- ホーム
- CompTIA
- CAS-004-JPN - CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner (CASP+) Exam (CAS-004日本語版)
- CompTIA.CAS-004-JPN.v2024-03-04.q164
- 質問64
有効的なCAS-004-JPN問題集はJPNTest.com提供され、CAS-004-JPN試験に合格することに役に立ちます!JPNTest.comは今最新CAS-004-JPN試験問題集を提供します。JPNTest.com CAS-004-JPN試験問題集はもう更新されました。ここでCAS-004-JPN問題集のテストエンジンを手に入れます。
CAS-004-JPN問題集最新版のアクセス
「620問、30% ディスカウント、特別な割引コード:JPNshiken」
製品開発チームは、リリース前にレビューのためにコード スニペットを送信しました。
手順
コード スニペットを分析し、コード スニペットごとに脆弱性を 1 つ選択し、修正を 1 つ選択します。
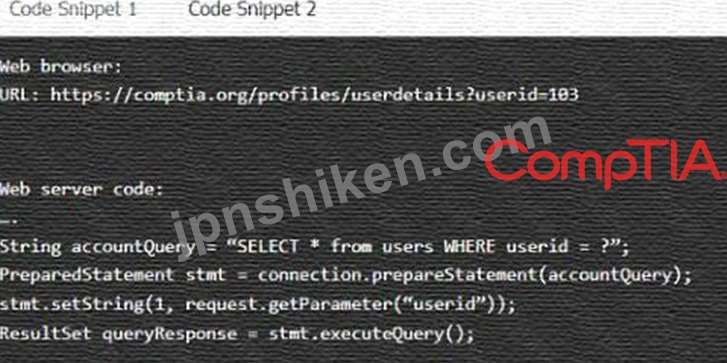
コードのスニペット 1
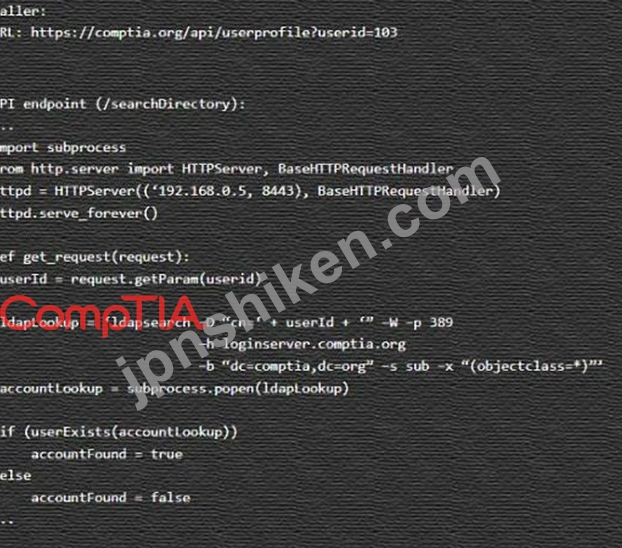
コードスニペット 2
脆弱性 1:
SQLインジェクション
クロスサイトリクエスト偽造
サーバー側のリクエストフォージェリ
間接的なオブジェクト参照
クロスサイトスクリプティング
修正 1:
userid フィールドの入力サニタイズを実行します。
queryResponseの出力エンコーディングを実行し、
usex:ia がログイン ユーザーに属していることを確認してください。
URL を検査し、任意のリクエストを禁止します。
偽造防止トークンを実装します。
脆弱性 2
1) サービス拒否
2) コマンドインジェクション
3) SQLインジェクション
4) 認証バイパス
5) GET 経由で渡される認証情報
修正2
A) プリペアドステートメントを実装してバインドする
変数。
B)serve_forever 命令を削除します。
C) 「認証された」値が GET パラメータによって上書きされないようにします。
D) 機密パラメータには HTTP POST を使用する必要があります。
E) userid フィールドの入力サニタイズを実行します。
手順
コード スニペットを分析し、コード スニペットごとに脆弱性を 1 つ選択し、修正を 1 つ選択します。
コードのスニペット 1

コードスニペット 2

脆弱性 1:
SQLインジェクション
クロスサイトリクエスト偽造
サーバー側のリクエストフォージェリ
間接的なオブジェクト参照
クロスサイトスクリプティング
修正 1:
userid フィールドの入力サニタイズを実行します。
queryResponseの出力エンコーディングを実行し、
usex:ia がログイン ユーザーに属していることを確認してください。
URL を検査し、任意のリクエストを禁止します。
偽造防止トークンを実装します。
脆弱性 2
1) サービス拒否
2) コマンドインジェクション
3) SQLインジェクション
4) 認証バイパス
5) GET 経由で渡される認証情報
修正2
A) プリペアドステートメントを実装してバインドする
変数。
B)serve_forever 命令を削除します。
C) 「認証された」値が GET パラメータによって上書きされないようにします。
D) 機密パラメータには HTTP POST を使用する必要があります。
E) userid フィールドの入力サニタイズを実行します。
正解:
See the solution below in explanation.
