- ホーム
- Microsoft
- DP-300J - Administering Relational Databases on Microsoft Azure (DP-300日本語版)
- Microsoft.DP-300J.v2024-04-26.q135
- 質問123
有効的なDP-300J問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、DP-300J試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新DP-300J試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com DP-300J試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここでDP-300J問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
DP-300J問題集最新版のアクセス
「464問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
Azure Data Lake StorageGen2コンテナがあります。
データはコンテナに取り込まれ、データ統合アプリケーションによって変換されます。その後、データは変更されません。ユーザーはコンテナー内のファイルを読み取ることはできますが、ファイルを変更することはできません。
次の要件を満たすデータアーカイブソリューションを設計する必要があります。
新しいデータは頻繁にアクセスされるため、できるだけ早く利用できるようにする必要があります。
5年以上経過したデータへのアクセスはまれですが、要求された場合は1秒以内に利用可能である必要があります。
7年以上経過したデータにはアクセスしません。 7年後、データは可能な限り低いコストで永続化する必要があります。
必要な可用性を維持しながら、コストを最小限に抑える必要があります。
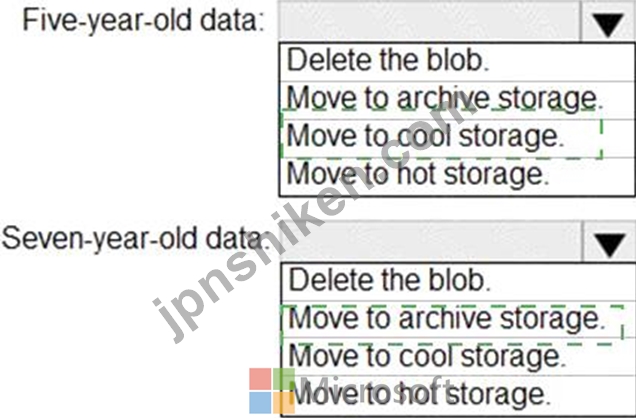
データをどのように管理する必要がありますか?回答するには、回答領域で適切なオプションを選択します。
注:正しい選択はそれぞれ1ポイントの価値があります。

データはコンテナに取り込まれ、データ統合アプリケーションによって変換されます。その後、データは変更されません。ユーザーはコンテナー内のファイルを読み取ることはできますが、ファイルを変更することはできません。
次の要件を満たすデータアーカイブソリューションを設計する必要があります。
新しいデータは頻繁にアクセスされるため、できるだけ早く利用できるようにする必要があります。
5年以上経過したデータへのアクセスはまれですが、要求された場合は1秒以内に利用可能である必要があります。
7年以上経過したデータにはアクセスしません。 7年後、データは可能な限り低いコストで永続化する必要があります。
必要な可用性を維持しながら、コストを最小限に抑える必要があります。
データをどのように管理する必要がありますか?回答するには、回答領域で適切なオプションを選択します。
注:正しい選択はそれぞれ1ポイントの価値があります。

正解:
Explanation:
Text, table Description automatically generated
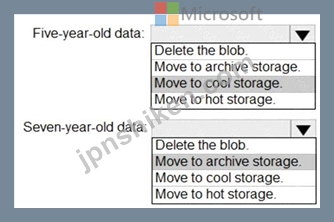
Box 1: Move to cool storage
The cool access tier has lower storage costs and higher access costs compared to hot storage. This tier is intended for data that will remain in the cool tier for at least 30 days. Example usage scenarios for the cool access tier include:
Short-term backup and disaster recovery
Older data not used frequently but expected to be available immediately when accessed Large data sets that need to be stored cost effectively, while more data is being gathered for future processing Note: Hot - Optimized for storing data that is accessed frequently.
Cool - Optimized for storing data that is infrequently accessed and stored for at least 30 days.
Archive - Optimized for storing data that is rarely accessed and stored for at least 180 days with flexible latency requirements, on the order of hours.
