- ホーム
- Microsoft
- AZ-104J - Microsoft Azure Administrator (AZ-104日本語版)
- Microsoft.AZ-104J.v2023-07-24.q259
- 質問239
有効的なAZ-104J問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、AZ-104J試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新AZ-104J試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com AZ-104J試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここでAZ-104J問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
AZ-104J問題集最新版のアクセス
「815問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
次の表に示すAzure仮想ネットワークがあります。
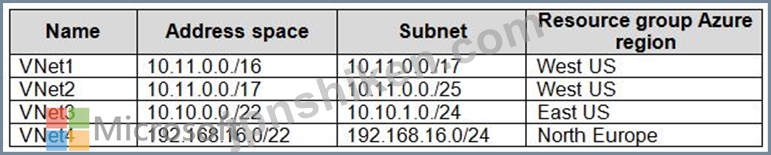
VNet1からどの仮想ネットワークにピアリング接続を確立できますか?

VNet1からどの仮想ネットワークにピアリング接続を確立できますか?
正解:C
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/tutorial-connect-virtual-networks-portal You can connect virtual networks to each other with virtual network peering. These virtual networks can be in the same region or different regions (also known as Global VNet peering). Once virtual networks are peered, resources in both virtual networks are able to communicate with each other, with the same latency and bandwidth as if the resources were in the same virtual network.
Global VNet Peering is now generally available in all Azure public regions, excluding the China, Germany, and Azure Government regions.
The address space is the most critical configuration for a VNet in Azure. This is the IP range for the entire network that will be divided into subnets. The address space can almost be any IP range that you wish (public or private). You can add multiple address spaces to a VNet. To ensure this VNet can be connected to other networks, the address space should never overlap with any other networks in your environment. If a VNet has an address space that overlaps with another Azure VNet or on-premises network, the networks cannot be connected, as the routing of traffic will not work properly.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/tutorial-connect-virtual-networks-portal
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-in/updates/general-availability-global-vnet-peering/#:~:text=Global%20VNet%20Peering%20is%20now,transit%20over%20the%20public%20internet.
https://www.microsoftpressstore.com/articles/article.aspx?p=2873369
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/tutorial-connect-virtual-networks-portal You can connect virtual networks to each other with virtual network peering. These virtual networks can be in the same region or different regions (also known as Global VNet peering). Once virtual networks are peered, resources in both virtual networks are able to communicate with each other, with the same latency and bandwidth as if the resources were in the same virtual network.
Global VNet Peering is now generally available in all Azure public regions, excluding the China, Germany, and Azure Government regions.
The address space is the most critical configuration for a VNet in Azure. This is the IP range for the entire network that will be divided into subnets. The address space can almost be any IP range that you wish (public or private). You can add multiple address spaces to a VNet. To ensure this VNet can be connected to other networks, the address space should never overlap with any other networks in your environment. If a VNet has an address space that overlaps with another Azure VNet or on-premises network, the networks cannot be connected, as the routing of traffic will not work properly.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/tutorial-connect-virtual-networks-portal
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-in/updates/general-availability-global-vnet-peering/#:~:text=Global%20VNet%20Peering%20is%20now,transit%20over%20the%20public%20internet.
https://www.microsoftpressstore.com/articles/article.aspx?p=2873369
- 質問一覧「259問」
- 1コメント質問1 Azure サブスクリプションがある 新しいストレージ アカウントの...
- 質問2 次のリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります。 * VNet...
- 質問3 米国東部2リージョンにVNET1という名前の仮想ネットワークを含む...
- 質問4 仮想マシン構成の継続的な一貫性を管理するには、Azure Automati...
- 質問5 次の展示に示す階層を含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります。 ...
- 質問6 Subscription1およびSubscription2という名前のAzureサブスクリ...
- 質問7 Azure AD Connect for Azure Active Directoryシームレスシング...
- 質問8 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問9 あなたの会社はニューヨークとロサンゼルスにオフィスを構えてい
- 質問10 webapp1という名前のAzure Webアプリがあります。 VNET1という名...
- 質問11 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 VM1という名前のオンプレ...
- 質問12 次のAzureResource Manager(ARM)テンプレートを開発して、リソ...
- 質問13 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問14 Azure Active Directory(Azure AD)Premiumにサインアップしま...
- 質問15 あなたは、adatum.comという名前のAzure Active Directory(Azur...
- 質問16 Windows Server 2016を実行するServer1という名前のオンプレミス...
- 質問17 次の表に示すリソースを含む Azure サブスクリプションがありま...
- 質問18 Azure Active Directory(Azure AD)テナントがあります。 すべ...
