- ホーム
- Oracle
- 1z0-061-JPN - Oracle Database 12c: SQL Fundamentals (1z0-061日本語版)
- Oracle.1z0-061-JPN.v2020-05-25.q118
- 質問80
有効的な1z0-061-JPN問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、1z0-061-JPN試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新1z0-061-JPN試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com 1z0-061-JPN試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここで1z0-061-JPN問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
1z0-061-JPN問題集最新版のアクセス
「340問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
展示を表示し、CUSTOMERSテーブルの構造を調べます。
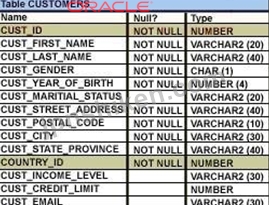
1つのステートメントでサブクエリまたは結合を実行する必要がある2つのタスクはどれですか。
(2つ選択してください。)

1つのステートメントでサブクエリまたは結合を実行する必要がある2つのタスクはどれですか。
(2つ選択してください。)
正解:D,E
Describe the Types of Problems That the Subqueries Can Solve
There are many situations where you will need the result of one query as the input for another.
Use of a Subquery Result Set for Comparison Purposes
Which employees have a salary that is less than the average salary? This could be answered by two statements, or by a single statement with a subquery. The following example uses two statements:
select avg(salary) from employees;
select last_name from employees where salary < result_of_previous_query ; Alternatively, this example uses one statement with a subquery:
select last_name from employees where salary < (select avg(salary)from employees); In this example, the subquery is used to substitute a value into the WHERE clause of the parent query: it is returning a single value, used for comparison with the rows retrieved by the parent query.
The subquery could return a set of rows. For example, you could use the following to find all departments that do actually have one or more employees assigned to them:
select department_name from departments where department_id in
(select distinct(department_id) from employees);
There are many situations where you will need the result of one query as the input for another.
Use of a Subquery Result Set for Comparison Purposes
Which employees have a salary that is less than the average salary? This could be answered by two statements, or by a single statement with a subquery. The following example uses two statements:
select avg(salary) from employees;
select last_name from employees where salary < result_of_previous_query ; Alternatively, this example uses one statement with a subquery:
select last_name from employees where salary < (select avg(salary)from employees); In this example, the subquery is used to substitute a value into the WHERE clause of the parent query: it is returning a single value, used for comparison with the rows retrieved by the parent query.
The subquery could return a set of rows. For example, you could use the following to find all departments that do actually have one or more employees assigned to them:
select department_name from departments where department_id in
(select distinct(department_id) from employees);
- 質問一覧「118問」
- 質問1 トランザクションを終了させる3つのステートメント/コマンドはど...
- 質問2 サブクエリに関して正しいものはどれですか。
- 質問3 テーブル結合のUSING句に関して正しいのは、次の2つのステートメ...
- 質問4 2007年1月1日から日付までの日数を計算する必要があります。日付...
- 質問5 展示を表示し、PROMOTIONSテーブルの構造を調べます。次のSQLス...
- 質問6 トランザクションテーブルに提案された構造を調べます。 (Exhibi...
- 質問7 テーブルを作成するときのデフォルトの動作はどれですか?
- 質問8 データ操作言語ステートメント_____。
- 質問9 Oracleデータベースに組み込まれているSQL関数を使用して、列に...
- 質問10 同義語に関して正しい説明はどれですか。
- 質問11 TRANSACTIONSテーブルに提案された構造を調べます。 (Exhibit) ...
- 質問12 シーケンスについて正しいことは何ですか?
- 質問13 INVOICEテーブルの構造を調べます。 示す: (Exhibit) どの2つの...
- 質問14 従業員と部門のデータ: 従業員 (Exhibit) 部門 (Exhibit) EMPLO...
- 質問15 トランザクションテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit) 正午ま...
- 質問16 単一行関数に関して正しい2つのステートメントはどれですか。 (...
- 質問17 シーケンスは次のように作成します。 1から始まるシーケンスseq1...
- 質問18 CUSTOMERSテーブルのCUSTOMER_NAME列が値を保持することを保証す...
- 質問19 次のCREATE SEQUENCEステートメントを評価します。 シーケンスの...
- 質問20 salesテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit) 次のcreate tableス...