Box 2: Move to archive storage
Example usage scenarios for the archive access tier include:
Long-term backup, secondary backup, and archival datasets
Original (raw) data that must be preserved, even after it has been processed into final usable form Compliance and archival data that needs to be stored for a long time and is hardly ever accessed Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/storage-blob-storage-tiers
- 質問一覧「135問」
- 質問1 Table1とTable2という名前の2つのテーブルを含むDB1という名前の...
- 質問2 DB1 という名前の Azure SQL データベースがあります。 データセ...
- 質問3 Always On 可用性グループを使用する高可用性構成で、Azure 仮想...
- 質問4 あなたはビジネス目標を評価しています。 サービス契約に基づい
- 質問5 2つの100GBデータベースをAzureに移動することを計画しています...
- 質問6 MicrosoftAzureでマネージドデータウェアハウスソリューションを...
- 質問7 展示に示されているように、AzureSQLデータベースの長期保存ポリ...
- 質問8 DB1 という名前の Microsoft SQL Server 2019 データベースと、S...
- 質問9 SQLServerがインストールされているAzure仮想マシンが10台ありま...
- 質問10 Pool1という名前のApacheSparkプールを含むWS1という名前のAzure...
- 質問11 DevServer1という名前のAzureSQLデータベースサーバーを含むApp1...
- 質問12 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問13 Table 1 という名前のテーブルを含む DB1 という名前の Azure SQ...
- 質問14 DB1という名前のデータベースを含むAzure仮想マシン上にSQLServe...
- 質問15 General Purpose サービス レベルに DB1 という名前の Azure SQL...
- 質問16 AzureSQLマネージドインスタンスがあります。 Transact-SQLを使...
- 質問17 Azure仮想マシンにAlwaysOn可用性グループがデプロイされていま...
- 質問18 DW1という名前のAzureSynapseAnalyticsのエンタープライズデータ...
- 質問19 SQLVMI という名前の Azure Virtual Machines インスタンス上の ...
- 質問20 DB1 という名前の Azure SQL データベースがあります。 DB1 を暗...
- 質問21 DB1 という名前の 2 TB Microsoft SQL Server 2019 データベース...
- 質問22 Azure SQL 論理サーバーがあります。 次のスクリプトを実行しま...
- 質問23 vCore購入モデルを使用してプロビジョニングされた20のAzureSQL...
- 質問24 Azure仮想マシン上にSQLServerがあります。 次の展示に示されて...
- 質問25 SQLDb1 という名前の Azure SQL データベースを含む Azure サブ...
- 質問26 Azure Virtual Machines 上の SQL Server のインスタンスを含む ...
- 質問27 SQL1という名前のAzure仮想マシン上のSQLServerのインスタンスが...
- 質問28 Azure Synapse Analyticsで、Customersという名前のテーブルを含...
- 質問29 AzureSQLデータベースがあります。 次の展示に示すように、パフ...
- 質問30 DB3という名前のAzureSQLデータベースがあります。 展示に示され...
- 質問31 論理 SQL サーバーを含む Azure サブスクリプションがあります。...
- 質問32 10個のAzureSQLデータベースをホストするsqlsrv1という名前のAzu...
- 質問33 ResourceGroup1という名前のリソースグループ内の同じAzureSQLデ...
- 質問34 Table1という名前のテーブルを含むDB1という名前のMicrosoftSQLS...
- 質問35 Pool1という名前のAzureSynapse Analytics専用SQLプールと、Acco...
- 質問36 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問37 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問38 contoso.com という名前の Azure AD テナントにリンクされている...
- 質問39 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問40 監視要件を満たすために、どの監査ログの宛先を使用する必要があ
- 質問41 ADF1という名前のAzureData Factoryインスタンスと、WS1およびWS...
- 質問42 SQL1という名前のAzureSQLマネージドインスタンスと、App1および...
- 質問43 AzureSQLデータベースとAzureWebアプリを含むアプリをデプロイす...
- 質問44 Azure Virtual Machines 上に 50 個の SQL Server インスタンス...
