
- 質問219 When unicast reverse path forwarding is configured on an int...
- 質問220 Which statement describes the difference between a manually ...
- 質問221 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) For which reason is EIGRP fa...
- 質問222 Which configuration is applied to a device so that it blocks...
- 質問223 A network engineer has configured a tracking object to monit...
- 質問224 Which location within the network is preferred when using a ...
- 質問225 What appears in the other router routing table? #loopback EI...
- 質問226 What is a function of NPTv6?
- 質問227 A network engineer executes the show ip sla statistics comma...
- 質問228 Which method allows IPv4 and IPv6 to work together without r...
- 質問229 What are the three modes of Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding?...
- 質問230 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) An engineer is enabling VPN ...
- 質問231 Which LAN feature enables a default gateway to inform its en...
- 質問232 What configurations does PPPoE allow? (Choose two.)...
- 質問233 Which IPv6 address correctly compresses the IPv6 unicast add...
- 質問234 What is the purpose of the route-target command?...
- 質問235 Which option to the command service timestamps debug enables...
- 質問236 OSPF routers that communicate with other network routers lik...
- 質問237 Choose the best IP SLA deployment cycle that reduce deployme...
- 質問238 When the tunnel interface is configured in default mode, whi...
- 質問239 If you configure one router in your network with the auto-co...
- 質問240 Which three TCP enhancements can be used with TCP selective ...
- 質問241 A router is configured for redistribution to advertise EIGRP...
- 質問242 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) A network engineer is modify...
- 質問243 A network engineer is configuring a routed interface to forw...
- 質問244 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which statement about the co...
- 質問245 The following configuration is applied to a router at a bran...
- 質問246 (Exhibit) How many times was SPF alrogithm executed on R4 fo...
- 質問247 Which two reductions are the correct reductions if the IPv6 ...
- 質問248 Which address is an IPv6 multicast address?...
- 質問249 For a GRE tunnel to be up between two routers, which of the ...
- 質問250 What are two important differences between OSPFv2 and OSPFv3...
- 質問251 Which CLI command can you enter to permit or deny IPv6 traff...
- 質問252 Which algorithm is used by EIGRP to determine the best path ...
- 質問253 An engineer executes the ip flow ingress command in interfac...
- 質問254 Which command do you enter on router R6 so that BGP supports...
- 質問255 Which two address types are included in NAT? (Choose two.)...
- 質問256 During a recent OSPF election among three routers, RTA was e...
- 質問257 Which two types of authentication does EIGRP offer? (Choose ...
- 質問258 Which two statements about 6to4 tunneling are accurate? (Cho...
- 質問259 Which two statements about NetFlow templates are true? (Choo...
- 質問260 Which Cisco Express Forwarding table or tables hold forwardi...
- 質問261 Which statement best describes the following two OSPF comman...
- 質問262 In a point-to-multipoint Frame Relay topology, which two met...
- 質問263 Which two GRE features can you configure to prevent fragment...
- 質問264 What command can you enter to configure an enable password t...
- 質問265 Which command instruct a PPPoE client to obtain its IP addre...
- 質問266 Refer to the exhibit. A new TAC engineer came to you for adv...
- 質問267 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which statement about this n...
- 質問268 Which feature can mitigate fragmentation issues within netwo...
- 質問269 Which two types of threshold can you configure for tracking ...
- 質問270 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which option prevents routin...
- 質問271 IP SLA network with a configuration snippet...
- 質問272 Which two commands must you configure on a DMVPN hub to enab...
- 質問273 Which option is one way to mitigate asymmetric routing on an...
- 質問274 An EUl-64 bit address is formed by inserting which 16-bit va...
- 質問275 Which two EIGRP metrics have nonzero K values by default? (C...
- 質問276 For security purposes, an Ipv6 traffic filter was configured...
- 質問277 Which two options for authenticating a user who is attemptin...
- 質問278 Which SNMP model and level can provide DES encryption?...
- 質問279 Which two authentication protocols does PPP support? (Choose...
- 質問280 Which of the following are characteristics of TACACS+? (Choo...
- 質問281 What do we prioritize with LLQ?...
- 質問282 If you want to migrate an IS-IS network to another routing p...
- 質問283 Which Cisco VPN technology uses AAA to implement group polic...
- 質問284 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Network users on the 10.1.2....