- 質問21 すべての顧客の姓のリストと、顧客のテーブルから与信限度を生成
- 質問22 展示を表示し、製品と販売の表を調べます。 (Exhibit) 次のクエ...
- 質問23 サブクエリに関する正しい2つのステートメントはどれですか。 (...
- 質問24 EMPLOYEESテーブルには次の列があります。 苗字。 VARCHAR2(35...
- 質問25 PRIC E_LISTテーブルの構造とデータを調べます:Name Null?タイ...
- 質問26 ORDER BY句に関して正しいのは、次の2つのステートメントですか...
- 質問27 インラインビューを最もよく表しているのはどれですか。
- 質問28 展示を表示し、CUSTOMERSおよびSALESテーブルの構造を調べます。...
- 質問29 次の説明でORDERSテーブルを作成しました。 示す: (Exhibit) テ...
- 質問30 PromotionsテーブルのPROMO_BEGIN_DATE列のデータを調べます。 (...
- 質問31 見解に関して正しいものはどれですか? (3つ選択してください。...
- 質問32 展示を表示し、COSTSおよびPROMOTIONSテーブルの構造を調べます...
- 質問33 CustomersテーブルのCUST_NAME列のデータを調べます。 (Exhibit)...
- 質問34 このステートメントは失敗します: 従業員に一意のビットマップ
- 質問35 制約に関して正しい説明はどれですか。 (2つ選択してください。...
- 質問36 4つの列を含むORDERSという名前のテーブルを作成する必要があり...
- 質問37 どの2つのステートメントがトランザクションを完了しますか? (...
- 質問38 各顧客の与信限度が次のように増分されたレポートを作成する必要
- 質問39 展示を見て、ORDテーブルの構造を調べます。 示す: (Exhibit) ...
- 質問40 展示を表示し、PRODUCTSテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit) ...
- 質問41 展示を見る; PROMOTIONSテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit) ...
- 質問42 2001年3月19日を次のような形式で表示するSQLステートメント 「2...
- 質問43 iSQL * Plusコマンドとは
- 質問44 PRICE_LISTテーブルの構造とデータを調べます。 名前 。ヌル 。...
- 質問45 銀行アプリケーション用のテーブルを作成する必要があります。表
- 質問46 展示を表示して、プロモーションテーブルの構造を調べます。 次
- 質問47 次のクエリを調べます。 (Exhibit) このクエリの出力は何ですか...
- 質問48 CUST_TRANSテーブルの構造とデータを調べます。 (Exhibit) 日付...
- 質問49 サブクエリに関して正しいのはどの2つのステートメントですか? ...
- 質問50 翌月の最初の月曜日の日付を表示して、次のコマンドを発行します
- 質問51 次の列仕様とデータ型を使用して、salesテーブルを作成するとし...
- 質問52 DEPARTMENT_ID 30の従業員をHIRE_DATEの順に1行にリストする必要...
- 質問53 iSQL * Plusコマンドはどれですか? (該当するものをすべて選択...
- 質問54 SLSは、SH.SALESテーブルのプライベートシノニムです。 ユーザー...
- 質問55 制約に関して正しい説明はどれですか。 (2つ選択してください。...
- 質問56 NULL値を含む列でグループ関数を使用するとどうなりますか?
- 質問57 展示を表示し、プロモーションテーブルのPROMO_NAME列とPROMO_EN...
- 質問58 カウント関数に関して正しい2つのステートメントはどれですか。
- 質問59 リレーショナルデータベース(RDB)モデルとオブジェクト指向デ...
- 質問60 展示を表示し、CUSTOMERSテーブルの構造を調べます。 姓がA、B、...
- 質問61 CUSTOMERSテーブルには次の列があります。 CUSTOMER_ID列は、テ...
- 質問62 展示を表示して、PROMOTIONS、SALES、CUSTOMERテーブルの構造を...
- 質問63 CUSTJTRANSテーブルの構造とデータを調べます。 カストラン 名前...
- 質問64 展示を表示し、CUSTOMERSテーブルの構造を調べます。どのステー...
- 質問65 展示を表示し、PROMOTIONSテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit)...
- 質問66 セーブポイントに関して正しいものはどれですか? (2つ選択して...
- 質問67 2007年10月11日の日付を「10月11日、2000」と単語で表示する必要...
- 質問68 CUSTOMERSテーブルのCUST_NAME列のデータを調べます。 CUST_NAME...