- 質問45 SSISDBデータベースを含むAzure仮想マシン上にSQLServer2019があ...
- 質問46 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問47 Azure SynapseAnalyticsにデータウェアハウスがあります。 デー...
- 質問48 SERVER1データベースのユーザー認証を構成する必要があります。...
- 質問49 Azure仮想マシンを構築しています。 2つの1-TiB、P30プレミアム...
- 質問50 Customerという名前のテーブルを含むAzureSQLデータベースがあり...
- 質問51 Server1という名前のサーバーを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあ...
- 質問52 Azure サブスクリプションをお持ちです。 PowerShell を使用して...
- 質問53 Azure Virtual Machines 上に VM1 という名前の SQL Server のイ...
- 質問54 Azure Virtual Machines 上に SQL1 という名前の SQL Server の...
- 質問55 db1 という名前のデータベースがあります。 db1 のログには、次...
- 質問56 1時間ごとにトリガーされるAzureDataFactoryパイプラインがあり...
- 質問57 sqldb1 という名前の Azure SQL データベースがあります。 クエ...
- 質問58 オンプレミスのMicrosoftSQLServerデータベースをAzureに移行す...
- 質問59 DB1という名前のAzureSQLデータベースがあります。 DB1に接続し...
- 質問60 ある会社は、ApacheSpark分析を使用して侵入検知データを分析す...
- 質問61 AzureSQLマネージドインスタンスがあります。 SQLエージェントジ...
- 質問62 Web サイト分析システムから、ダウンロード、リンクのクリック、...
- 質問63 DB1という名前のAzureSQLデータベースがあります。 DB1の自動チ...
- 質問64 SQL Server 2019 または Windows Server 2019 を実行する Azure ...
- 質問65 Azure Virtual Machines 上に VM1 という名前の SQL Server のイ...
- 質問66 Azure SQL マネージド インスタンス、db1 という名前のデータベ...
- 質問67 あなたの会社はセキュリティカメラからの画像を分析し、異常な活
- 質問68 Azure SynapseAnalyticsでエンタープライズデータウェアハウスを...
- 質問69 Azure SQLDatabaseのマネージドインスタンスがあります。 インス...
- 質問70 Employeesという名前のテーブルを含むAzureSQLデータベースがあ...
- 質問71 SQLVM1 という名前の Azure 仮想マシン上の SQL Server のインス...
- 質問72 DB1 という名前の Azure SCX データベースを保存します。 D61 の...
- 質問73 次のTransact-SQLクエリがあります。 (Exhibit) クエリによって...
- 質問74 Azure Marketplace SQL Server 2019 Enterprise イメージを使用...
- 質問75 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問76 Azure サブスクリプションをお持ちです。 Azure Virtual Machine...
- 質問77 Db1という名前のデータベースを含むAzure仮想マシン上にSQLServe...
- 質問78 DB1 という名前の Azure SQL データベースがあります。DB1 には...
- 質問79 トランザクションデータの分析ストレージソリューションを設計す
- 質問80 技術的な要件を満たすために、リアルタイム処理のためにどのカウ
- 質問81 データベースをAzureSQLDatabaseマネージドインスタンスにデプロ...
- 質問82 論理 SQL サーバーを含む Azure サブスクリプションがあります。...
- 質問83 SQLMi1という名前のAzureSQLマネージドインスタンスとBackupdbと...
- 質問84 AzureSQLデータベースがあります。データベースには、列ストアイ...
- 質問85 factSalesという名前のテーブルを含むAzureSQLデータベースがあ...
- 質問86 AzureSQLデータベースがあります。 次の展示に示すように、クエ...
- 質問87 PostgreSQLデータベースを移行するには何を使用する必要がありま...
- 質問88 Azure仮想マシン上にSQLServerがあります。 Microsoft SQL Serve...
- 質問89 contoso.comという名前のドメインを使用するAzureサブスクリプシ...
- 質問90 次の表に示すリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります...
