- ホーム
- Microsoft
- 70-461J - Querying Microsoft SQL Server 2012/2014 (70-461日本語版)
- Microsoft.70-461J.v2020-04-28.q92
- 質問55
有効的な70-461J問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、70-461J試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新70-461J試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com 70-461J試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここで70-461J問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
70-461J問題集最新版のアクセス
「252問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
SQL Serverデータベースを開発します。 データベースには、次のT-SQLステートメントで定義されたテーブルが含まれています。
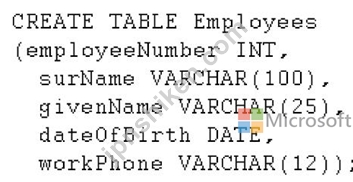
この表には、surName、givenName、およびdateOfBirthの各フィールドの値の組み合わせに基づく重複レコードが含まれています。
重複したレコードを削除する必要があります。
関連するTransact-SQL文をどのように完成させるべきですか? 答えを得るには、適切なコードセグメントを解答エリアの正しい場所にドラッグします。 各コードセグメントは、1回、複数回、またはまったく使用されないことがあります。 コンテンツを表示するには、分割バーをペインの間にドラッグするかスクロールする必要があります。
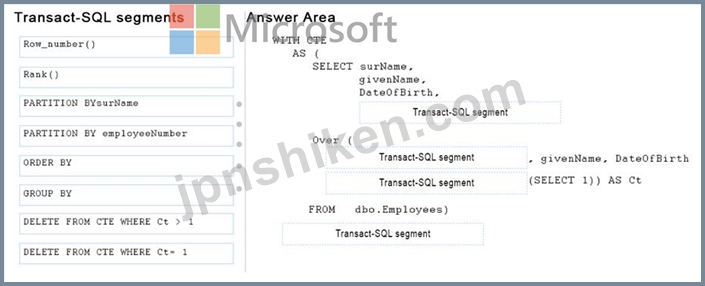

この表には、surName、givenName、およびdateOfBirthの各フィールドの値の組み合わせに基づく重複レコードが含まれています。
重複したレコードを削除する必要があります。
関連するTransact-SQL文をどのように完成させるべきですか? 答えを得るには、適切なコードセグメントを解答エリアの正しい場所にドラッグします。 各コードセグメントは、1回、複数回、またはまったく使用されないことがあります。 コンテンツを表示するには、分割バーをペインの間にドラッグするかスクロールする必要があります。

正解:

Explanation:
Example:
let us write a query which will delete all duplicate data in one shot. We will use a CTE (Common Table Expression) for this purpose. We will read in future posts what a CTE is and why it is used. On a lighter note, CTE's can be imagined as equivalent to temporary result sets that can be used only in an underlying SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE or CREATE VIEW statement.
;WITH CTE AS
(
SELECT Name
, City
, [State]
, ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY Name, City, [State] ORDER BY [Name]) AS Rnum FROM Persons ) DELETE FROM CTE WHERE Rnum <> 1 In the code by saying WHERE Rnum <> 1, we are asking SQL Server to keep all the records with Rank 1, which are not duplicates, and delete any other record. After executing this query in SQL Server Management Studio, you will end up with no duplicates in your table. To confirm that just run a simple query against your table.
Reference:
http://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/22706.how-to-remove-duplicates-from-a-table-in-sql-server.aspx
- 質問一覧「92問」
- 質問1 データベースには、CustomerIDおよびNameという列を持つCustomer...
- 質問2 あなたはデータベースアプリケーションを開発します。 4つのテー...
- 質問3 あなたは、ContosoDbという名のMicrosoft SQL Server 2012データ...
- 質問4 複数のネストされたクエリを含む新しいビジネスレポートのクエリ
- 質問5 Microsoft SQL Server 2012データベースを使用します。 顧客名と...
- 質問6 データベースには、展示品に示すような表が含まれています。 ([...
- 質問7 展示に示されているテーブルを含むSalesという名前のデータベー...
- 質問8 あなたは、領域内のContosoDbという名の穏やかなデータベースを...
- 質問9 次の列を含むOrderDetailsという名前のテーブルを作成する必要が...
- 質問10 あなたは、展示に示すようにデータベース構造をサポートします。
- 質問11 あなたは、アプリケーションをサポートするMicrosoft SQL Server...
- 質問12 次のTransact-SQLステートメントを使用してテーブルを作成します...
- 質問13 あなたは、旅行アプリケーションのためのデータベースを開発しま
- 質問14 学生の年半ば成績を記録するためにStudentCode、SubjectCodeおよ...
- 質問15 展示に示されているテーブルを含むSalesという名前のデータベー...
- 質問16 Microsoft SQL Serverデータベースを開発します。 製品情報を格...
- 質問17 Profitsという名のテーブルは、領域の中で毎年儲けられる総利益...
- 質問18 あなたは、旅行アプリケーションのためのデータベースを開発しま
- 質問19 StudentCode、SubjectCode、およびMarks列を持つ表を作成して、...
- 質問20 自動車メーカー用のSQL Serverデータベースを開発しています。 ...
- 質問21 次の要件を満たすカーソルを作成する必要があります。 *できるだ...
- 質問22 データベースには、次のTransact-SQLステートメントを実行して作...
- 質問23 会社のすべての販売データを含むSQL Serverデータベースがありま...
- 質問24 Sales.InvoiceSchemaという名前のXMLスキーマコレクションがあり...
- 質問25 あなたは、アプリケーションをサポートするMicrosoft SQL Server...
- 質問26 TICKETSという名前のデータベースのストアドプロシージャを展開...
- 質問27 あなたは歯科医、精神病医および内科医のためのデータを含んでい
- 質問28 あなたは、Microsoft SQL Server 2012データベースを開発します...
- 質問29 あなたは、データベース・アプリケーションを開発するために、Mi...
- 質問30 Productsという名前のテーブルを含むMicrosoft SQL Server 2012...
- 質問31 Productsという名前のテーブルを含むMicrosoft SQL Server 2012...
- 質問32 あなたはMicrosoft SQL Serverデータベースを持っています。 デ...
- 質問33 ショッピングカート・アプリケーションを開発するために、あなた
- 質問34 会社の給与計算システムをサポートするために、Microsoft Azure ...
- 質問35 あなたは、Customersという名前のテーブルを含むMicrosoft SQL S...
- 質問36 Microsoft SQL ServerとMicrosoft Azure SQLデータベース用のデ...
- 質問37 次の要件を満たすクエリを作成する必要があります。 *クエリは、...
- 質問38 Profitsという名のテーブルは、領土内の各年製総利益を格納しま...
- 質問39 展示に示されているテーブルを含むデータベースがあります。 ([...
- 質問40 あなたは、Microsoft SQL Server 2012を用いてデータベース・ア...
- 質問41 Sales.Detailsという名前のテーブルから各OrderIDの合計売上を計...
- 質問42 書籍に関する情報を含むXML列を持つ表を使用して作業しています...
- 質問43 Microsoft SQL Server 2012サーバーを管理します。 新しい機能を...
- 質問44 次のクエリに従って日次レポートを生成します。 (Exhibit) クエ...
- 質問45 あなたは、データベースアプリケーションを開発するためにMicros...
- 質問46 Microsoft SQL Serverデータベースを開発します。 データベース...
- 質問47 あなたは、ContosoDbという名前のMicrosoft SQL Server 2012のデ...
- 質問48 あなたは、いくつかのステートメントを含むトランザクションのコ
- 質問49 あなたは、OrderDetailという名前のテーブルを含むMicrosoft SQL...
- 質問50 アプリケーションは各国のストアド・プロシジャーを含んでいます
- 質問51 あなたは、ContosoDbという名のMicrosoft SQL Server 2012データ...
- 質問52 あなたは、ContosoDbという名のMicrosoft SQL Server 2012データ...
- 質問53 あなたは、価格情報を含むデータベースを開発しています。一定の
- 質問54 あなたは、価格情報が含まれたデータベースを開発しています。固
- 質問55 SQL Serverデータベースを開発します。 データベースには、次のT...
- 質問56 あなたは、ショッピング·アプリケーションをサポートするMicroso...
- 質問57 あなたは、Microsoft SQL Server 2012データベースを開発します...
- 質問58 SQL Serverデータベース用のテーブルを設計しています。 テーブ...
- 質問59 次のコードセグメント中で示されるようなストアド・プロシジャー
- 質問60 以下に示すようなテーブルを含むデータベースがあります。 (Exhi...
- 質問61 あなたは、独立ソフトウェア・ベンダーのデータベース開発者です
- 質問62 次のストアドプロシージャを作成します。 (行番号は参照用にの
- 質問63 データベースはSalesOrdersという名前のテーブルを含みます。テ...
- 質問64 Microsoft Azure SQLデータベースインスタンスを管理します。 ト...
- 質問65 Microsoft SQL Serverデータベースを開発します。製品情報を保存...
- 質問66 電子商取引WebサイトをサポートするMicrosoft SQL Serverデータ...
- 質問67 会社の販売データと営業担当者を保存したSALESという名前のデー...
- 質問68 あなたは、Microsoft SQL Server 2012サーバーでホストされてい...
- 質問69 あなたは、ビジネスに不可欠な高アクティビティOLTPシステムをホ...
- 質問70 あなたは、次のクエリに応じて毎日のレポートを生成します。 (Ex...
- 質問71 大規模な多国籍企業向けのSQL Serverデータベースを開発します。...
- 質問72 あなたは、以下のコラムを持っているBlogEntryという名前のテー...
- 質問73 ショッピングカート・アプリケーションを開発するために、あなた
- 質問74 データベースには、展示品に示すような表が含まれています。 ([...
- 質問75 展示に示されているテーブルを含むデータベースがあります。 ([...
- 質問76 あなたは、FILESTREAM対応のデータベースに対する一組の問合わせ...
- 質問77 あなたの会社のすべての顧客データを含むSQL Serverデータベース...
- 質問78 あなたがOrdersHistoncalというヒープを含むMicrosoft SQL Serve...
- 質問79 Customerという名前のテーブルが含まれるデータベースがあります...
- 質問80 あなたは、Microsoft SQL Server 2012データベースのデータベー...
- 質問81 ContosoDbという名前のMicrosoft SQL Serverデータベースを管理...
- 質問82 次の関連表を含むデータベースがあります。 (Exhibit) OrderSumm...
- 質問83 次のコードを使用して作成されたビューがあります。 (Exhibit) ...
- 質問84 Microsoft SQL Server Management Studioを使用して、発注書アプ...
- 質問85 いくつかのデータベースをサポートするMicrosoft SQL Serverイン...
- 質問86 Productsという名前のテーブルを含むMicrosoft SQL Serverデータ...
- 質問87 Wholesaleガラス製造会社のストアドプロシージャを開発します。 ...
- 質問88 anonlineストアWebサイトの注文情報を格納するMicrosoft SQL Ser...
- 質問89 あなたは、ContosoDbという名前のMicrosoft SQL Server 2012のデ...
- 質問90 すでにデータが含まれているdbo.Bookという名前のテーブルにBook...
- 質問91 SQL Serverデータベースを使用する注文入力システムを設計してい...
- 質問92 複数のSQL Serverクエリがあります。 クエリを最適化してパフォ...

