- ホーム
- Microsoft
- DP-300J - Administering Relational Databases on Microsoft Azure (DP-300日本語版)
- Microsoft.DP-300J.v2023-08-25.q98
- 質問43
有効的なDP-300J問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、DP-300J試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新DP-300J試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com DP-300J試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここでDP-300J問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
DP-300J問題集最新版のアクセス
「464問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
Server1という名前のサーバー上にDatabaseAという名前のAzureSQLデータベースインスタンスがあります。
App1という名前の新しいユーザーをDatabaseAに追加し、App1にdb_datacenter権限を付与する予定です。 App1はSQLServer認証を使用します。
App1を作成する必要があります。このソリューションでは、同じ資格情報を使用してApp1に他のデータベースへのアクセスを許可できるようにする必要があります。
どの3つのアクションを順番に実行する必要がありますか?回答するには、適切なアクションをアクションのリストから回答領域に移動し、正しい順序で配置します。

App1という名前の新しいユーザーをDatabaseAに追加し、App1にdb_datacenter権限を付与する予定です。 App1はSQLServer認証を使用します。
App1を作成する必要があります。このソリューションでは、同じ資格情報を使用してApp1に他のデータベースへのアクセスを許可できるようにする必要があります。
どの3つのアクションを順番に実行する必要がありますか?回答するには、適切なアクションをアクションのリストから回答領域に移動し、正しい順序で配置します。

正解:
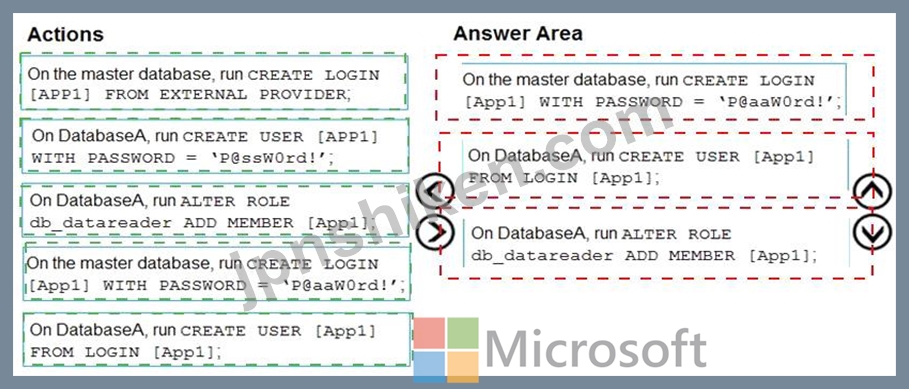
Explanation

Step 1: On the master database, run CREATE LOGIN [App1] WITH PASSWORD = 'p@aaW0rd!' Logins are server wide login and password pairs, where the login has the same password across all databases.
Here is some sample Transact-SQL that creates a login:
CREATE LOGIN readonlylogin WITH password='1231!#ASDF!a';
You must be connected to the master database on SQL Azure with the administrative login (which you get from the SQL Azure portal) to execute the CREATE LOGIN command.
Step 2: On DatabaseA, run CREATE USER [App1] FROM LOGIN [App1]
Users are created per database and are associated with logins. You must be connected to the database in where you want to create the user. In most cases, this is not the master database. Here is some sample Transact-SQL that creates a user:
CREATE USER readonlyuser FROM LOGIN readonlylogin;
Step 3: On DatabaseA run ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD Member [App1]
Just creating the user does not give them permissions to the database. You have to grant them access. In the Transact-SQL example below the readonlyuser is given read only permissions to the database via the db_datareader role.
EXEC sp_addrolemember 'db_datareader', 'readonlyuser';
Reference:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/adding-users-to-your-sql-azure-database/
- 質問一覧「98問」
- 質問1 df1という名前のAzureData Factoryバージョン2(V2)データファ...
- 質問2 次の展示に示すように、Azure DataFactoryインスタンスのバージ...
- 質問3 AzureDatabricksで1日1回バッチ処理を実行することを計画してい...