- 質問285 Refer to the exhibit. Which statement about the configuratio...
- 質問286 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which command is used to con...
- 質問287 A company is deploying a multicast application that must be ...
- 質問288 A network engineer configures two connected routers to run O...
- 質問289 Which STP feature can reduce TCNs on ports that are connecte...
- 質問290 Which two protocols can be affected by MPP? (Choose two.)...
- 質問291 Which functions are included in the two-message rapid exchan...
- 質問292 Which two configurations can a PPPoE client support? (Choose...
- 質問293 Which condition prevents the establishment of a DMVPN tunnel...
- 質問294 A network engineer initiates the ip sla responder tcp-connec...
- 質問295 If you run the command auto-cost reference-bandwidth 10000 o...
- 質問296 (Exhibit) A senior network engineer tries to propagate a sum...
- 質問297 Which Cisco IOS VPN technology leverages Ipsec, mGRE, dynami...
- 質問298 A Network engineer wants to configure logging to compile and...
- 質問299 (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer is troubl...
- 質問300 A network engineer is notified that several employees are ex...
- 質問301 You are configuring a Microsoft client to call a PPP server ...
- 質問302 In IPv6, the interfaces running OSPF can be configured with ...
- 質問303 A network engineer is configuring a solution to allow failov...
- 質問304 Refer to the exhibit. What two statements are true? (Choose ...
- 質問305 In which two areas does OSPF send a summary route by default...
- 質問306 Observe the exhibit. (Exhibit) If the command variance 3 wer...
- 質問307 Which Netflow version supports MPLS?...
- 質問308 A network engineer is trying to modify an existing active NA...
- 質問309 Which location is traffic from IP SLAs?...
- 質問310 What are three reasons to control routing updates via route ...
- 質問311 The Neighbor Discovery Protocol in ipv6 is replaced with whi...
- 質問312 When a new PC is connected to the network, which step must i...
- 質問313 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which two statements are tru...
- 質問314 Which two statements about AAA implementation in a Cisco rou...
- 質問315 Which two statements are true about 6to4 tunnels? (Choose tw...
- 質問316 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) A network engineer receives ...
- 質問317 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) After configuring the rotes,...
- 質問318 A network administrator notices that the BGP state and logs ...
- 質問319 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) The excerpt was taken from t...
- 質問320 Which statement describes what this command accomplishes whe...
- 質問321 Which command should be added to RTB under router bgp 100 to...
- 質問322 Which two statements about GRE tunnel interfaces are true? (...
- 質問323 Which IP SLA operation requires Cisco endpoints?...
- 質問324 Which two tasks must you perform when you install SSH on a C...
- 質問325 Which two OSPF area types filter type 4 and type 5 LSAs? (Ch...
- 質問326 Which condition must be met before two EVN devices can conne...
- 質問327 Which protocol does VRF-Lite support?...
- 質問328 Where the output will be shown of the command debug conditio...
- 質問329 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which statement about redist...
- 質問330 A network engineer recently deployed Easy Virtual Networking...
- 質問331 A network engineer wants to implement an SNMP notification p...
- 質問332 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Based on this FIB table, whi...
- 質問333 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) R1 is configured with VRF-Li...
- 質問334 What is the reasons of command: router(config)# snmp-server ...
- 質問335 When a tunnel interface is configured in the default mode, w...
- 質問336 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which option represents the ...
- 質問337 Which two tasks does a DHCP relay agent perform? (Choose two...
- 質問338 What number is a valid representation for the 200F:0000:AB00...
- 質問339 Into which two types of areas would an area border router (A...
- 質問340 (Exhibit) Refer to exhibit. A network engineer is unable to ...
- 質問341 What are the four main steps in configuring a GRE tunnel ove...
- 質問342 You get a call from a network administrator who tells you th...
- 質問343 Which two statements about OSPF E1 routes are true? (Choose ...
- 質問344 Congestion in the network. What is the effect on UDP?...
- 質問345 Which two tasks must you perform to configure a BGP peer gro...
- 質問346 (Exhibit) The configuration of R1 to R6 are posted below for...
- 質問347 Which Technology supports overlapping IP address on a single...
- 質問348 An administrator types in the command router ospf 1 and rece...
- 質問349 To enable policy-based routing, which function specifies the...