- 質問19 storage1という名前のAzureStorageアカウントに対してAzureActiv...
- 質問20 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問21 注:質問は、同じ設定を表すいくつかの質問に含まれています。た
- 質問22 wwwcontoso.com をホストするために、contoso.azurewebsites.net...
- 質問23 VNET1 という名前の仮想ネットワークを含む Azure サブスクリプ...
- 質問24 次の表のリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります。 (E...
- 質問25 Windows Server 2019を実行するVM1という名前のAzure仮想マシン...
- 質問26 技術要件を満たす特定のソリューションを推奨する必要があります
- 質問27 WebApp1という名前のAzure Webアプリがあります。 開発者は、本...
- 質問28 注この質問は、同じ見方を示す一連の質問の一部です。一部の質問
- 質問29 Active Directoryドメインに同期されているcontoso.comという名...
- 質問30 contoso.onmicrosoft.comという名前のAzure Active Directory(A...
- 質問31 Azure BlobストレージとAzure Fileストレージを使用するstorage1...
- 質問32 ActiveDirectoryの問題を解決する必要があります。 あなたは何を...
- 質問33 VM1とVM2という名前の2つのAzure仮想マシンで実行されるApp1とい...
- 質問34 次の展示に示すように構成するVM1という名前のAzure仮想マシンを...
- 質問35 App1という名前のAzureAppServicesWebアプリがあります。 WebDep...
- 質問36 注:質問は、同じ設定を表すいくつかの質問に含まれています。た
- 質問37 オンプレミスのActive Directoryと同期し、次の表に示すユーザー...
- 質問38 次のユーザーを含むContoso.comという名前のAzure Active Direct...
- 質問39 ローカル冗長ストレージ(LRS)を使用するstorage1という名前の...
- 質問40 VM1とVM2という名前の2つのAzure仮想マシンがあります。 RSV1お...
- 質問41 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問42 米国西部、米国中部、米国東部のAzureリージョンにWebアプリがあ...
- 質問43 Subnet1という名前のサブネットを含むVNet1という名前のAzure仮...
- 質問44 app1という名前のAzureAppServiceWebアプリがあります。 次の展...
- 質問45 Azure Active Directory(Azure AD)テナントがあります。 Azure...
- 質問46 次の表に示す仮想ネットワークを含む Azure サブスクリプション...
- 質問47 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問48 次の表に示すリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります...
- 質問49 次の表に示すリソースを含むSubscription1という名前のAzureサブ...
- 質問50 ASP1という名前のAzure App Serviceプランで実行されるWebApp1と...
- 質問51 サイト間VPNを使用してオンプレミスネットワークに接続するVNet1...
- 質問52 注:質問は、同じ設定を表すいくつかの質問に含まれています。た
- 質問53 次の表に示すAzure仮想マシンを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあ...
- 質問54 次の資料に示すロール割り当てファイルがあります。 (Exhibit)...
- 質問55 次の表に示すAzure管理グループがあります。 (Exhibit) 次の表に...
- 質問56 VM1という名前のAzure仮想マシンを含むAzureサブスクリプション...
- 質問57 注:質問は、同じ設定を表すいくつかの質問に含まれています。た
- 質問58 次の表に示すストレージアカウントを含むSubscription1というAzu...
- 質問59 5つのインスタンスを含むAzure仮想マシンスケールセットをできる...
- 質問60 次の表に示すユーザーを含むAzureActive Directory(Azure AD)...
- 質問61 次の表に示すリソースグループを含むAzureサブスクリプションが...
- 質問62 既存の仮想マシンに基づいてAzure Resource Managerテンプレート...
- 質問63 次の展示に示すApp Serviceプランがあります。 (Exhibit) App Se...
- 質問64 VM1という名前のAzure仮想ネットワークを含むSubscription1とい...
- 質問65 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 次の要件を満たすカスタム...
- 質問66 次の表のリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります。 (E...
- 質問67 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問68 VM1という名前のAzure仮想マシンを含むAzureサブスクリプション...
- 質問69 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問70 次のリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります。 * 100...
- 質問71 次の表に示すリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります...
- 質問72 次のプロバイダーが登録されているSubscription1という名前のAzu...
- 質問73 WebApp1とWebApp2という名前の2つのAzure Webアプリをデプロイす...
- 質問74 次の表に示す仮想ネットワークを含む Azure サブスクリプション...
- 質問75 次の表に示すリソースを含む Azure サブスクリプションがありま...
- 質問76 ネットワークにadatum.comという名前のオンプレミスのActive Dir...
- 質問77 次の表に示すリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります...
- 質問78 contoso.comという名前のAzure Active Directory(Azure AD)テ...