- 質問4 AzureSQLデータベースを使用するソリューションを計画しています...
- 質問5 Table1とTable2という名前の2つのテーブルを含むDB1という名前の...
- 質問6 次の表に示すリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります...
- 質問7 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問8 R を主要言語としてサポートするが、Scala と SQL もサポートす...
- 質問9 server1という名前のサーバー上にdb1という名前のAzureSQLデータ...
- 質問10 Pool1という名前のAzureSynapse Analytics専用SQLプールと、Acco...
- 質問11 DevServer1という名前のAzureSQLデータベースサーバーを含むApp1...
- 質問12 Azure仮想マシン上にSQLServerがあります。 Microsoft SQL Serve...
- 質問13 Azure SynapseAnalytics専用のSQLプールがあります。 PDW_SHOWSP...
- 質問14 Server1という名前のサーバーを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあ...
- 質問15 Azure SQL 論理サーバーがあります。 次のスクリプトを実行しま...
- 質問16 監視要件を満たすために、どの監査ログの宛先を使用する必要があ
- 質問17 DB1という名前のオンプレミスMicrosoftSQL Server2016データベー...
- 質問18 AzSQL1という名前のAzureSQLサーバー上にDB1という名前の新しいA...
- 質問19 ResourceGroup1という名前のリソースグループ内の同じAzureSQLデ...
- 質問20 可用性グループにAzure仮想マシン上のSQLServerがあります。 可...
- 質問21 Pool1という名前のAzureSynapse Analytics専用SQLプールと、DB1...
- 質問22 Azure Virtual Machines インスタンス上の SQL Server にデータ...
- 質問23 オンプレミスのMicrosoftSQLServerデータベースをAzureSQLDataba...
- 質問24 Azure Data Lake StorageGen2アカウントへのソースデータの増分...
- 質問25 Azureサブスクリプション内のすべての新規および既存のAzureSQL...
- 質問26 AzureSQLデータベースの可用性戦略を推奨する必要があります。戦...
- 質問27 次の展示に示すように、AzureポータルでAzureSQLデータベースを...
- 質問28 ResearchDB1の認証を実装する必要があります。ソリューションは...
- 質問29 DB1という名前のAzureSQLデータベースがあります。 タイプCHAR(...
- 質問30 Azure SynapseAnalyticsサーバーレスSQLプールにデータベースを...
- 質問31 AzureSQLマネージドインスタンスがあります。 Transact-SQLを使...
- 質問32 新しいAzureサブスクリプションがあります。 Server1という名前...
- 質問33 2つの100GBデータベースをAzureに移動することを計画しています...
- 質問34 Azure SynapseAnalytics専用のSQLプールにテーブルを作成するこ...
- 質問35 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2を使用するアプリケーションを開発...
- 質問36 DB1という名前のデータベースをホストするオンプレミスのMicroso...
- 質問37 VNet1という名前の仮想ネットワーク上にVM1という名前のAzure仮...
- 質問38 次の表に示すリソースを含む Azure サブスクリプションがありま...
- 質問39 Db1 という名前のデータベースをホストする SQL Server on Azure...
- 質問40 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問41 contoso.com という名前の Azure AD テナントにリンクされている...
- 質問42 SQL1という名前のAzure仮想マシン上にSQLServerがあります。 SQL...
- 質問43 Server1という名前のサーバー上にDatabaseAという名前のAzureSQL...
- 質問44 DB1 という名前の Azure SQL データベースがあります。 データセ...
- 質問45 次の資料に示すように、Azure SQL データベースのバックアップを...
- 質問46 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問47 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問48 PaaSプロトタイプに基づいて、どのAzure SQLデータベース計算層...
- 質問49 DB1という名前の50TBのMicrosoftSQLServerデータベースがありま...
- 質問50 Windows Server2019を実行するAzure仮想マシン上にSQLServer2019...
- 質問51 Azure StreamAnalyticsジョブがあります。 ジョブに十分なストリ...