Explanation
Code Snippet 1
Vulnerability 1: SQL injection
SQL injection is a type of attack that exploits a vulnerability in the code that interacts with a database. An attacker can inject malicious SQL commands into the input fields, such as username or password, and execute them on the database server. This can result in data theft, data corruption, or unauthorized access.
Fix 1: Perform input sanitization of the userid field.
Input sanitization is a technique that prevents SQL injection by validating and filtering the user input values before passing them to the database. The input sanitization should remove any special characters, such as quotes, semicolons, or dashes, that can alter the intended SQL query. Alternatively, the input sanitization can use a whitelist of allowed values and reject any other values.
Code Snippet 2
Vulnerability 2: Cross-site request forgery
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is a type of attack that exploits a vulnerability in the code that handles web requests. An attacker can trick a user into sending a malicious web request to a server that performs an action on behalf of the user, such as changing their password, transferring funds, or deleting data. This can result in unauthorized actions, data loss, or account compromise.
Fix 2: Implement anti-forgery tokens.
Anti-forgery tokens are techniques that prevent CSRF by adding a unique and secret value to each web request that is generated by the server and verified by the server before performing the action. The anti-forgery token should be different for each user and each session, and should not be predictable or reusable by an attacker.
This way, only legitimate web requests from the user's browser can be accepted by the server.
Explanation
Code Snippet 1
Vulnerability 1: SQL injection
SQL injection is a type of attack that exploits a vulnerability in the code that interacts with a database. An attacker can inject malicious SQL commands into the input fields, such as username or password, and execute them on the database server. This can result in data theft, data corruption, or unauthorized access.
Fix 1: Perform input sanitization of the userid field.
Input sanitization is a technique that prevents SQL injection by validating and filtering the user input values before passing them to the database. The input sanitization should remove any special characters, such as quotes, semicolons, or dashes, that can alter the intended SQL query. Alternatively, the input sanitization can use a whitelist of allowed values and reject any other values.
Code Snippet 2
Vulnerability 2: Cross-site request forgery
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is a type of attack that exploits a vulnerability in the code that handles web requests. An attacker can trick a user into sending a malicious web request to a server that performs an action on behalf of the user, such as changing their password, transferring funds, or deleting data. This can result in unauthorized actions, data loss, or account compromise.
Fix 2: Implement anti-forgery tokens.
Anti-forgery tokens are techniques that prevent CSRF by adding a unique and secret value to each web request that is generated by the server and verified by the server before performing the action. The anti-forgery token should be different for each user and each session, and should not be predictable or reusable by an attacker.
This way, only legitimate web requests from the user's browser can be accepted by the server.
- 質問一覧「164問」
- 質問1 技術者は、現在のサーバー ハードウェアが古くなっていると判断
- 質問2 組織は、リモート作業をサポートするために BYOD 標準を検討して...
- 質問3 エンジニアリング チームは、特殊な在庫管理目的に使用するモバ
- 質問4 Web サービス プロバイダーは、契約上の要件を満たすために現在...
- 質問5 セキュリティ アナリストが、1 台のサーバーで悪意のある PowerS...
- 質問6 組織の既存のインフラストラクチャには、データセンター間のサイ
- 質問7 ある企業は、新しいマルウェアによるエンドポイントでの複数のサ
- 質問8 DevOps チームは、新しい課金システムをサポートする PaaS ソリ...
- 質問9 ある組織は、専門的なヘルプ デスク サービスについてパートナー...
- 質問10 監査人は、Web アプリケーションからのログを確認して、インシデ...
- 質問11 複数のサードパーティ組織を使用してサービスを提供する大手銀行
- 質問12 セキュリティ エンジニアは、会社のマルチホーム SFTP サーバー...
- 質問13 セキュリティ アナリストは、企業のクラウド ログでネットワーク...