- 質問79 次の表に示すリソースを含むSubscription1という名前のAzureサブ...
- 質問80 次の評価プロパティを持つAzure Migrateプロジェクトがあります...
- 質問81 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問82 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 Azure Resource Manager(...
- 質問83 Azure サブスクリプションがあります。 Deploy.json という名前...
- 質問84 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問85 test-migrationという名前のリソースグループにTestMigという名...
- 質問86 Azure Import / Exportサービスを使用してファイルをストレージ...
- 質問87 NSG1およびNSG2の計画された変更を実装します。 次の各ステート...
- 質問88 3つのオフィスとAzureActive Directory(Azure AD)テナントを含...
- 質問89 AzureBackupによって保護されているAzureLinux仮想マシンがあり...
- 質問90 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 APP1という名前のアプリを...
- 質問91 ホットスポット 次の表に示すファイル共有を含むAzureサブスクリ...
- 質問92 10個の仮想マシンを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります。 仮...
- 質問93 次のAzure Resource Managerテンプレートを使用して、Azureコン...
- 質問94 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 Azure Resource Managerテ...
- 質問95 ネットワークにActive Directoryドメインが含まれています。ドメ...
- 質問96 次の表に示すリソースを含む Sub1 という名前の Azure サブスク...
- 質問97 Azure virtual for Server2の適切なサイズが必要です。 あなたは...
- 質問98 Contosoのストレージ要件を特定する必要があります。 次の各ステ...
- 質問99 アクション 1: Azure ロジック アプリを作成する (Exhibit) アク...
- 質問100 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問101 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 次の展示に示すように構成...
- 質問102 次のストレージアカウントを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあり...
- 質問103 次の表に示すオブジェクトを含むcontoso.comという名前のActive ...
- 質問104 次の展示に示すように、Azureストレージアカウントを持っていま...
- 質問105 VM1とVM2という名前の2つの仮想マシンを含むAzureサブスクリプシ...
- 質問106 VNet1という名前の仮想ネットワークを含むAzureサブスクリプショ...
- 質問107 Active Directoryドメインに同期されているContoso.comという名...
- 質問108 VM3が技術要件を満たしていないことがわかります。 問題がNSGに...
- 質問109 次の表に示す仮想マシンを含むAzureサブスクリプションがありま...
- 質問110 あなたの会社にはサーバル部門があります。各部門には、多数の仮
- 質問111 あなたは、adatum.comという名前のAzure Active Directory(Azur...
- 質問112 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問113 storageaccount1という名前のAzureStorageアカウントを含むAzure...
- 質問114 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問115 contoso.comという名前のActive Directoryフォレストがあります...
- 質問116 次の表に示すリソースを含む Azure サブスクリプションがありま...
- 質問117 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問118 App1のAzureへの移行を計画しています。 ネットワークセキュリテ...
- 質問119 VM1とVM2をバックエンドのうんちに追加する必要があります!LB1...
- 質問120 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。オンプレミスのWindows2016...
- 質問121 次の表に示すリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります...
- 質問122 ブループリントファイルをAzureに移動する必要があります。 あな...
- 質問123 次の表に示すリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります ...
- 質問124 Test RGという名前のリソースグループを含むAzureサブスクリプシ...
- 質問125 Subscription1という名前のAzureサブスクリプションがあります。...
- 質問126 ネットワークは、次の図に示すように構成されています。 (Exhibi...
- 質問127 次の展示に示すように、Azureポリシーがあります。 (Exhibit) ポ...
- 質問128 Azure AD テナントにリンクされている Azure サブスクリプション...
- 質問129 次の表に示すリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります...
- 質問130 App1という名前の分散型オンプレミスアプリをAzureサブスクリプ...
- 質問131 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問132 認証要件を満たすように環境を準備する必要があります。 どの2つ...
- 質問133 Azureストレージアカウントを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあり...
- 質問134 RG26という名前のリソースグループを含むAzureサブスクリプショ...
- 質問135 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問136 RG1 という名前のリソース グループを含む Subcription1 という...
- 質問137 Admin1のユーザー要件を満たす必要があります。 あなたは何をす...
- 質問138 storageacct1234という名前のストレージアカウントと、User1およ...
- 質問139 次の表に示すリソースを含む Azure サブスクリプションがありま...
- 質問140 Windows Server 2016 を実行する 5 つの Azure 仮想マシンがあり...
- 質問141 次の表に示すリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります...
- 質問142 VNet1という名前の仮想ネットワークを含むAzureサブスクリプショ...
- 質問143 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問144 Azure Application Gatewayのパフォーマンスの問題をトラブルシ...