- 質問91 FileTablesおよびFilestream機能を使用するオンプレミスのMicros...
- 質問92 VNet1という名前の仮想ネットワーク上にVM1という名前のAzure仮...
- 質問93 DB1という名前のオンプレミスMicrosoftSQL Server2016データベー...
- 質問94 db1 という名前のデータベースをホストするオンプレミスの Micro...
- 質問95 Azure SQL データベースがあります。 遅延クエリ実行が RESOURCE...
- 質問96 DB1 という 10 TB の SQL データベースをホストする SQL Server ...
- 質問97 [email protected]という名前のユーザーとSQLMI1という名前のAzu...
- 質問98 AzSQL1という名前のAzureSQLサーバー上にDB1という名前の新しいA...
- 質問99 AzureSQLデータベースがあります。 ユーザーは、ストアドプロシ...
- 質問100 Db1 という名前のデータベースをホストする SQL Server on Azure...
- 質問101 Azure サブスクリプションをお持ちです。 4 つのデータベースを...
- 質問102 次の表に示すリソースを含む Azure サブスクリプションがありま...
- 質問103 Azureに移行した後、ManufacturingSQLDb1の構成を推奨する必要が...
- 質問104 Azure Synapse Analyticsで、スタースキーマにWebサイトのトラフ...
- 質問105 Azure Virtual Machines インスタンス上の 2 つの SQL Server を...
- 質問106 Azure Synapse Analytics サーバーレス SQL プールを使用して、A...
- 質問107 あなたの会社は、Azure StreamAnalyticsを使用してデバイスを監...
- 質問108 Azure SynapseAnalytics専用のSQLプールにテーブルを作成するこ...
- 質問109 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問110 DB1という名前のデータベースを含むAzure仮想マシン上にSQLServe...
- 質問111 40個のAzureSQLデータベースがあり、それぞれが異なる顧客用です...
- 質問112 SQL1 という名前の Azure SQL データベースを含む Azure サブス...
- 質問113 Azure SynapseAnalytics専用のSQLプールで日付ディメンションテ...
- 質問114 Azure サブスクリプションをお持ちです。 Azure Resource Manage...
- 質問115 Microsoft SQL Server のインスタンスをホストする VMI という名...
- 質問116 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問117 ResearchDB1のデータ保持を構成するための実装計画を提供する必...
- 質問118 5つのデータベースをホストするSQL1という名前のオンプレミスのM...
- 質問119 Azure StreamAnalyticsジョブがあります。 ジョブに十分なストリ...
- 質問120 Azure SynapseAnalytics専用のSQLプールがあります。 PDW_SHOWSP...
- 質問121 SQL1 という名前の新しい Azure SQL マネージド インスタンスを...
- 質問122 顧客がデータベースオブジェクトを作成できるようにするためのソ
- 質問123 Azure Data Lake StorageGen2コンテナがあります。 データはコン...
- 質問124 RG1 という名前のリソース グループを含む Azure サブスクリプシ...
- 質問125 DB1という名前のデータベースを含むAzure仮想マシン上にSQLServe...
- 質問126 MI1という名前のAzureSQLマネージドインスタンスがあります。 MI...
- 質問127 Orders という名前のテーブルを含む DB1 という名前の Azure SQL...
- 質問128 汎用サービス レベルに DB1 という名前の Azure SQL データベー...
- 質問129 DB1という名前のデータベースを含むAzure仮想マシン上にSQLServe...
- 質問130 df1という名前のAzureData Factoryバージョン2(V2)データファ...
- 質問131 server1という名前のサーバー上にdb1という名前のAzureSQLデータ...
- 質問132 PaaSプロトタイプに基づいて、どのAzure SQLデータベース計算層...
- 質問133 Windows Server 2019を実行するVM1とVM2という名前の2つのAzure...
- 質問134 SOL1 という名前の Azure SQL データベースがあります。 SQL1 の...
- 質問135 Databasebackups という名前のストレージ アカウントを含む Azur...