- 質問14 ある企業は、ホリデー シーズンの準備として、小売販売を管理す
- 質問15 大手多国籍メーカーのセキュリティ アーキテクトは、トラフィッ
- 質問16 ある組織は、機密の PI I やパスポート番号などの ID 情報を処理...
- 質問17 サイバーセキュリティ アナリストは、潜在的なインシデントが発
- 質問18 セキュリティ アナリストが次の脆弱性評価レポートをレビューし
- 質問19 金融部門の企業は、電子メールを介してかなりの数の顧客取引要求
- 質問20 企業は、接続文字列が確実に保護されるように、秘密キーと公開キ
- 質問21 最近のデータ侵害は、クラウドベースの生産性スイートを使用して
- 質問22 組織の財務システムが最近攻撃されました。フォレンジック アナ
- 質問23 ソフトウェア開発会社は、ソーシャル メディア プラットフォーム...
- 質問24 最近、アプリケーション サーバーが TLS 1.3 を優先するようにア...
- 質問25 クラウド セキュリティ エンジニアは、クラウドでホストされる W...
- 質問26 セキュリティ エンジニアは、企業ネットワークからのセキュリテ
- 質問27 従来のオンプレミスのインフラストラクチャ構成と比較して、CSP ...
- 質問28 セキュリティ アナリストがクライアントに代わって脆弱性評価を
- 質問29 次のコントロールのうち、特権の乱用を主に検出するが、それを防
- 質問30 HVAC 請負業者は、会社の拠点で機器の問題をリモートでサポート/...
- 質問31 ある建築会社はセキュリティ チームと協力して、一般に漏洩した
- 質問32 お客様から、www.test.com の Web サイトに接続してサービスを利...
- 質問33 企業は、管理された検出および応答サービスを実行する MSSP にア...
- 質問34 セキュリティ管理者は、セキュリティ実装ガイドラインに従ってア
- 質問35 製薬会社は最近、顧客向けの Web ポータルでセキュリティ違反を...
- 質問36 多数の電子メールが報告されており、セキュリティ アナリストが
- 質問37 開発者は、プログラムの各モジュールの整合性を維持し、悪意のあ
- 質問38 新しいオンライン ファイル ホスティング サービスが提供されて...
- 質問39 銀行のリスク委員会に最新の指標を提供する最高情報セキュリティ
- 質問40 組織のハント チームは、永続的な脅威が存在し、企業ネットワー
- 質問41 組織は、最新の評価で特定されたリスクを修復または軽減するため
- 質問42 脅威ハンティング チームは、ネットワーク内で発生する可能性の
- 質問43 ストリーミング コンテンツへの継続的な可用性を必要とする大手
- 質問44 セキュリティ エンジニアは、侵害の可能性が報告された直後に、
- 質問45 衛星通信 ISP は、非推奨のハードウェアとソフトウェアを使用し...
- 質問46 フォレンジック対応でステガナリシス技術を使用する利点は次のう
- 質問47 小さな会社は、運用コストを削減する必要があります。ベンダーは
- 質問48 ある企業は、モバイル アプリケーションを使用せずにブラウザ経
- 質問49 セキュリティ エンジニアは、特定の Windows ワークステーション...
- 質問50 ある会社は、グローバル サービスの展開を準備しています。 GDPR...
- 質問51 次のうち、パスワードレス認証ソリューションを実装することの最
- 質問52 新人開発者は、高度な RISC マシン (ARM) CPU に対する新しいマ...
- 質問53 準同型暗号化の一般的な使用例を最もよく説明しているものは次の
- 質問54 監査人は、保存されている文書をスキャンして機密テキストを見つ
- 質問55 脆弱性スキャナーは、企業の Linux サーバーの 1 つで、オープン...
- 質問56 ソフトウェア開発会社の管理者は、デジタル署名を使用して会社の
- 質問57 ある会社は、インターネットへのゲスト WiFi アクセスを提供し、...
- 質問58 セキュリティ アナリストは SIEM イベントをレビューしています...
- 質問59 セキュリティ エンジニアは、次のような最近のデータ侵害インシ
- 質問60 CSP の観点から最も重要なクラウド固有のリスクは次のうちどれで...
- 質問61 大学は、独自のアイデンティティ管理システムを通じて、すべての
- 質問62 次のプロトコルのうち、PAN ネットワークの作成を可能にする低電...
- 質問63 ホスピタリティ企業は、顧客 PLL を含むデータ侵害を経験しまし...