- 質問69 展示を表示し、製品テーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit) produ...
- 質問70 どのテーブル作成ステートメントが有効ですか? (Exhibit)...
- 質問71 iSQL * Plusコマンドとは
- 質問72 展示を表示し、PROMOTIONSテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit)...
- 質問73 シンプルなビューではなく、複雑なビューの特徴的な特徴はどれで
- 質問74 展示を表示し、PROMOTIONSテーブルのPROMO_CATEGORY列とPROMO_CO...
- 質問75 SPARESテーブルのPART_CODE列には、次の値のリストが含まれてい...
- 質問76 トランザクションはどの3つの状況で完了しますか?
- 質問77 システム権限はどれですか?
- 質問78 展示を表示し、PROMOSTIONSテーブルの構造を調べます。 示す: (...
- 質問79 現在シンガポールに在住しており、シカゴのリモートデータベース
- 質問80 展示を表示し、CUSTOMERSテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit) ...
- 質問81 展示を表示し、CUSTOMERSテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit) ...
- 質問82 展示を表示して、customersテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit...
- 質問83 CUSTOMERSテーブルのデータを調べます。 (Exhibit) 顧客の詳細と...
- 質問84 展示を表示し、INVOICEテーブルの構造とデータを調べます。 (Exh...
- 質問85 あなたはABC.comでデータベース管理者として働いています。展示...
- 質問86 EMPLOYEESテーブルとNEW_EMPLOYEESテーブルの構造を調べます。 ...
- 質問87 EMPLOYEESテーブルとNEW_EMPLOYEESテーブルの構造を調べます。 (...
- 質問88 展示を表示し、PROMOTIONSテーブルの構造を調べます。 示す: (E...
- 質問89 MARKSテーブルの構造を調べます。 示す: (Exhibit) どの2つのス...
- 質問90 インデックスに関して正しい2つのステートメントはどれですか。 ...
- 質問91 展示を表示し、CUSTOMERSテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit) ...
- 質問92 展示を表示して、EMPLOYEESテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit...
- 質問93 次のSQLステートメントを評価します。 (Exhibit) サブクエリによ...
- 質問94 展示を表示し、ORDERSテーブルとCUSTOMERSテーブルの構造を調べ...
- 質問95 サブクエリを使用できる4つの句はどれですか。 (4つ選択してく...
- 質問96 展示を表示し、製品テーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit) 次の...
- 質問97 制約に関して正しい説明はどれですか。 (2つ選択してください。...
- 質問98 あなたはABC.comでデータベース管理者として働いています。あな...
- 質問99 列のUNIQUE制約にはインデックスが必要です。 次のうち正しいシ...
- 質問100 学生と教員のテーブルの構造については、別紙をご覧ください。 (...
- 質問101 2007年1月1日から日付までの日数を計算する必要があります。 日...
- 質問102 サブクエリに関して正しい説明はどれですか。
- 質問103 展示を表示し、PRODUCTSテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit) ...
- 質問104 次のクエリを評価します。 SQL> SELECT TRUNC(ROUND(156.00...
- 質問105 取引に関して正しい説明はどれですか。 (該当するものをすべて
- 質問106 サブクエリに関して正しいことは何ですか?
- 質問107 AMOUNT_SOLDが最も低い製品のsalesテーブルの行の5%を表示し、...
- 質問108 次のSQLステートメントを評価します。 示す: (Exhibit) 上記の...
- 質問109 値1890.55を$ 1、890.55と表示するSQLステートメントはどれです...
- 質問110 展示を表示し、CUSTOMERSテーブルの説明を調べます。 (Exhibit) ...
- 質問111 SHIPMENTSテーブルの構造を調べます。 (Exhibit) SHIPMENT_DATE...
- 質問112 次のクエリを発行します。 SQL> SELECT AVG(MAX(qty)) FR...
- 質問113 どの2つの場合に外部結合を使用しますか? (2つ選択してくださ...
- 質問114 有効なCREATE [TABLEステートメントはどれですか?
- 質問115 次の関係のタイプと例を調べます。 1。 1対1 a)生徒への教師 ...
- 質問116 展示を表示して、製品の構造と販売テーブルを調べます。 (Exhibi...
- 質問117 CREATE VIEW特権が付与されます。これによって何ができるように...
- 質問118 テーブルに関して正しいものはどれですか? (2つ選択してくださ...