- 質問145 Kubernetesクラスターにサービスがデプロイされています。 別の...
- 質問146 storage1 という名前のストレージ アカウントを含む Azure サブ...
- 質問147 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 次の展示に示すAzure Stor...
- 質問148 Active Directoryドメインに同期されているcontoso.comという名...
- 質問149 WebApp1という名前のAzure Webアプリを開発しています。 WebApp1...
- 質問150 VM1という名前のAzure仮想マシンがあります。 AzureはVM1からイ...
- 質問151 オンプレミス ネットワークに VPN ゲートウェイが含まれています...
- 質問152 コンテナー化されたWebアプリケーションをAzureにデプロイしてい...
- 質問153 次の図に示すように、Policy1という名前のRecovery Servicesボル...
- 質問154 次の表に示すユーザーを含むcontoso.comという名前のAzure Activ...
- 質問155 VNet1という名前の仮想ネットワークに接続するVM1という名前のAz...
- 質問156 VNET2のピアリングは、次の展示に示すように構成されています。 ...
- 質問157 画像を保存するstorage1という名前のAzureStorageアカウントがあ...
- 質問158 次の要件を満たすAzureストレージアカウントを作成する必要があ...
- 質問159 次のストレージアカウントを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあり...
- 質問160 次の表に示す 8 つの仮想マシンとリソースを含む Azure サブスク...
- 質問161 次の表に示すリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります...
- 質問162 VM1という名前のAzure仮想マシンがあります。 Azure Backupを使...
- 質問163 Azureロードバランサーを作成しています。 IPv6ロードバランシン...
- 質問164 5,000のユーザーアカウントを含むAzure Active Directory(Azure...
- 質問165 ASP1という名前のAzureAppServiceプランがあります。 ASP1のCPU...
- 質問166 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 ユーザーは、ホームまたは...
- 質問167 VNet1、VNet2、VNet3という名前の3つの仮想ネットワークを含むAz...
- 質問168 Subscription1という名前のAzureサブスクリプションがあります。...
- 質問169 次の表に示すリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります...
- 質問170 オンプレミスネットワークには、Share1という名前のSMB共有が含...
- 質問171 Windows Server 2019を実行し、次の表に示すように構成されてい...
- 質問172 Azure Event Gridに接続するためのカスタムAzure関数アプリを構...
- 質問173 Workspace1という名前のAzureLogAnalyticsワークスペースを含むS...
- 質問174 App1 という名前の Azure App Services Web アプリがあります。 ...
- 質問175 オンプレミスネットワークにはVPNゲートウェイが含まれています...
- 質問176 10個のAzure Webアプリのデプロイに使用されるAzureリソースマネ...
- 質問177 コンピューターというコンピューターがあります。これには、VNet...
- 質問178 計画されているインフラストラクチャをサポートするには、Azure ...
- 質問179 storage1という名前のAzureStorageアカウントがあります。 app1...
- 質問180 次の表に示すストレージアカウントを含むAzureサブスクリプショ...
- 質問181 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問182 注:質問は、同じ設定を表すいくつかの質問に含まれています。た
- 質問183 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問184 Azureサブスクリプションがあります 複数のデータディスクを持つ...
- 質問185 VNET1、VNET2、およびVNET3という名前の3つの仮想ネットワークを...
- 質問186 contoso.onmicrosoft.comという名前のAzure Active Directoryテ...
- 質問187 Subcription1.hasという名前のAzureサブスクリプションがある Su...
- 質問188 すべてのA2ureファイル共有にGroup4AzureRBAC読み取り専用アクセ...
- 質問189 Subscription1という名前のAzureサブスクリプションがあります。...
- 質問190 Subscription1という名前のAzureサブスクリプションがあります。...
- 質問191 次の表に示す割り当てを含むSubscription1というAzureサブスクリ...
- 質問192 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問193 次の表のリソースを含むSubscription1という名前のAzureサブスク...
- 質問194 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 複数のポッドを含むAzureK...
- 質問195 オンプレミスネットワークには、Azure Active Directory(Azure ...
- 質問196 財務部門の監査人にどのブレードを使用するように指示する必要が
- 質問197 Azure 仮想マシンのデプロイに使用される Azure Resource Manage...
- 質問198 次の表に示すリソースを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあります...
- 質問199 次の表のリソースを含む Subscription1 という名前の Azure サブ...
- 質問200 Azure Network Watcherを使用して、次のタスクを実行することを...
- 質問201 Windows Server 2019を実行するVM1という名前のAzure仮想マシン...
- 質問202 Azure Resource Managerテンプレートを使用して、仮想マシンスケ...