- 質問64 製品開発チームは、リリース前にレビューのためにコード スニペ
- 質問65 フィッシング演習中に、少数の特権ユーザーが失敗リストの上位に
- 質問66 セキュリティ管理者は、組織をゼロトラスト アーキテクチャに移
- 質問67 ある会社が新しいビデオカードをリリースしたところです。供給が
- 質問68 内部リソースの制約により、管理チームは主要なセキュリティ ア
- 質問69 最高情報セキュリティ責任者 (CISO) は新しい会社と協力しており...
- 質問70 攻撃者が発電サイトに侵入し、安全計装システムを無効にしました
- 質問71 セキュリティ アーキテクトはセキュリティ ポリシーを更新し、2 ...
- 質問72 セキュリティ アナリストは、ハッカーがいくつかのキーを発見し
- 質問73 セキュリティ ソリューションは、サンドボックス環境を使用して
- 質問74 アナリストは政府機関から IOC のリストを受け取りました。この...
- 質問75 最高情報セキュリティ責任者 (CISO) は、会社全体の反論 BCP/DR ...
- 質問76 セキュリティ アナリストが、バッファ オーバーフロー攻撃の可能...
- 質問77 ある企業が、顧客向けの外部アプリケーションを作成しました。セ
- 質問78 クライアントは、認証を必要としない一連の負荷分散された API ...
- 質問79 ある企業は、顧客向けの本番システムのほとんどをクラウド向けの
- 質問80 ある企業は、CRM プラットフォーム全体をすべてのユーザーに一度...
- 質問81 内部リソースの制約のため、管理チームは主任セキュリティ アー
- 質問82 デジタル トランスフォーメーションを実施中の企業は、CSP の回...
- 質問83 エンジニアリング チームは、正常に接続するためにクライアント
- 質問84 セキュリティ監査人は、エンターテイメント デバイスの動作方法
- 質問85 捜査官は、最近のデータ侵害が、ニュース購読サービスを提供する
- 質問86 セキュリティ エンジニアは、最近デプロイされた Web アプリケー...
- 質問87 最高情報セキュリティ責任者 (CISO) は、内部ホストの脆弱性スキ...
- 質問88 侵入テスターは、Windows サーバーでルート アクセス権を取得し...
- 質問89 セキュリティは、マーケティング部門が組織のソーシャル メディ
- 質問90 新興企業の最高情報セキュリティ責任者は、セキュリティ エンジ
- 質問91 セキュリティ管理者は、水平方向の移動攻撃に対してドメイン コ
- 質問92 地域と予算の制約により、組織のサテライト オフィスには、組織
- 質問93 セキュリティ アーキテクトは、環境内で重要なセキュリティ機能
- 質問94 組織は、ベスト プラクティスのセキュリティ構成に対してすべて
- 質問95 セキュリティ アーキテクトは、次の提案されている企業ファイア
- 質問96 ネットワーク チームは、会社の全従業員に安全なリモート アクセ...
- 質問97 企業は、対象データの処理および保管の制約を定義するパートナー
- 質問98 ベンダーロックインに関連するリスクは次のうちどれですか? (2...
- 質問99 システム管理者には、コマンド アンド コントロール サーバーと...
- 質問100 アプリケーション開発者は、アプリケーションにサードパーティの
- 質問101 組織は、運用環境のシステムをオンプレミス環境からクラウド サ
- 質問102 最高セキュリティ責任者 (CSO) は、同社を襲ったランサムウェア...
- 質問103 セキュリティ アーキテクトは、リモート ワーカーが高度に分散し...
- 質問104 (Exhibit) 組織は災害復旧と業務継続を計画しています。 説明書 ...
- 質問105 ある会社は顧客向けにいくつかの API を公開しており、キーを使...
- 質問106 ワークステーション、サーバー、ラップトップなどの資産の完全な
- 質問107 ある組織は知的財産データをオンプレミスから CSP に移動してお...
- 質問108 ネットワーク アーキテクトは、すべてのローカル サイトを中央の...
- 質問109 セキュリティ アーキテクトは、ソフトウェア会社が廃業したため
- 質問110 ある組織が開発したソーシャル メディア アプリケーションは、世...
- 質問111 最高セキュリティ責任者 (CSO) は、セキュリティ チームに対し、...
- 質問112 ある組織は、企業のモバイル デバイス ユーザーに対して、企業の...
- 質問113 データ流出の申し立てを調査している地方自治体は、悪意のあるユ
- 質問114 ある企業は、データベースに保存されているデータを隠すソリュー
- 質問115 最高情報セキュリティ責任者 (CISO) は、企業の現在のデータ廃棄...