- 質問52 db1 という名前のデータベースがあります。 db1 のログには、次...
- 質問53 Customerという名前のテーブルを含むAzureSQLデータベースがあり...
- 質問54 PipelineAとPipelineBという名前の2つのパイプラインを持つAzure...
- 質問55 1時間ごとにトリガーされるAzureDataFactoryパイプラインがあり...
- 質問56 展示に示されているように、AzureSQLデータベースの長期保存ポリ...
- 質問57 Azure Data Lake StorageGen2コンテナがあります。 データはコン...
- 質問58 次の表に示すリソースを含む Azure サブスクリプションがありま...
- 質問59 Azure仮想マシン上にSQLServerがあります。 次の要件を満たす4TB...
- 質問60 10個のAzureSQLデータベースをホストするsqlsrv1という名前のAzu...
- 質問61 AzureSQLデータベースとAzureWebアプリを含むアプリをデプロイす...
- 質問62 SQL1という名前のAzureSQLマネージドインスタンスと、App1および...
- 質問63 Table1 という名前のテーブルを含む という名前の Azure SQL デ...
- 質問64 次のAzureResourceManagerテンプレートがあります。 (Exhibit) ...
- 質問65 index1 という名前の非クラスター化インデックスを含む DBI とい...
- 質問66 次のAzureDataFactoryパイプラインがあります。 System1からデー...
- 質問67 SalesSQLDb1の統計更新を実装する必要があります。ソリューショ...
- 質問68 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 Azure Resource Manager(...
- 質問69 Twitterフィードデータレコードのデータ保持ソリューションを設...
- 質問70 5つのデータベースをホストするSQL1という名前のオンプレミスのM...
- 質問71 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問72 server1という名前のサーバー上にdb1という名前のAzureSQLデータ...
- 質問73 D61 という名前の Azure SQL データベースがあります。 DB1 に割...
- 質問74 Azure SQLDatabaseのマネージドインスタンスがあります。 インス...
- 質問75 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問76 DB1という名前のデータベースを含むAzure仮想マシン上にSQLServe...
- 質問77 30の新しいデータベースに適切な購入モデルと展開オプションを推...
- 質問78 Azure StreamAnalyticsジョブを監視しています。 バックログ入力...
- 質問79 小売店テーブルの代理キーを実装する必要があります。ソリューシ
- 質問80 Azure仮想マシンでホストされているSQLServerデータベースのデー...
- 質問81 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問82 DB1という名前のAzureSQLデータベースがあります。 Azureポータ...
- 質問83 Microsoft SQL Server 2017 サーバーがあります。 サーバーを Az...
- 質問84 Web層、アプリケーション層、およびMicrosoft SQLServer層を含む...
- 質問85 db1 という名前のデータベースをホストする SQL1 という名前のオ...
- 質問86 Salesという名前のプライベート証明書を含むDB1という名前のAzur...
- 質問87 Azureに移行した後、ManufacturingSQLDb1の構成を推奨する必要が...
- 質問88 DB1という名前のデータベースを含むAzure仮想マシン上にSQLServe...
- 質問89 DB1という名前のデータベースを含むAzure仮想マシン上にSQLServe...
- 質問90 Windows Server 2019を実行し、AG1という名前のMicrosoft SQL Se...
- 質問91 MI1という名前のAzureSQLマネージドインスタンスがあります。 MI...
- 質問92 AzureSQLデータベースがあります。 プランキャッシュが、一度だ...
- 質問93 販売データのストリーミング集計を実行するには、どのウィンドウ
- 質問94 新しいAzureSQLデータベースがあります。データベースには、機密...
- 質問95 10個のパイプラインを含むAzureDataFactoryがあります。 各パイ...
- 質問96 Windows Server2019を実行するAzure仮想マシン上にSQLServer2019...
- 質問97 あなたの会社はセキュリティカメラからの画像を分析し、異常な活
- 質問98 Azure仮想マシンにAlwaysOn可用性グループがデプロイされていま...