- 質問350 Which statement about the NPTv6 protocol is true?...
- 質問351 Using new backup router in spite of faulty one in ospf domai...
- 質問352 How does an IOS router process a packet that should be switc...
- 質問353 (Exhibit) Based on the configuration information shown above...
- 質問354 Which two statements about NTP operation are true? (Choose t...
- 質問355 Which value does a Cisco router use as its default username ...
- 質問356 Which statement is true?
- 質問357 Your company uses Voice over IP (VoIP). The system sends UDP...
- 質問358 The following exhibit shows ipv6 route output. What would th...
- 質問359 A network access server using TACACS+ for AAA operations rec...
- 質問360 Which statement is true about an IPsec/GRE tunnel?...
- 質問361 What is the effect of the following two commands? (Choose tw...
- 質問362 What is the minimum privilege level to enter all commands in...
- 質問363 Where can NetFlow export data for long term storage and anal...
- 質問364 A router receives a routing advertisement for the same prefi...
- 質問365 A network engineer executes the commands logging host 172.16...
- 質問366 Which two options can you use to configure an EIGRP stub rou...
- 質問367 The network engineer types the follow commands in a router: ...
- 質問368 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) After configuring the routes...
- 質問369 A network engineer notices that transmission rates of sender...
- 質問370 Which address is used by the Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding...
- 質問371 Refer to the exhibit. Which command would verify if PBR reac...
- 質問372 Which two statements about NTP stratum are true? (Choose two...
- 質問373 Which statement about the use of tunneling to migrate to IPv...
- 質問374 What are two limitations when in use of NPTv6 for IPV6 vs IP...
- 質問375 Which three protocols are supported with EVN? (Choose three....
- 質問376 Which three steps are most helpful in verifying proper route...
- 質問377 Which technology is required on an EVN trunk interface?...
- 質問378 Which two features are provided by EIGRP for IPv6? (Choose t...
- 質問379 A customer requests policy-based routing. Packets arriving f...
- 質問380 Which technology does Easy Virtual Network use?...
- 質問381 A network engineer wants to notify a manager in the event th...
- 質問382 Which two statements about VRF-Lite configurations are true?...
- 質問383 What show command is used here? TCB Local Address Foreign Ad...
- 質問384 Which type of IPv6 address is an identifier for a single int...
- 質問385 Your network consists of a large hub-and-spoke Frame Relay n...
- 質問386 Which are new LSA types in OSPF for IPv6 (OSPFv3)? (Choose t...
- 質問387 OSPF chooses routes in which order, regardless of route's ad...
- 質問388 A network engineer is configuring two dedicated Internet con...
- 質問389 A network engineer needs to verify IP SLA operations on an i...
- 質問390 Which BGP option is required when load sharing over multiple...
- 質問391 Which NAT Command do you enter to disable dynamic ARP learni...
- 質問392 A network engineer is asked to create an SNMP-enabled proact...
- 質問393 A corporate policy requires PPPoE to be enabled and to maint...
- 質問394 Which two causes of latency are true? (Choose two.)...
- 質問395 A network engineer executes the show ip flow interface comma...
- 質問396 Which two statements about NetFlow version 9 are true? (Choo...
- 質問397 What is true about peer groups? (Choose two.)...
- 質問398 Which statement is true about the command ipv6 ospf 1 area 0...
- 質問399 (Exhibit) What is the correct configuration to enable router...
- 質問400 Which two effects of asymmetric routing are true? (Choose tw...
- 質問401 When implementing OSPFv3, which statement describes the conf...
- 質問402 To configure SNMPv3 implementation, a network engineer is us...
- 質問403 What are three IPv6 transition mechanisms? (Choose three)...
- 質問404 A network administrator is attempting to configure IP SLA to...
- 質問405 Refer to the following: Logging Console 7 Which option is on...
- 質問406 (Exhibit) Which of the following is true?...
- 質問407 A company's corporate policy has been updated to require tha...
- 質問408 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which technology can be empl...
- 質問409 A network administrator uses GRE over IPSec to connect two b...
- 質問410 Which type of address does OSPFv3 use to form neighbor adjac...
- 質問411 You have a router that has some interfaces configured with 1...
- 質問412 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) On the basis of the partial ...
- 質問413 You want to configure a device to select an OSPF-learned rou...