- 質問116 セキュリティ イベントを調査しているときに、アナリストは、ユ
- 質問117 セキュリティ チームは、組織を離れたスタッフ メンバーからの共...
- 質問118 暗号化ソリューションを活用して使用中のデータを保護すると、デ
- 質問119 ある企業は機密性の高いワークロードをクラウドに移行しており、
- 質問120 世界的な拠点を持つ地元の大学は、Web サイトと関連システムの全...
- 質問121 重大な気象現象により、すべてのシステムが障害復旧サイトに正常
- 質問122 監査人は、保存されている文書をスキャンして機密テキストを見つ
- 質問123 最高情報責任者 (CIO) は、システム管理者に、次の要件に基づい...
- 質問124 複数のサーバーの OS が、原因不明のほぼ同時にクラッシュしまし...
- 質問125 世界的なパンデミックにより、会社のすべてのスタッフがリモート
- 質問126 捜査または訴訟中に証拠の検索と収集が含まれるプロセスは次のど
- 質問127 ある銀行は、最新の脅威に対するセキュリティ対策を強化するため
- 質問128 SDN に関連するリスクは次のうちどれですか?
- 質問129 リスク戦略の一環として、企業はサイバーセキュリティ インシデ
- 質問130 ある企業は、新しい人工知能ベースの分析 SaaS ソリューションを...
- 質問131 シミュレーション あなたは、会社の特権ネットワークからの Nmap...
- 質問132 次の用語のうち、CASB またはサードパーティ エンティティへの暗...
- 質問133 PCI DSS v3.4 に基づいて、ある特定のデータベース フィールドに...
- 質問134 セキュリティ アナリストは、データがオンライン プロセスに注入...
- 質問135 セキュリティ コンサルタントは、Active Directory を持たない小...
- 質問136 立法者に対する新しい要件により、政府のセキュリティ チームは
- 質問137 ある企業のセキュリティ エンジニアが、新製品の市場投入で企業
- 質問138 ある会社は、稼働中のオンサイト データセンター全体にインスト
- 質問139 ある企業は、エクストラネット アプリケーションへのサプライヤ
- 質問140 セキュリティ エンジニアは、従業員ユーザーの Web トラフィック...
- 質問141 ある企業は、ストレージ コストを節約するために、顧客の PII を...
- 質問142 セキュリティ アーキテクトは、RDP の次の要件に対応するために...
- 質問143 企業のネットワーク上のホストが、SMB 経由で拡散していると思わ...
- 質問144 企業は、住宅ローン承認の要求を処理するために、EU に居住する...
- 質問145 企業の SOC は、特定の脆弱性を利用したアクティブなキャンペー...
- 質問146 ユーザーは、最近ネットワークに追加された新しいクラウド アプ
- 質問147 重大度の高い脆弱性が Web アプリケーションで発見され、企業に...
- 質問148 組織は、OT ネットワーク内のシステムの自動化機能を研究してい...
- 質問149 セキュリティ アーキテクトには、従業員の分散化とリモート化が
- 質問150 組織は、新しいオンライン デジタル バンクを展開しており、可用...
- 質問151 セキュリティ コンサルタントは、単一のアクセス ポイントを備え...
- 質問152 セキュリティ アナリストは、会社の WAF が適切に構成されていな...
- 質問153 企業は、資格情報を有効にするハッカーによって繰り返し侵害され
- 質問154 組織内のセキュリティ チームとビジネス ユニットの間の期待値を...
- 質問155 次のテクノロジのうち、CSP が複数のデータ ストレージに暗号化...
- 質問156 PaaS の責任共有モデルでは、顧客の責任は次のうちどれですか?...
- 質問157 システム管理者は、ネットワークに接続する前にホスト システム
- 質問158 セキュリティ アナリストは、サード パーティの侵入テスターに...
- 質問159 マネージド セキュリティ プロバイダー (MSP) は、完全なデジタ...
- 質問160 セキュリティ管理者は、内部関係者攻撃に対するインシデント対応
- 質問161 会社の財務部門は、システム上の暗号化されていないファイルにデ
- 質問162 コンサルタントは顧客のクラウド環境にアクセスする必要がありま
- 質問163 過去 1 年間の攻撃パターンを振り返ると、攻撃者は侵害を受けや...
- 質問164 ネットワーク管理者は、ラップトップを再起動しようとしているリ