- 質問203 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問204 RG1とRG2という名前の2つのリソースグループを含むAzureサブスク...
- 質問205 VM1とVM2という名前の2つのAzure仮想マシンがあります。 RSV1お...
- 質問206 contoso.comという名前のAzure Active Directory(Azure AD)テ...
- 質問207 次の展示に示すネットワークプロファイルを持つAzureKubernetes ...
- 質問208 AzureStorageアカウントstorageaccount1を含むAzureサブスクリプ...
- 質問209 VNET1という名前の仮想ネットワークを含むAzureサブスクリプショ...
- 質問210 Azure Resource Managerテンプレートを使用して、20のAzure仮想...
- 質問211 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問212 次の表に示すパブリック IP アドレスを持つ Azure サブスクリプ...
- 質問213 NSG1およびNSG2の計画された変更を実装します。 次の各ステート...
- 質問214 Azure サブスクリプションがあります。 次の Azure Resource Man...
- 質問215 次の表に示すパブリックIPアドレスを使用するAzureサブスクリプ...
- 質問216 VM1 という名前の Azure 仮想マシンがあります。 VM1 のネットワ...
- 質問217 注: この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。...
- 質問218 App1という名前のAzure App ServiceをホストするAzure App Servi...
- 質問219 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問220 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問221 Web管理者がWebアプリをできるだけ迅速にデプロイできるように、...
- 質問222 VMVという名前のA2ure仮想マシンがあります VM1のネットワークイ...
- 質問223 次の表に示すストレージ アカウントを含む Azure サブスクリプシ...
- 質問224 account1という名前のストレージアカウントを含むAzureサブスク...
- 質問225 次の表に示すパブリックロードバランサーを含むAzureサブスクリ...
- 質問226 次の表に示すリソースを含むAZPT1という名前のAzureサブスクリプ...
- 質問227 財務部門のユーザー向けに構成を自動化するソリューションを推奨
- 質問228 次の表に示すAzure仮想マシンがあります。 (Exhibit) VNNET1は、...
- 質問229 ネットワークには、contoso.comおよびeast.contoso.comという名...
- 質問230 AKS1という名前のAzure Kubernetes Service(AKS)クラスターが...
- 質問231 Azureストレージアカウントを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあり...
- 質問232 次の表に示す仮想マシンを含む Azure サブスクリプションがあり...
- 質問233 ライセンスを再度割り当てる前に、ライセンスの問題を解決する必
- 質問234 ニューヨークオフィスの接続要件を満たす必要があります。 あな
- 質問235 contoso.comという名前の登録済みDNSドメインがあります。 conto...
- 質問236 あなたの会社にはMicrosoftAzureサブスクリプションがあります。...
- 質問237 Subscription1という名前のAzureサブスクリプションがあります。...
- 質問238 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問239 次の表に示すAzure仮想ネットワークがあります。 (Exhibit) VNet...
- 質問240 Sub1 と Sub2 という名前の 2 つの Azure サブスクリプションが...
- 質問241 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問242 VMが存在するVNetのIPアドレス空間内に構成された静的プライベー...
- 質問243 最近、Admin1という名前のユーザーを含む新しいAzureサブスクリ...
- 質問244 注:この質問は、同じシナリオを提示する一連の質問の一部です。
- 質問245 注:質問は、同じ設定を表すいくつかの質問に含まれています。た
- 質問246 Azure仮想マシンにMicrosoft SQL Server Always On可用性グルー...
- 質問247 次の図に示すように、WEBPROD-AS-USE2という名前のAzure可用性セ...
- 質問248 サブスクリプション1という名前のAzureサブスクリプションと、Mi...
- 質問249 contoso.onmicrosoft.comという名前のAzure Active Directory(A...
- 質問250 WebApp1という名前のAzure Webアプリを作成します。 WebApp1には...
- 質問251 Azureサブスクリプションがあります。 すべてのユーザーに対して...
- 質問252 次の図に示す構成を持つVNet1という名前の仮想ネットワークがあ...
- 質問253 SQL1という名前のMicrosoft SQL Serverインスタンスを含むオンプ...
- 質問254 次の表に示すAzure仮想マシンがあります。 (Exhibit) VNET1、VNE...
- 質問255 Workspace1という名前のAzure Log Analyticsワークスペースを含...
- 質問256 VM1 という名前の仮想マシンと App1 という名前の Azure 関数を...
- 質問257 複数のオンプレミスの場所とAzure仮想ネットワークの間にルート...
- 質問258 VNet1とVNet2という名前の2つのAzure仮想ネットワークがあります...
- 質問259 VM1という名前の仮想マシンを含むAzureサブスクリプションがあり...