- 質問414 The Neighbor Discovery Protocol in IPv6 replaces which proto...
- 質問415 What would you configure on SNMPv3 to allow authentication a...
- 質問416 Other than a working EIGRP configuration, which option must ...
- 質問417 Which technology uses the many-to-one method of mapping IP a...
- 質問418 Which item does EIGRP IPv6 require before it can start runni...
- 質問419 You are configuring a static route. Which action must you ta...
- 質問420 (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. All interfaces on each route...
- 質問421 Which keyword of the aaa authentication ppp command applies ...
- 質問422 Under which circumstance will a branch ISR router contain in...
- 質問423 When does a Cisco router send an ICMP redirect?...
- 質問424 Which two statements about configuring Frame Relay point-to-...
- 質問425 Refer to the exhibit. The command is executed while configur...
- 質問426 Refer to the exhibit. Which option prevents routing updates ...
- 質問427 Which two statements about PAP and CHAP authentication are t...
- 質問428 Which protocols support DMVPN?
- 質問429 How should a router that is being used in a Frame Relay netw...
- 質問430 What is the function of the snmp-server manager command?...
- 質問431 Which two statements about DMVPN are true? (Choose two.)...
- 質問432 Scenario You have been asked to evaluate an OSPF network set...
- 質問433 Which functionality is required within an IP router that is ...
- 質問434 Which two options are components of a dual stack? (Choose tw...
- 質問435 In which two ways can split horizon issues be overcome in a ...
- 質問436 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) Which statement is correct r...
- 質問437 Refer to the exhibit. Router 1 cannot ping router 2 via the ...
- 質問438 Which statement is true about 6to4 tunneling?...
- 質問439 An administrator needs to setup an NTP client to provide upd...
- 質問440 Based on the configuration command below, which statement is...
- 質問441 Scenario You have been asked to evaluate how EIGRP is functi...
- 質問442 What does the show ip route vrf CISCO command display?...
- 質問443 Refer to the exhibit. Which three NTP features can be deduce...
- 質問444 Which access list used to filter upper layer protocol?...
- 質問445 When an IPv6 enabled host boots, it sends a router solicitat...
- 質問446 What command allows permit or deny IPv6 traffic?...
- 質問447 Which Cisco VPN technology can use multipoint tunnel, result...
- 質問448 A network engineer executes the show ip flow export command....
- 質問449 Which three problems result from application mixing of UDP a...
- 質問450 Refer to the exhibit. You want router r1 to perform unequal-...
- 質問451 Which command do you enter to filter only routing updates th...
- 質問452 Which feature can filter information at the interface level?...
- 質問453 Which DSL encapsulation method requires client software runn...
- 質問454 Which feature is an invalid redistribute command option for ...
- 質問455 If the total bandwidth is 64 kbps and the RTT is 3 seconds, ...
- 質問456 Which three benefits does the Cisco Easy Virtual Network pro...
- 質問457 Which two commands do you need to implement on a router to s...
- 質問458 Refer to the exhibit. When summarizing these routes, which r...
- 質問459 What two situations could require the use of multiple routin...
- 質問460 What is the NHRP role in DMVPN? (Choose two.)...
- 質問461 Which three functionalities are specific to stateful NAT64? ...
- 質問462 Refer to the exhibit. The DHCP client is unable to receive a...
- 質問463 RIPng ____________.
- 質問464 Which outbound access list, applied to the WAN interface of ...
- 質問465 (Exhibit) Refer to the exhibit. Which statement describes th...
- 質問466 What is the default value of TCP maximum segment size?...
- 質問467 Which purpose of the AAA accounting feature is true when you...
- 質問468 The Cisco SA 500 Series Security Appliances are built specif...
- 質問469 Various employees in the same department report to the netwo...
- 質問470 Which two statements are true of the OSPF link-state routing...
- 質問471 How is authentication handled with OSPFv3? Select the best r...
- 質問472 Which type of message does a device configured with the eigr...
- 質問473 Refer to the exhibit. (Exhibit) R1 and R2 belong to the RIP ...
- 質問474 Which IP SLA operation can be used to measure round-trip del...
- 質問475 (Exhibit) The configuration of R1 to R6 are posted below for...
- 質問476 A router was configured with the eigrp stub command. The rou...
- 質問477 Which statement about NTP authentication is true?...

